Mastering Surgical Shoe Procurement: Essential Strategies
Guide to Surgical Shoe
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for surgical shoe
- Understanding surgical shoe Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of surgical shoe
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for surgical shoe
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for surgical shoe
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for surgical shoe Sourcing
- Spotlight on Potential surgical shoe Manufacturers and Suppliers
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for surgical shoe
- Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the surgical shoe Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of surgical shoe
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for surgical shoe
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for surgical shoe
In the highly specialized realm of healthcare procurement, surgical shoes play a vital role in ensuring patient safety, infection control, and operational efficiency within medical facilities worldwide. For international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of sourcing high-quality surgical footwear is essential for maintaining compliance, reducing costs, and enhancing clinical outcomes.
This comprehensive guide offers a strategic overview of the global surgical shoe market, equipping buyers with critical insights on product types, materials, manufacturing standards, quality assurance, and supplier landscapes. It emphasizes actionable intelligence on cost structures, sourcing challenges, and regulatory considerations that are crucial for making informed procurement decisions in dynamic international markets.
By navigating this guide, B2B buyers will gain clarity on selecting reliable suppliers, evaluating product quality, and optimizing supply chain efficiency. Whether sourcing from established manufacturing hubs in Asia or emerging suppliers in developing regions, this resource aims to empower you to negotiate confidently, ensure compliance with local standards, and achieve sustainable procurement practices.
Ultimately, this guide serves as an essential tool for buyers seeking to enhance their surgical shoe procurement strategy, ensuring they meet the rigorous demands of healthcare providers worldwide while capitalizing on global market opportunities.
Understanding surgical shoe Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Surgical Shoe | Closed-toe, non-slip sole, adjustable straps or closures | Post-operative care, outpatient settings | Pros: Widely available, versatile; Cons: Limited in specialized support |
| Post-Operative Boot | Rigid, high ankle support, cushioned interior | Fracture stabilization, severe post-op recovery | Pros: High immobilization, customizable; Cons: Bulkier, higher cost |
| Diabetic/Offloading Shoe | Soft, padded, often with rocker sole, minimal closures | Diabetes foot ulcers, pressure offloading | Pros: Reduces pressure points, enhances healing; Cons: Less durable |
| Therapeutic/Medical Clog | Open-back, slip-on, lightweight, antimicrobial materials | Long-term care, elderly mobility aids | Pros: Easy to don/doff, comfortable; Cons: Less support for active use |
| Custom/Orthopedic Shoe | Fully customizable, tailored fit, orthotic support | Complex foot conditions, specific patient needs | Pros: Precise fit, optimal support; Cons: Higher lead times, costs |
Standard Surgical Shoe
This is the most common type, characterized by a simple, closed-toe design with a non-slip sole and adjustable straps or closures. It offers general post-operative support and is suitable for outpatient settings. For B2B buyers, these shoes are attractive due to their wide availability and moderate cost, making them ideal for bulk procurement. However, their basic design may lack specialized support features, which could limit their use in more complex cases.
Post-Operative Boot
Designed for severe recovery scenarios, these shoes feature rigid construction, high ankle support, and cushioned interiors to immobilize and stabilize the foot and ankle. They are highly suitable for fracture stabilization or major surgeries. For international buyers, key considerations include the need for durability, the potential for customization, and higher procurement costs. Their bulk and weight may impact shipping and storage, but their effectiveness in complex recoveries justify the investment.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Diabetic/Offloading Shoe
Specialized for pressure offloading, these shoes typically have soft, padded uppers, rocker soles, and minimal closures to reduce pressure points. They are vital in managing diabetic foot ulcers and preventing further tissue damage. B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing from suppliers that ensure strict quality control for safety and efficacy. While these shoes excel in healing, their lower durability and limited support for active use should be considered in procurement planning.
Therapeutic/Medical Clog
Open-back, slip-on designs made from lightweight, antimicrobial materials, these shoes provide comfort for long-term use and are easy to don and doff. They are commonly used in long-term care facilities and for elderly mobility. Buyers can benefit from volume discounts due to their simple manufacturing process. However, their support level is limited, making them less suitable for post-surgical stabilization or high-activity scenarios.
Custom/Orthopedic Shoe
These shoes are fully customizable, often incorporating orthotic inserts tailored to individual patient needs. They are essential for complex foot deformities or conditions requiring precise support. For B2B buyers, establishing relationships with specialized orthotic manufacturers can ensure consistent quality and lead times. Although they involve higher costs and longer lead times, their ability to meet specific medical requirements makes them indispensable for niche markets and high-value contracts.
Key Industrial Applications of surgical shoe
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of surgical shoe | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare & Medical | Operating room staff footwear to prevent contamination and slips | Ensures hygiene, reduces infection risk, enhances staff safety, and compliance | Material durability, slip resistance, compliance with medical standards |
| Pharmaceutical Manufacturing | Cleanroom footwear for controlled environment operations | Maintains contamination control, meets strict hygiene standards | Cleanroom certification, anti-static properties, ease of cleaning |
| Food Processing & Packaging | Slip-resistant shoes for workers in wet or greasy environments | Reduces workplace accidents, improves productivity, complies with safety regulations | Food-grade materials, slip resistance, comfort for long shifts |
| Industrial & Heavy Industry | Protective footwear for workers in construction or manufacturing sites | Provides foot protection against heavy objects, punctures, and impacts | Heavy-duty construction, puncture resistance, durability in harsh conditions |
| Laboratory & Research Facilities | Specialized footwear for lab environments requiring contamination control | Protects against chemical spills, maintains sterile conditions | Chemical resistance, ease of sterilization, comfort for prolonged use |
Healthcare & Medical
Surgical shoes in healthcare settings are primarily used by operating room staff to prevent contamination and slips. These shoes are designed with hygienic materials that are easy to disinfect, reducing the risk of infection transmission. For international buyers, especially from regions like Nigeria or the UK, sourcing surgical shoes that meet strict medical standards and offer slip resistance is critical. Reliable supply chains and compliance with local health regulations are essential to ensure safety and regulatory adherence.
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
In pharmaceutical cleanrooms, footwear must adhere to stringent hygiene and contamination control standards. Surgical shoes used in these environments are typically anti-static, easy to clean, and made from materials that do not shed particles. For B2B buyers in South America or the Middle East, sourcing certified cleanroom footwear that aligns with international standards (e.g., ISO certifications) ensures operational integrity and regulatory compliance, which are vital for maintaining product quality and avoiding costly contamination issues.
Food Processing & Packaging
Workers in food processing plants often operate in wet, greasy, or slippery conditions, making slip-resistant surgical shoes indispensable. These shoes help prevent workplace accidents, reduce downtime, and comply with safety regulations such as OSHA or equivalent standards. Buyers from regions like Europe or Africa should prioritize sourcing footwear with food-grade, non-slip soles and materials that withstand frequent cleaning and exposure to moisture, ensuring both safety and hygiene.
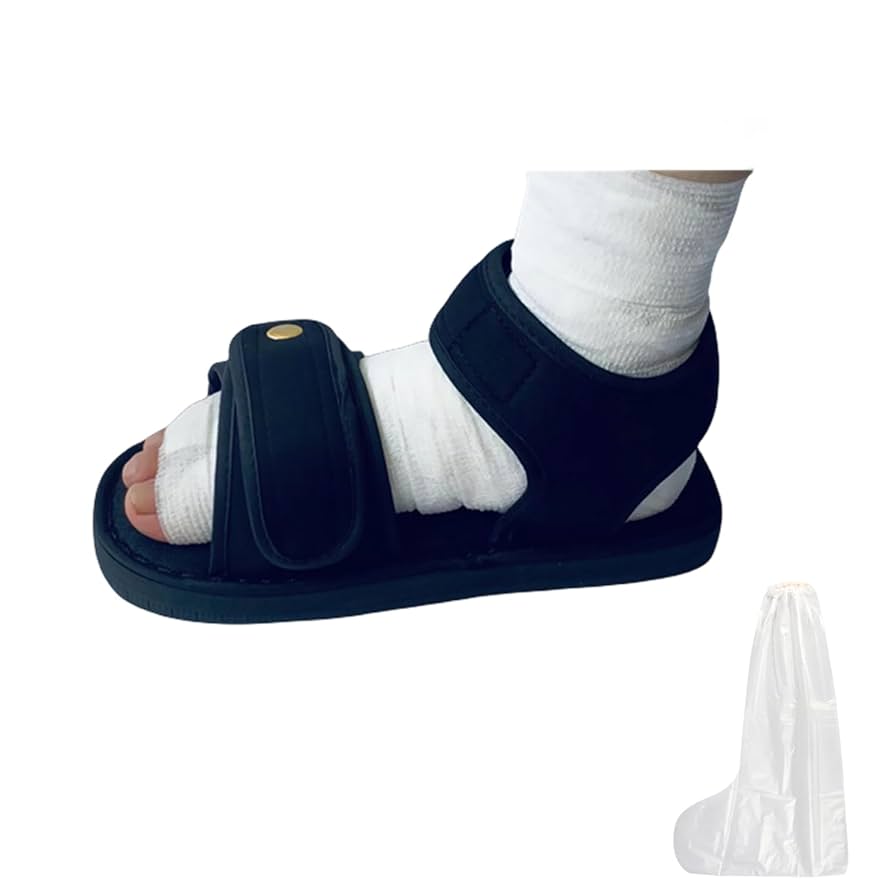
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Industrial & Heavy Industry
In construction, manufacturing, and heavy industry, footwear must provide maximum protection against impacts, punctures, and harsh environmental conditions. Surgical shoes designed for industrial applications often feature reinforced soles, puncture resistance, and durable materials. International B2B buyers should focus on sourcing footwear that meets industry-specific safety standards (e.g., ASTM, EN ISO) and offers long-term durability, especially in regions with challenging climates like the Middle East or South America.
Laboratory & Research Facilities
Laboratories require footwear that minimizes contamination risks and withstands exposure to chemicals. Surgical shoes in this sector often feature chemical-resistant materials, anti-slip soles, and ease of sterilization. For buyers in Europe or Africa, sourcing footwear that combines comfort with chemical and microbial resistance is crucial to maintaining sterile environments and ensuring personnel safety during extended shifts. Reliable suppliers offering certified products can significantly reduce operational risks.
This comprehensive understanding of industrial applications helps international B2B buyers identify the most suitable surgical shoe products, ensuring safety, compliance, and operational efficiency across diverse sectors and regions.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for surgical shoe
Material Analysis for Surgical Shoe Manufacturing
Selecting the appropriate materials for surgical shoes is crucial for ensuring product performance, safety, and compliance with international standards. For B2B buyers across regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of common materials can facilitate better procurement decisions and product customization.
1. Polyurethane (PU)
Key Properties:
Polyurethane is a versatile polymer known for its excellent abrasion resistance, flexibility, and impact absorption. It exhibits good chemical resistance and can withstand sterilization processes such as autoclaving, depending on formulation.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: Cost-effective, lightweight, good durability, and easy to mold into complex shapes. It offers excellent slip resistance and cushioning, enhancing wearer comfort.
– Cons: Susceptible to degradation under prolonged UV exposure and certain solvents. Its mechanical properties can vary depending on formulation, which may affect consistency across batches.
Impact on Application:
Polyurethane’s chemical resistance makes it suitable for environments with disinfectants and cleaning agents. However, its thermal stability should be verified for sterilization methods used in different regions.
International Buyer Considerations:
Polyurethane products often meet standards like ASTM F1671 for biological evaluation and ISO 10993 for biocompatibility, making them suitable for medical applications globally. Buyers should verify compliance with local regulations and standards such as CE marking in Europe or ANVISA in Brazil.
2. Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE)
Key Properties:
TPEs combine the elastic properties of rubber with the processability of plastics. They are flexible, resilient, and resistant to a broad spectrum of chemicals, including disinfectants.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: Excellent flexibility and comfort, easy to clean, and compatible with various sterilization methods. They are also recyclable, aligning with sustainability goals.
– Cons: Generally higher cost than standard plastics, and some formulations may have limited resistance to high temperatures or aggressive chemicals.
Impact on Application:
Ideal for the upper parts or straps of surgical shoes where flexibility and comfort are paramount. TPE’s chemical resistance supports longevity in disinfectant-rich environments.
International Buyer Considerations:
TPEs typically conform to standards such as ISO 10993 for biocompatibility and ASTM F963 for safety. Buyers should ensure supplier certifications for medical-grade TPEs and verify compatibility with sterilization methods prevalent in their markets.
3. Medical-Grade Silicone
Key Properties:
Silicone is renowned for its high-temperature stability, biocompatibility, and inertness. It withstands repeated sterilization cycles without degradation and is resistant to UV, ozone, and many chemicals.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: Superior biocompatibility, flexibility, and durability. It offers excellent thermal stability, making it suitable for autoclaving and other sterilization methods.
– Cons: Higher material and manufacturing costs. Its softness can sometimes compromise structural support, and it may be prone to tearing under excessive stress.
Impact on Application:
Silicone’s inertness makes it ideal for components in direct contact with skin or bodily fluids. Its stability under sterilization processes ensures longevity and safety.
International Buyer Considerations:
Silicone materials often meet stringent standards such as ISO 10993 and ASTM F138 for biocompatibility. Buyers should confirm supplier compliance with regional standards like the European Medical Device Regulation (MDR) or the US FDA requirements.
4. Stainless Steel (e.g., 304, 316 grades)
Key Properties:
Stainless steel offers exceptional strength, corrosion resistance, and ease of sterilization. It is highly durable and maintains structural integrity under various environmental conditions.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: Long-lasting, corrosion-resistant, and suitable for high-temperature sterilization. It provides excellent support and stability for structural components.
– Cons: Heavier and more expensive than plastics or elastomers. Manufacturing complexity increases with precision requirements, and it may be less comfortable for parts in direct contact with skin.
Impact on Application:
Primarily used for structural elements or supportive frameworks within surgical shoes. Its corrosion resistance makes it suitable for environments with high humidity or saline exposure.
International Buyer Considerations:
Compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 or EN 10088 ensures material quality. Buyers should verify supplier certifications and ensure the steel grades meet regional regulatory requirements, especially for reusable surgical equipment.
Summary Table of Materials for Surgical Shoes
| Material | Typical Use Case for surgical shoe | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyurethane (PU) | Outsoles, cushioning components | Cost-effective, durable, impact absorption | Susceptible to UV degradation, variable quality | Low |
| Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE) | Straps, flexible upper parts | Flexible, chemical resistant, recyclable | Higher cost, limited high-temp resistance | Med |
| Medical-Grade Silicone | Inner linings, skin-contact parts | Biocompatible, high-temperature stability | Higher cost, potential tearing under stress | High |
| Stainless Steel (304/316) | Structural framework, support parts | Strong, corrosion-resistant, sterilizable | Heavy, costly, less comfortable for direct contact | High |
This detailed analysis aims to empower international B2B buyers with the insights needed to select materials aligned with regional standards, environmental conditions, and cost considerations. Proper material choice not only enhances product performance but also ensures compliance with health and safety regulations across markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for surgical shoe
Manufacturing Processes for Surgical Shoes
The production of surgical shoes involves a series of meticulously controlled stages to ensure both functional performance and compliance with international standards. The process can be broadly segmented into material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation
High-quality raw materials form the foundation of a reliable surgical shoe. Typically, manufacturers select medical-grade polymers, thermoplastics, or rubber compounds that meet biocompatibility standards. Leather or synthetic uppers are also prepared, often adhering to hypoallergenic criteria. Material procurement involves rigorous supplier qualification, especially critical for B2B buyers from regions like Nigeria or South America, where supply chain variability may exist.
Forming and Molding
The core shaping of the sole and upper components is achieved through injection molding, compression molding, or thermoforming techniques. Precision molds are designed to produce consistent, ergonomic shapes that provide support and comfort. Advanced CAD/CAM technologies are increasingly employed to enhance accuracy, reduce waste, and ensure rapid prototyping for custom orders.
Assembly
The assembled surgical shoe integrates the upper, sole, and any additional supportive elements such as insoles or anti-slip pads. Automated assembly lines with robotic welding or adhesive application are common for large-scale production, ensuring uniformity. For customized or low-volume orders, manual assembly may be used, emphasizing craftsmanship and quality.
Finishing
Final steps include trimming excess material, applying surface treatments, and performing thorough cleaning to eliminate contaminants. Surface finishes often involve anti-microbial coatings or treatments to meet healthcare hygiene standards. Labeling, packaging, and sterilization preparations are completed at this stage, aligned with the end-use requirements.
Quality Assurance (QA) and Control (QC) Practices
Ensuring the safety, durability, and compliance of surgical shoes is paramount, especially for international B2B transactions. The QA/QC process integrates global standards and industry-specific certifications, with multiple checkpoints throughout manufacturing.
International Standards and Certifications
– ISO 9001: Most reputable manufacturers operate under ISO 9001, ensuring a comprehensive quality management system that emphasizes continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
– CE Marking (European Conformity): For European markets, CE certification confirms compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection directives, including EN 14983 standards for safety footwear.
– API & Other Industry-Specific Certifications: In specialized sectors, certifications such as API standards for industrial safety footwear may apply, especially if the shoes are designed for specific medical or industrial environments.
QC Checkpoints
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials and components are inspected upon arrival using visual assessment, dimensional checks, and material testing to verify specifications before production begins.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, continuous monitoring ensures each stage—molding, assembly, finishing—meets predefined parameters. Techniques include dimensional inspections, adhesion tests, and functional assessments such as slip resistance and support stability.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipment, finished shoes undergo comprehensive testing, including physical durability, impact resistance, microbiological safety, and sterilization validation if applicable.
Testing Methods and Verification
– Mechanical Testing: Tensile, compression, and flexural tests to assess structural integrity.
– Environmental Testing: Exposure to temperature, humidity, and chemical agents to simulate real-world conditions.
– Biocompatibility Testing: Ensures materials do not cause adverse reactions, critical for healthcare environments.
– Slip Resistance Testing: Ensures soles meet standards such as ASTM F2913 or EN 13287 for safe traction.
How B2B Buyers Can Verify Supplier QC
– Audit Procedures: Conduct on-site audits to evaluate manufacturing practices, equipment calibration, cleanliness, and employee training.
– Inspection Reports and Certificates: Request detailed QC documentation, including test reports, certificates of compliance, and batch traceability data.
– Third-Party Inspection: Engage independent inspection agencies (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas) for unbiased verification of product quality and conformity.
– Sample Testing: Perform independent testing on samples received to confirm adherence to specified standards before large orders.
Considerations for International B2B Buyers
From Africa and South America
Buyers should prioritize manufacturers with robust IQC and FQC processes, as supply chain reliability may vary. Establish clear communication channels and request detailed documentation, including ISO and local certifications. Consider engaging third-party inspectors to verify QC processes, especially when importing from regions with differing regulatory landscapes.
From the Middle East and Europe
European buyers are often more accustomed to stringent compliance and may require CE or ISO 13485 (for medical devices) certifications. They should perform rigorous audits and insist on comprehensive testing reports. Leveraging third-party inspection services can facilitate compliance verification and reduce risks associated with product recalls or non-conformance.
Overall Strategy for B2B Buyers
– Supplier Qualification: Select manufacturers with proven certifications, transparent QC procedures, and a track record of compliance.
– Regular Audits: Schedule periodic audits to maintain oversight and ensure ongoing adherence to quality standards.
– Sample and Batch Testing: Always verify product samples and perform random batch testing upon receipt to catch potential quality deviations early.
– Clear Contractual Terms: Define QC requirements explicitly in purchase agreements, including documentation, testing protocols, and non-conformance procedures.
By integrating these detailed manufacturing and QC insights into procurement strategies, international B2B buyers can significantly mitigate risks, ensure product consistency, and foster long-term, compliant supply relationships for surgical shoes across diverse markets.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for surgical shoe Sourcing
Cost Structure Breakdown for Surgical Shoe Sourcing
Understanding the detailed components that contribute to the cost of surgical shoes is essential for international buyers aiming to optimize procurement budgets. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: High-quality, medical-grade materials such as antimicrobial fabrics, specialized soles, and durable plastics or metals. Material costs typically account for 30-50% of the total unit price, influenced heavily by specifications and certifications (e.g., ISO, CE).
-
Labor: Manufacturing labor costs vary significantly across regions. Asian suppliers often offer lower wages, whereas European and Middle Eastern manufacturers may charge premium rates due to higher living standards and stricter labor regulations. Labor costs generally range from 10-25% of the total price.
-
Manufacturing Overheads: These include equipment depreciation, factory utilities, and administrative expenses. Overheads are relatively stable but can fluctuate based on factory automation levels and operational efficiencies.
-
Tooling and Setup Fees: For customized designs or new models, tooling costs can be substantial, often ranging from a few hundred to several thousand dollars, amortized over the order volume. These costs are typically one-time but impact per-unit pricing for small runs.
-
Quality Control and Certifications: Ensuring compliance with international standards (e.g., FDA, CE, ISO) adds to costs, particularly if third-party testing or certification processes are involved. These expenses can add 5-10% to initial setup costs but are crucial for market access.
-
Logistics and Shipping: Shipping costs are influenced by weight, volume, destination country, and chosen Incoterms. Buyers should factor in customs duties, taxes, and potential delays, especially when sourcing from regions with complex import regulations.
-
Profit Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin of 10-25%, depending on order volume, exclusivity agreements, and market competitiveness.
Key Price Influencers
Several factors drive the final pricing and should be carefully negotiated:
-
Order Volume & Minimum Order Quantities (MOQ): Larger orders generally unlock volume discounts, reducing per-unit costs. Buyers from regions like Nigeria or South America should aim for high-volume contracts to leverage economies of scale.
-
Specifications & Customization: Custom features, branding, or specialized designs increase costs. Clear communication of requirements helps avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials & Certifications: Higher-grade materials and compliance with international standards elevate costs but are often necessary for market acceptance and safety compliance.
-
Supplier Capabilities & Reliability: Established manufacturers with good track records may charge premium prices but offer better quality assurance, shorter lead times, and more reliable delivery.
-
Incoterms & Shipping Terms: FOB (Free on Board) is common, allowing buyers to manage shipping logistics, potentially reducing costs. DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) includes all costs but may carry higher unit prices.
Strategic Tips for International Buyers
-
Negotiate for Better Terms: Leverage order volume, long-term partnerships, or upfront payments to negotiate discounts and favorable payment terms.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just unit price but also shipping, customs, quality assurance, and after-sales support. Sometimes paying slightly more upfront reduces downstream costs and risks.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Prices can vary significantly based on regional market conditions, currency fluctuations, and supplier capacity. Always request detailed quotations breaking down costs to identify potential savings.
-
Sample and Pilot Orders: Conduct sampling before large commitments to verify quality and compliance, avoiding costly rework or returns.
Price Range and Indicative Costs
While prices can vary widely depending on specifications and sourcing region, typical unit costs for standard surgical shoes range from $5 to $15 USD for bulk orders (minimum order quantities of 1,000 units or more). Custom or highly specialized models may range from $20 to $50 USD per unit for smaller quantities.
Disclaimer: These prices are indicative and subject to change based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific project requirements.
By thoroughly analyzing these cost components and influencing factors, international B2B buyers can make informed sourcing decisions, optimize their procurement strategy, and ensure competitive pricing without compromising quality and compliance.
Spotlight on Potential surgical shoe Manufacturers and Suppliers
- (No specific manufacturer data was available or requested for detailed profiling in this section for surgical shoe.)*
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for surgical shoe
Critical Technical Properties of Surgical Shoes
1. Material Grade and Composition
The choice of materials directly impacts the durability, comfort, and sterilization compatibility of surgical shoes. High-grade, medical-grade thermoplastics or rubber compounds are standard, ensuring resistance to chemicals and repeated sterilization cycles. For B2B buyers, verifying material certifications (e.g., ISO 13485 compliance) guarantees product safety and regulatory adherence across different markets.
2. Structural Tolerance and Precision
Manufacturers must maintain strict dimensional tolerances to ensure proper fit and compatibility with other surgical equipment. Tolerance levels typically range within ±0.5 mm for critical dimensions. Accurate sizing reduces return rates and improves user confidence, especially when sourcing large quantities for hospital procurement.
3. Slip Resistance and Traction
Surgical environments demand shoes with high slip-resistance properties to prevent accidents. The coefficient of friction (COF) should meet industry standards (e.g., ASTM F2913). For B2B buyers, confirming these specs helps ensure safety compliance and reduces liability risks.
4. Sterilization Compatibility
Surgical shoes must withstand sterilization methods such as autoclaving, chemical sterilization, or UV treatment without degradation. Materials should be rated for high-temperature exposure and chemical resistance. This property is critical for maintaining hygiene standards and avoiding product failure during sterilization cycles.
5. Weight and Ergonomics
Lightweight designs enhance comfort for healthcare professionals during long shifts. Ergonomically optimized shoes reduce fatigue and improve performance. Buyers should seek detailed specifications on weight per unit and ergonomic features, especially when sourcing for large healthcare institutions.
6. Color and Finish
While primarily aesthetic, color coding (e.g., blue for sterile zones) aids in infection control protocols. Uniform finishes facilitate easier cleaning and sterilization. Suppliers should provide options for customization to meet branding or regulatory requirements in different regions.
Industry and Trade Terminology for Surgical Shoes
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to companies that produce surgical shoes which are then branded and sold by other firms. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial when negotiating pricing, quality control, and intellectual property rights in international sourcing.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
The smallest batch size a manufacturer is willing to produce. MOQs impact procurement planning, especially for buyers with limited budgets or specific project scales. Clarifying MOQs upfront helps avoid overstocking or supply shortages.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
A formal request sent by buyers to suppliers to obtain detailed pricing, lead times, and terms. Effective RFQs streamline the procurement process and facilitate comparison across multiple vendors, essential for international buyers aiming for best value.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Standardized trade terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that define responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Common Incoterms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance & Freight) clarify delivery obligations and costs, reducing misunderstandings in cross-border transactions.
5. Lead Time
The period from order placement to product delivery. Knowing supplier lead times enables better planning, especially when managing inventory levels across different regions with varying logistics efficiencies.
6. Quality Certification
Standards such as ISO 13485, CE marking, or FDA approval validate the safety and efficacy of surgical shoes. For international buyers, verifying these certifications ensures compliance with local regulations and reduces market entry risks.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can make informed decisions, negotiate effectively, and establish reliable supply chains for surgical shoes. Prioritizing specifications aligned with regional standards and clear communication of trade terms will facilitate smoother procurement processes and long-term partnerships.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the surgical shoe Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global surgical shoe market is experiencing steady growth driven by expanding healthcare infrastructures, increased awareness of infection control, and rising demand for specialized medical footwear. Key drivers include technological advancements in materials, improved ergonomic designs, and a focus on safety standards, especially amid ongoing innovations in infection prevention protocols.
Emerging B2B sourcing trends highlight the shift toward localized manufacturing in regions such as Southeast Asia and Eastern Europe, which offer cost efficiencies and shorter supply chains. For buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, this presents opportunities to negotiate better lead times and reduce logistical complexities. For instance, European buyers benefit from proximity to high-quality European manufacturers, while Middle Eastern markets are increasingly sourcing from Asia to capitalize on competitive pricing.
Digital transformation is also reshaping procurement processes. Many suppliers now leverage online platforms, virtual sampling, and real-time inventory tracking, facilitating more transparent and agile sourcing. Additionally, there is a growing preference for suppliers offering customizable solutions to meet specific clinical or safety standards, which is crucial for B2B buyers seeking tailored product offerings.
Sustainability considerations are becoming central to procurement decisions. Buyers are increasingly scrutinizing supply chains for compliance with environmental standards, seeking suppliers with certifications such as ISO 14001 or FSC. The trend toward eco-friendly materials and manufacturing processes is not only driven by regulatory pressures but also by a growing demand from healthcare providers and end-users for sustainable products.
Overall, B2B buyers should focus on establishing partnerships with suppliers who demonstrate technological innovation, agility in sourcing, and a commitment to sustainability to stay competitive in this evolving market landscape.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are now integral to strategic procurement in the surgical shoe sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes—particularly related to the use of non-renewable resources, chemical emissions, and waste—has prompted buyers to prioritize suppliers committed to green practices. For example, suppliers employing biodegradable or recyclable materials reduce environmental footprints and align with global sustainability goals.
Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management Systems) and FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) are becoming essential benchmarks for ethical sourcing. These certifications demonstrate a supplier’s commitment to minimizing environmental impact and ensuring responsible resource use. For B2B buyers from regions like Nigeria, Brazil, or the UK, partnering with certified suppliers can enhance brand reputation and meet regulatory standards across different markets.
Moreover, ethical labor practices are critical, especially considering the global scrutiny over supply chain transparency. Buyers should seek suppliers that adhere to fair labor standards, avoid child labor, and ensure safe working conditions. Transparency is often evidenced through third-party audits and supply chain disclosures.
In terms of materials, there is a notable shift toward ‘green’ materials such as natural rubber, organic textiles, and low-impact dyes. These materials not only reduce ecological footprints but also appeal to healthcare providers and consumers increasingly committed to sustainability. Incorporating sustainable practices into sourcing strategies can also mitigate risks related to regulatory non-compliance, reputational damage, and supply disruptions caused by environmental crises or social activism.
In summary, integrating sustainability and ethics into procurement practices is vital for long-term competitiveness. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers with verified green credentials and transparent supply chains to meet evolving regulatory, consumer, and institutional expectations.
Brief Evolution/History (Optional)
The surgical shoe sector has evolved from basic, utilitarian designs to highly specialized, technologically advanced products. Historically, manufacturing focused primarily on functionality and cost-efficiency, with limited regard for environmental or social impacts. Over the past two decades, increasing regulatory standards and consumer awareness have driven a shift toward sustainability, ethical sourcing, and innovation.
In the early 2000s, the introduction of antimicrobial and ergonomic features marked a significant development, improving patient safety and comfort. More recently, digital tools such as 3D printing and CAD/CAM systems have revolutionized customization and rapid prototyping, enabling manufacturers to meet specific clinical needs more efficiently.
This evolution reflects a broader industry trend toward integrating sustainability into product design and supply chain management. For B2B buyers, understanding this progression underscores the importance of partnering with forward-thinking suppliers who invest in innovation, quality, and responsible sourcing practices. Such collaborations not only ensure compliance with evolving standards but also position buyers as leaders in sustainable healthcare solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of surgical shoe
1. How can I verify the credibility and reliability of a surgical shoe supplier internationally?
Verifying supplier credibility is crucial to mitigate risks. Start by requesting industry certifications such as ISO 13485, CE marking, or FDA approval, depending on your target market. Conduct thorough background checks through trade associations, online B2B marketplaces, and customer reviews. Request references from previous clients, especially those in your region or similar markets. Additionally, consider visiting the supplier’s manufacturing facility if feasible, or hire third-party inspection services to conduct audits. Reliable suppliers should be transparent about their manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and compliance standards, ensuring consistent product quality for your market.
2. What customization options are typically available for surgical shoes, and how do they impact lead times and costs?
Most international suppliers offer customization such as branding (logos, labels), color options, sizing, and specific material preferences. Advanced customization like specialized designs, antimicrobial treatments, or unique sizes may require additional lead time and incur higher costs. Clear communication of your specifications upfront is essential to get accurate quotes. Customization generally adds 2-4 weeks to standard lead times; therefore, plan your procurement schedule accordingly. Negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) for customized products, as higher customization levels often require larger orders to justify setup costs.
3. What are typical MOQs, lead times, and payment terms for importing surgical shoes?
MOQs vary widely, typically ranging from 500 to 5,000 pairs, depending on the supplier and customization level. Lead times generally span from 4 to 12 weeks, influenced by order volume, complexity, and manufacturing location. Payment terms are often negotiated; common arrangements include 30% upfront payment with 70% balance before shipment, or letters of credit for larger orders. Some suppliers may offer flexible terms for trusted partners or bulk buyers. Establish clear agreements early, and consider using escrow or trade finance solutions to mitigate payment risks, especially when dealing with new suppliers.
4. What quality assurance certifications should I look for when sourcing surgical shoes internationally?
Key certifications include ISO 13485 (medical device quality management), CE marking (European conformity), FDA registration (for US markets), and other regional compliance standards. These certifications demonstrate adherence to international safety, efficacy, and quality standards. Request copies of certificates and test reports during supplier evaluation. Also, inquire about their internal quality control processes, batch testing, and inspection procedures. Suppliers with robust QA systems are more likely to deliver consistent, high-quality products, reducing your post-import risks related to recalls, liability, or customer dissatisfaction.
5. How can I manage logistics effectively when importing surgical shoes from overseas?
Effective logistics management involves selecting reliable freight forwarders experienced in medical device shipments. Consider incoterms that allocate responsibilities clearly, such as FOB or CIF, to control costs and liabilities. Be aware of import regulations, tariffs, and customs procedures in your country—these can significantly impact delivery timelines and costs. Use tracking systems and maintain open communication with your logistics partners. For urgent needs, explore air freight options; for cost efficiency, sea freight is typical. Ensure all shipping documentation, including certificates of origin and compliance, is complete to facilitate smooth customs clearance.
6. What should I do if there is a dispute over product quality or delivery?
Establish a clear dispute resolution process before placing orders, including clauses for arbitration or local legal action. If quality issues arise, document them thoroughly with photos, inspection reports, and communication records. Engage with the supplier promptly to seek corrective actions, such as replacements or refunds, per your contractual terms. Consider involving third-party inspectors or mediators to facilitate resolution. Maintaining open, professional communication is key. If disputes cannot be resolved amicably, consult legal experts familiar with international trade laws to enforce contractual rights and minimize financial loss.
7. How do I ensure compliance with regional standards and regulations for surgical shoes in my target market?
Research specific standards applicable in your region—such as CE marking for Europe, FDA approval for the US, or national standards in Nigeria or South America. Communicate these requirements clearly to your supplier and request documentation demonstrating compliance. Engage local regulatory consultants if necessary to interpret certification needs and assist with registration procedures. Ensure products meet labeling, packaging, and safety standards to avoid customs delays or legal issues. Regularly update your knowledge of evolving regulations to maintain ongoing compliance and avoid market entry barriers.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
8. What are best practices for building long-term relationships with international surgical shoe suppliers?
Develop transparent communication channels and set clear expectations from the outset. Start with smaller orders to evaluate product quality and supplier responsiveness before scaling up. Foster trust through timely payments, constructive feedback, and collaborative problem-solving. Visit suppliers’ facilities when possible to build rapport and verify operations. Maintain consistent quality standards and share market insights to help suppliers innovate. Establish long-term contracts with flexible terms to accommodate changing needs. Building mutual understanding and reliability will lead to better pricing, priority service, and smoother negotiations over time.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for surgical shoe
Final Thoughts and Future Perspectives
Effective strategic sourcing of surgical shoes is essential for international B2B buyers aiming to optimize quality, cost-efficiency, and supply chain resilience. By prioritizing supplier vetting, leveraging regional manufacturing advantages, and fostering long-term partnerships, buyers can secure reliable access to innovative products that meet stringent healthcare standards.
As the global healthcare landscape evolves, staying adaptable and informed about emerging suppliers and technological advancements will be critical. Embracing digital procurement tools and fostering transparent communication channels can further enhance sourcing strategies and mitigate risks.
Looking ahead, buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should view strategic sourcing not just as a cost-saving measure but as a strategic competitive advantage. Proactively engaging with diverse suppliers and investing in supply chain resilience will position your organization for sustained growth in the dynamic surgical footwear market.
Take action now—build robust sourcing frameworks that align with your long-term healthcare objectives, ensuring quality, compliance, and innovation are at the core of your procurement strategy.