Master Sourcing High-Quality Gel Shoe Inserts for Global
Guide to Gel Shoe Inserts
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for gel shoe inserts
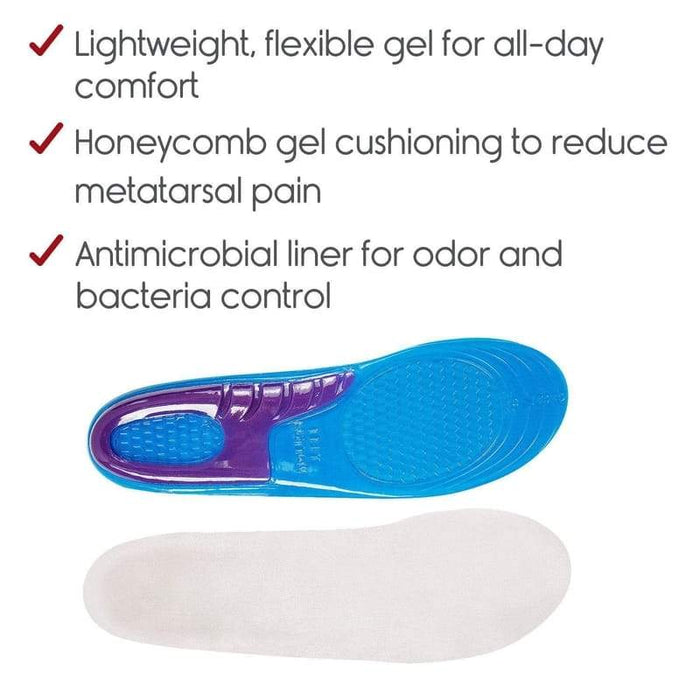
- Understanding gel shoe inserts Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of gel shoe inserts
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for gel shoe inserts
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for gel shoe inserts
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for gel shoe inserts Sourcing
- Spotlight on Potential gel shoe inserts Manufacturers and Suppliers
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for gel shoe inserts
- Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the gel shoe inserts Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of gel shoe inserts
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for gel shoe inserts
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for gel shoe inserts
In today’s competitive footwear industry, gel shoe inserts have become a vital component for brands seeking to enhance comfort, durability, and customer satisfaction. Their growing demand spans global markets, driven by increasing awareness of foot health, lifestyle shifts towards active living, and a preference for premium footwear solutions. For international B2B buyers, especially from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including countries like Spain and France—sourcing high-quality gel inserts presents both a strategic opportunity and a complex challenge.
This comprehensive guide is designed to empower you with actionable insights into every facet of the gel shoe insert supply chain. From understanding the various types and materials used to manufacturing processes and quality control standards, you’ll gain clarity on sourcing reliable suppliers. We will explore key market trends, cost considerations, and regulatory factors that influence purchasing decisions across different regions.
Whether you are looking to diversify your product offerings, improve existing lines, or establish new supplier relationships, this guide provides the knowledge needed to navigate the global market confidently. By understanding critical factors such as supplier credibility, manufacturing capabilities, and pricing strategies, you will be better equipped to make informed sourcing decisions that support sustainable growth and competitive advantage in your target markets.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Understanding gel shoe inserts Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full-Length Gel Inserts | Cover entire footbed, providing uniform cushioning | Shoe manufacturing, orthotics, sports footwear | Pros: High comfort, versatile; Cons: Slightly bulkier, higher cost |
| Heel Gel Cushions | Focused on heel area, often with enhanced shock absorption | Athletic shoes, dress shoes, orthotic devices | Pros: Targeted relief, easy to retrofit; Cons: Limited coverage |
| Metatarsal Gel Pads | Designed to cushion ball of foot, relieve forefoot pressure | Custom orthotics, casual footwear | Pros: Specialized support, reduces forefoot pain; Cons: May shift over time |
| Arch Support Gel Inserts | Contoured gel providing arch elevation and stability | Orthopedic shoes, high-performance footwear | Pros: Improves foot posture, reduces fatigue; Cons: Fit-sensitive |
| Customizable Gel Inserts | Modular design allowing shape adjustments and targeted pressure relief | Premium orthotics, bespoke footwear | Pros: High customization, precise support; Cons: Higher price point |
Full-Length Gel Inserts
Full-length gel inserts are designed to span the entire footbed, offering comprehensive cushioning and shock absorption. They are suitable for a broad range of footwear, including casual, athletic, and orthopedic shoes. For B2B buyers, sourcing these inserts involves evaluating material quality, durability, and compatibility with various shoe sizes. They are ideal for mass production lines or custom orthotic solutions, providing consistent comfort across product lines. While offering excellent comfort, they tend to be bulkier and may increase manufacturing costs, which should be balanced against consumer demand for premium cushioning.
Heel Gel Cushions
Heel gel cushions are specialized inserts that focus solely on the heel area, providing targeted shock absorption and pressure relief. These are especially popular in athletic and dress shoes, where heel impact is significant. B2B buyers should consider the adhesive quality, thickness, and durability of these cushions to ensure they stay in place during wear. They are easy to retrofit into existing shoe designs, making them attractive for aftermarket and OEM applications. Their primary advantage is delivering focused support, but they may lack coverage for other foot areas, limiting their use in comprehensive orthotic solutions.
Metatarsal Gel Pads
Metatarsal gel pads are crafted to cushion the ball of the foot, alleviating forefoot pain and pressure. They are often used in orthotic devices or added to casual footwear for comfort. For B2B procurement, considerations include the pad’s adhesive strength, flexibility, and size options to accommodate different shoe styles. These pads are highly valued in medical and comfort footwear segments, but their tendency to shift or wear out over time necessitates sourcing high-quality, durable materials. Their specialized support makes them a key component in therapeutic footwear lines.
Arch Support Gel Inserts
Arch support gel inserts are contoured to elevate and stabilize the arch, helping to correct overpronation and reduce fatigue. They are widely used in orthopedic, athletic, and casual shoes. B2B buyers should prioritize inserts with consistent shape retention, reliable adhesive, and compatibility with various shoe types. These inserts enhance overall foot stability and comfort, making them attractive for health-conscious markets. However, fit sensitivity and sizing variability require careful selection and potentially custom solutions, especially in premium or bespoke product lines.
Customizable Gel Inserts
These inserts feature modular or adjustable designs, allowing manufacturers or end-users to customize support areas for specific needs. They are typically used in high-end orthotics or bespoke footwear. For B2B buyers, key considerations include the availability of different modules, ease of assembly, and material quality. Customizable gel inserts offer a premium, tailored experience, but their higher production costs and complexity may limit mass-market applications. They are best suited for niche markets demanding personalized orthotic solutions, offering significant differentiation opportunities.
Key Industrial Applications of gel shoe inserts
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of gel shoe inserts | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare & Medical | Orthopedic footwear for patients with foot conditions | Enhances patient comfort, reduces recovery time, and improves compliance | Medical-grade materials, biocompatibility certifications, consistent quality standards |
| Sports & Athletics | Performance footwear for athletes and active users | Improves shock absorption, reduces injury risk, and boosts athlete performance | High durability, impact resistance, and customization options |
| Workwear & Safety | Anti-fatigue and comfort insoles for industrial workers | Reduces fatigue, enhances safety, and increases productivity | Heavy-duty resilience, long-lasting materials, compliance with safety standards |
| Footwear Manufacturing | Custom insoles for footwear brands and OEMs | Differentiates products with superior comfort, supports brand loyalty | Consistent supply, flexible sizing, and customization capabilities |
| Hospitality & Tourism | Comfort-enhancing insoles for hotel and airline staff | Improves employee comfort during long shifts, reduces foot-related health issues | Cost-effective, easy to integrate, and scalable supply chains |
Healthcare & Medical
Gel shoe inserts are extensively used in orthopedic footwear designed for patients with conditions such as plantar fasciitis, diabetic foot ulcers, or post-surgical recovery. These inserts provide targeted cushioning and support, alleviating pain and preventing further injury. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America where healthcare infrastructure varies, sourcing medical-grade, biocompatible gel inserts that meet stringent health standards is crucial. Reliable supply chains and certification ensure compliance with local regulatory requirements, enabling seamless integration into healthcare products.
Sports & Athletics
In the sports sector, gel shoe inserts serve as performance-enhancing components in athletic shoes. They absorb shock during high-impact activities, reduce fatigue, and lower injury risks for athletes and fitness enthusiasts. For European markets like France and Spain, where sports tourism and active lifestyles are prominent, sourcing high-performance, durable gel inserts is essential. Buyers should prioritize impact-resistant materials with customization options to cater to different sports disciplines, ensuring product differentiation and customer satisfaction.
Workwear & Safety
Industrial workers, especially in sectors like construction, manufacturing, and logistics, require footwear with superior comfort and safety features. Gel shoe inserts act as anti-fatigue solutions, reducing long-term foot and leg strain, which can lead to increased productivity and fewer health-related absences. For Middle Eastern and African markets with hot climates and physically demanding jobs, sourcing resilient, long-lasting gel inserts that withstand harsh conditions and meet safety standards (e.g., EN, OSHA) is vital for maintaining workforce wellbeing and operational efficiency.
Footwear Manufacturing
OEMs and footwear brands incorporate gel shoe inserts to enhance the comfort and appeal of their products. Customizable inserts allow brands to differentiate in crowded markets across Europe and Latin America, fostering brand loyalty. International buyers should focus on sourcing flexible, scalable gel insert solutions that support various shoe styles and sizes. Consistent quality and reliable supply chains are critical to meet manufacturing timelines and maintain product quality.
Hospitality & Tourism
Hotels, airlines, and cruise lines seek comfortable footwear solutions for their staff, who often stand for long hours. Gel shoe inserts provide immediate comfort, reduce fatigue, and help prevent foot-related health issues, ultimately improving employee wellbeing and service quality. For markets in the Middle East and Europe, sourcing cost-effective yet durable gel inserts that can be easily integrated into existing uniform footwear is essential. Scalability and timely delivery are key to supporting large-scale deployment across hospitality chains.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for gel shoe inserts
Analysis of Common Materials for Gel Shoe Inserts
1. Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU)
Key Properties:
TPU is a versatile polymer known for its excellent flexibility, abrasion resistance, and elasticity. It maintains performance over a wide temperature range (-40°C to 80°C) and exhibits good chemical resistance, including oils and greases. Its transparency and ease of processing make it popular in consumer goods, including gel shoe inserts.
Pros & Cons:
* Pros:*
– High durability and flexibility, ensuring long-lasting cushioning.
– Good resistance to tearing and deformation under pressure.
– Relatively easy to mold and shape during manufacturing, reducing production costs.
- Cons:*
- Slightly higher material cost compared to simpler plastics.
- Requires precise processing conditions to avoid defects.
- Environmental concerns due to limited biodegradability.
Impact on Application:
TPU’s chemical resistance allows it to withstand sweat and moisture exposure typical in footwear, maintaining performance over time. Its flexibility ensures comfort, but it may need additional treatments or coatings for enhanced moisture management.
International Buyer Considerations:
TPU generally complies with global standards such as ASTM and EN ISO. For markets like Europe, compliance with REACH regulations is essential. Buyers in Africa, South America, and the Middle East should verify local import standards, especially regarding chemical safety and environmental regulations.
2. Silicone Gel
Key Properties:
Silicone gel is a soft, viscoelastic material with excellent shock absorption and thermal stability (-50°C to 200°C). It resists aging, UV exposure, and environmental degradation, making it ideal for cushioning applications.
Pros & Cons:
* Pros:*
– Superior shock absorption, reducing impact stress on the foot.
– Excellent temperature stability and chemical inertness.
– Resistant to UV, ozone, and moisture, extending product lifespan.
- Cons:*
- Higher manufacturing complexity and cost due to specialized molding processes.
- Less resilient to shear forces, which can cause deformation over time.
- Potential for leakage if not properly encapsulated.
Impact on Application:
Silicone gel provides consistent cushioning, ideal for high-impact zones in footwear. Its inert nature ensures compatibility with various materials, but careful sealing is necessary to prevent leakage.
International Buyer Considerations:
Silicone gel’s inertness simplifies compliance with international safety standards. However, buyers should confirm that the silicone formulation adheres to local regulations, especially concerning medical-grade or food-grade certifications if applicable. European markets often require REACH compliance, while African and Middle Eastern markets may have specific import restrictions.
3. EVA (Ethylene Vinyl Acetate)
Key Properties:
EVA is a lightweight, flexible foam material with good shock absorption and resilience. It offers moderate temperature resistance (-20°C to 70°C) and excellent processability, making it suitable for mass production.
Pros & Cons:
* Pros:*
– Cost-effective and widely available, ideal for large-scale manufacturing.
– Good flexibility and cushioning properties.
– Easy to mold into complex shapes, reducing tooling costs.
- Cons:*
- Less durable under prolonged exposure to UV and environmental elements.
- Can degrade over time, especially in high-temperature environments.
- Limited resistance to oils and certain chemicals.
Impact on Application:
EVA’s lightweight nature enhances comfort, but its susceptibility to environmental degradation necessitates protective coatings or treatments for outdoor or humid environments common in Africa and South America.
International Buyer Considerations:
EVA complies with many international standards, but buyers should verify specific chemical safety certifications, especially in markets with strict regulations like the EU. Its low cost makes it attractive for large orders, but durability considerations should inform application environments.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for gel shoe inserts | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) | Flexible cushioning, durable inserts | High durability and flexibility | Slightly higher cost, environmental concerns | Med |
| Silicone Gel | Shock absorption in high-impact zones | Excellent shock absorption and temperature stability | Higher manufacturing complexity, potential leakage | High |
| EVA | Lightweight, general cushioning | Cost-effective, easy to mold | Less durable in harsh environments, UV sensitivity | Low |
This comprehensive analysis helps international B2B buyers from diverse regions select the most appropriate materials based on performance, cost, and compliance considerations. Understanding these material properties ensures better product quality, regulatory adherence, and market suitability.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for gel shoe inserts
Manufacturing Processes of Gel Shoe Inserts
The production of gel shoe inserts involves a series of carefully controlled stages, each critical to ensuring product quality, durability, and safety. Understanding these stages enables B2B buyers to better evaluate supplier capabilities and compliance.
1. Material Preparation and Raw Material Inspection
The manufacturing process begins with sourcing high-quality raw materials, primarily medical-grade or thermoplastic gels, foaming agents, and supportive base materials such as EVA or PU foam. Suppliers typically conduct Incoming Quality Control (IQC) to verify the consistency, purity, and compliance of these materials with international standards like ISO 9001 or industry-specific certifications. For B2B buyers, requesting detailed IQC reports or third-party test results can provide assurance of raw material integrity.
2. Forming and Molding
The core of gel insert production involves molding the gel components into the desired shape. Common techniques include compression molding or injection molding, which ensure uniformity and precision. Advanced manufacturers may employ computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) systems to produce molds with tight tolerances, reducing variability across batches. The gel is typically cured within molds under controlled temperature and pressure conditions to achieve optimal consistency.
3. Assembly and Integration
Post-molding, gel components are assembled with supportive substrates, often via adhesive bonding or lamination. This step requires strict process controls to prevent delamination or defects. Automated assembly lines equipped with vision systems or laser inspection are standard in reputable factories, ensuring each insert meets dimensional and aesthetic specifications. Suppliers should provide detailed process documentation and batch records for traceability.
4. Finishing and Packaging
The final stage involves trimming excess material, surface finishing, and packaging. Surface treatments may include anti-slip coatings or branding embossments. Proper packaging—sealed in moisture-proof, UV-protected materials—preserves product integrity during transit. Quality checks at this stage include FQC (Final Quality Control), verifying dimensions, appearance, and packaging integrity.
Quality Assurance (QA) and Standards in Manufacturing
Robust quality assurance protocols are vital for consistent product performance and compliance with international regulations.
1. International Standards and Certifications
– ISO 9001: Most reputable manufacturers operate under ISO 9001, ensuring their quality management systems meet global benchmarks.
– CE Marking: For products sold within the European Economic Area, CE certification confirms compliance with safety, health, and environmental directives.
– Additional Certifications: Depending on the market, certifications such as API (for industrial-grade products), FDA approval (for medical applications), or local standards (e.g., ANVISA in Brazil) may be relevant.
2. Quality Control Checkpoints
– IQC (Incoming Quality Control): Verifies raw materials before production begins. Tests include tensile strength, gel consistency, and purity.
– IPQC (In-Process Quality Control): Monitors production parameters such as temperature, pressure, and curing times. Visual inspections and dimensional checks ensure ongoing conformity.
– FQC (Final Quality Control): Conducted on finished products, including stress testing, adhesion testing, and appearance inspection.
3. Common Testing Methods
– Mechanical Testing: Compression and tensile tests assess durability under load.
– Chemical Testing: Ensures no harmful substances leach from the gel, complying with REACH or other chemical safety regulations.
– Environmental Testing: Simulates conditions like moisture, heat, or UV exposure to confirm long-term stability.
How B2B Buyers Can Verify Supplier QC
International buyers should adopt rigorous due diligence practices to verify the efficacy of a supplier’s quality systems:
- Factory Audits: Conduct or commission third-party audits to assess manufacturing facilities, quality management systems, and compliance records. Focus on hygiene, process controls, and traceability systems.
- Review Quality Documentation: Request detailed inspection reports, test certificates, and batch traceability records. Suppliers should provide comprehensive documentation demonstrating adherence to standards.
- Third-party Inspections: Engage independent inspection agencies (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas) for pre-shipment inspections, especially when importing large quantities or entering new supplier relationships.
- Sample Testing: Perform independent testing of samples to validate product claims, especially for critical parameters like gel safety, adhesion, and physical durability.
Specific Considerations for International B2B Buyers
Different regions have unique regulatory landscapes and quality expectations:
- Africa & South America: Buyers should prioritize suppliers with ISO 9001 certification and adherence to local safety standards (e.g., INMETRO in Brazil). Consider suppliers with experience exporting to these markets, ensuring familiarity with customs and import regulations.
- Middle East: Emphasize CE marking and compliance with Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) standards. Suppliers with certifications aligned with local authorities can streamline approval processes.
- Europe (e.g., Spain, France): Stringent compliance with REACH, CE, and possibly ISO 13485 for medical-grade products is essential. Buyers should verify the presence of comprehensive documentation and conduct regular audits to maintain standards.
In summary, manufacturing gel shoe inserts involves precise molding, assembly, and finishing processes under strict quality controls. For B2B buyers, especially from diverse regions, verifying supplier quality through audits, documentation, and third-party testing is critical. Establishing clear expectations and maintaining open communication channels with suppliers will facilitate consistent product quality and regulatory compliance across international markets.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for gel shoe inserts Sourcing
Cost Structure Breakdown
Understanding the cost components involved in sourcing gel shoe inserts is fundamental for effective pricing and negotiation. The primary cost drivers include:
-
Materials: High-quality gel, foam, fabric linings, and adhesives constitute the core material costs. Premium materials with enhanced durability or added features (e.g., antimicrobial properties) typically increase expenses. Material costs can vary significantly depending on sourcing regions and supplier relationships.
-
Labor: Manufacturing labor costs are generally lower in regions like Asia but can be higher in Europe or the Middle East. Efficient factories with skilled labor can reduce per-unit costs, but buyers should consider the impact on quality and turnaround times.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: Includes factory utilities, equipment maintenance, and administrative expenses. Overhead costs are influenced by factory size, location, and operational efficiencies.
-
Tooling and Setup: Initial tooling costs for molds and production setup can be substantial, especially for customized designs or small batch runs. These are typically amortized over large order volumes, reducing per-unit costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure product consistency and compliance with standards such as ISO or specific regional certifications. Investing in QC can slightly elevate costs but reduces the risk of costly returns or rework.
-
Logistics and Shipping: International shipping costs depend on destination, shipping mode (air vs. sea), and logistics providers. Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) significantly influence who bears shipping costs and risks.
-
Profit Margin: Suppliers typically aim for a margin of 10-30%, depending on product complexity, volume, and market competitiveness. Larger, consistent orders often enable better margins through negotiation.
Price Influencers
Several factors directly impact the final price for international buyers:
-
Order Volume & MOQ: Higher volumes usually attract lower unit prices due to economies of scale. Many suppliers set Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) to ensure production viability; negotiating MOQs is often possible for larger or repeat orders.
-
Customization & Specifications: Customized gel inserts—such as specific sizes, shapes, or branding—generally increase costs due to additional tooling, design, and QC requirements. Standard models are more cost-effective.
-
Materials & Quality Certifications: Sourcing premium, certified materials (e.g., FDA-approved gel or eco-friendly fabrics) can elevate costs but also add value and market appeal.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, production capacity, and geographic location influence pricing. Established suppliers with higher quality standards may charge premium but offer reliability.
-
Incoterms & Shipping: FOB (Free on Board) terms shift shipping costs to the buyer, while CIF (Cost, Insurance, Freight) includes them, impacting total landed costs. Buyers should evaluate logistics costs carefully.
Buyer Tips for Cost Optimization
-
Negotiate Volume Discounts: Leverage larger orders or long-term partnerships to secure better pricing and flexible MOQs. For buyers from regions like Africa or South America, consolidating orders can reduce per-unit costs.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just unit price but also shipping, customs duties, tariffs, and potential rework costs. For European buyers, understanding VAT and import regulations is crucial.
-
Standardization & Flexibility: Opt for standard designs to minimize tooling costs, but be open to slight modifications that can reduce expenses or improve product-market fit.
-
Leverage Incoterms Strategically: Evaluate whether FOB or CIF offers better control over logistics costs. In regions with established freight networks, FOB may offer cost savings.
-
Price Transparency & Negotiation: Request detailed quotations that specify costs for materials, tooling, QC, and logistics. Transparent pricing fosters better negotiations and minimizes surprises.
Price Range and Market Considerations
Indicative pricing for bulk orders of gel shoe inserts generally ranges from $1.50 to $4.50 per pair, depending on volume, customization, and quality standards. Standard models tend toward the lower end, while customized, certified, or premium-quality inserts are positioned higher.
For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, regional factors such as import duties, tariffs, and local market demand influence final landed costs. It’s advisable to obtain multiple quotes from different suppliers and consider long-term relationships for better terms.
Disclaimer: Prices are indicative and can fluctuate based on market conditions, raw material costs, and supplier capacity. Buyers should conduct thorough due diligence and negotiate terms tailored to their specific requirements.
Spotlight on Potential gel shoe inserts Manufacturers and Suppliers
- (No specific manufacturer data was available or requested for detailed profiling in this section for gel shoe inserts.)*
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for gel shoe inserts
Critical Technical Properties of Gel Shoe Inserts
1. Material Grade and Composition
The quality of gel used in shoe inserts is fundamental. High-grade medical or industrial-grade gel ensures durability, consistent cushioning, and safety. For B2B buyers, understanding the specific gel composition—such as silicone, thermoplastic elastomers, or polyurethane—is vital, as it influences flexibility, resilience, and compatibility with various footwear types.
2. Cushioning Density
Cushioning density refers to the firmness or softness of the gel material. It is typically measured in Shore hardness units. A lower Shore hardness indicates softer, more cushioning inserts, suitable for comfort-focused applications, while higher values provide firmer support. Selecting the appropriate density affects customer satisfaction and product performance.
3. Tolerance and Dimensional Accuracy
Manufacturers must adhere to strict tolerance levels, often within ±0.5 mm, to ensure inserts fit precisely into designated shoe sizes and styles. Precise dimensions reduce returns, improve comfort, and maintain consistency across production batches, which is crucial for large orders.
4. Thermal Stability and Durability
Gel inserts should maintain their properties across temperature variations common in different climates. High thermal stability prevents deformation or degradation over time, ensuring longevity and consistent support, especially important for markets in regions with extreme temperatures.
5. Compression Set Resistance
This property measures the material’s ability to recover after compression. High resistance minimizes permanent deformation, ensuring the insert retains its shape and cushioning over prolonged use. For B2B buyers, selecting gel with superior compression set resistance enhances product lifespan and customer satisfaction.
6. Biocompatibility and Safety Standards
Compliance with international safety standards such as ISO 10993 or REACH is essential, especially for medical or orthotic-grade inserts. Non-toxic, hypoallergenic gels reduce liability and appeal to health-conscious consumers worldwide.
Common Industry and Trade Terms
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to companies that produce gel inserts tailored to other brands’ specifications. Understanding OEM relationships helps buyers negotiate custom designs, branding, and specifications directly with manufacturers, often at lower costs.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
The smallest quantity a supplier is willing to produce or sell in a single order. For international buyers, negotiating MOQs is critical to balancing inventory costs with production efficiency, especially when entering new markets or testing product acceptance.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
A formal process where buyers solicit price, lead times, and technical details from multiple suppliers. Sending clear RFQs with detailed specifications accelerates sourcing and ensures competitive pricing.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Standardized trade terms published by ICC that define responsibilities for buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms (like FOB, CIF, DDP) helps international buyers manage logistics costs and risks effectively.
5. Lead Time
The period from placing an order to product delivery. Efficient suppliers with shorter lead times enable faster market entry and inventory management, especially important for seasonal or trend-driven markets.
6. Certification and Compliance
Standards such as ISO, ASTM, or regional certifications (e.g., CE in Europe) ensure products meet safety, quality, and environmental regulations. Buyers should verify supplier certifications to mitigate legal and safety risks in their markets.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms enables B2B buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to make informed decisions. Clear communication of specifications, expectations, and compliance standards ensures smoother procurement processes, better product quality, and stronger supplier relationships.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the gel shoe inserts Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global gel shoe inserts market is experiencing robust growth driven by increasing consumer demand for comfort, orthotic support, and customized footwear solutions. Key drivers include rising awareness of foot health, aging populations in developed regions, and the expanding athletic and casual footwear sectors. For international B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these drivers is essential to align sourcing strategies with market demand.
Emerging technological trends such as advanced polymer formulations and improved manufacturing processes are enhancing the durability, flexibility, and shock absorption capabilities of gel inserts. Digitalization in sourcing—like blockchain for traceability and AI-driven demand forecasting—is transforming supply chain efficiency. Buyers should leverage these innovations to optimize procurement, reduce lead times, and ensure product quality.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Market dynamics vary regionally. In Europe, regulatory standards and sustainability mandates are shaping product specifications, favoring eco-friendly and ethically sourced materials. Middle Eastern markets are increasingly demanding premium, luxury-influenced products with high-performance features. South American and African markets, while still developing, show growth potential through local manufacturing collaborations and cost-effective sourcing options.
For B2B buyers, establishing strong relationships with regional manufacturers and suppliers that prioritize innovation, quality assurance, and flexible order volumes is crucial. Staying informed about shifts in consumer preferences and technological advancements will enable strategic sourcing and competitive advantage in this evolving sector.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a critical criterion for B2B procurement in the gel shoe inserts industry. Environmentally conscious buyers from Europe, the Middle East, and increasingly from South America and Africa are demanding products that minimize ecological impact throughout their lifecycle. This includes sourcing raw materials from renewable or recycled sources, reducing reliance on non-biodegradable plastics, and adopting greener manufacturing practices.
Ethical sourcing also plays a pivotal role. Ensuring that raw materials—such as silicone and other polymers—are obtained through fair labor practices and transparent supply chains enhances brand reputation and compliance with international standards. Certifications like ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and SA8000 (Social Accountability) are valuable indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability and ethical practices.
‘Green’ certifications and eco-labels can serve as differentiators in highly competitive markets. For instance, suppliers that utilize biodegradable gel formulations or recycled packaging materials appeal to environmentally conscious buyers. Moreover, adopting circular economy principles—like designing products for recyclability or facilitating take-back programs—can help meet stringent regulatory requirements and foster long-term supplier relationships rooted in sustainability.
By prioritizing suppliers with verifiable sustainability credentials, B2B buyers can reduce risks related to regulatory non-compliance, enhance supply chain resilience, and meet growing consumer and legislative demands for responsible sourcing.
Brief Evolution/History
The gel shoe inserts industry has evolved significantly over the past two decades, transitioning from basic cushioning products to sophisticated, high-performance solutions. Initially driven by simple comfort needs, the market has shifted toward innovation with the incorporation of advanced polymers and ergonomic designs. This evolution reflects broader footwear industry trends emphasizing health, customization, and sustainability.
For B2B buyers, understanding this progression is essential for strategic sourcing. Early market players focused primarily on cost, often sourcing from low-cost regions with limited quality controls. Today, the emphasis is on product innovation, regulatory compliance, and sustainable practices. This shift has prompted manufacturers to invest in R&D, adopt environmentally friendly materials, and develop certifications that appeal to global markets.
The industry’s history underscores the importance of agility and innovation in maintaining competitive advantage. By partnering with suppliers who have a proven track record of evolution—embracing new technologies and sustainability—they can better meet the diverse needs of markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This historical perspective also highlights opportunities for differentiation through quality, eco-friendliness, and product customization in a rapidly changing landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of gel shoe inserts
-
How can I verify the credibility and reliability of gel shoe insert suppliers internationally?
To ensure supplier credibility, conduct comprehensive due diligence including checking certifications (ISO, CE, SGS), requesting references from previous clients, and reviewing their manufacturing facilities via virtual tours or third-party audits. Look for suppliers with transparent communication, clear product documentation, and positive trade reviews. Participating in trade shows or industry expos can also help establish trust. Additionally, verify their compliance with international quality standards and inquire about their experience exporting to your target markets. Building strong, transparent relationships minimizes risks and ensures consistent product quality. -
What customization options are typically available for gel shoe inserts, and how do they impact lead times and costs?
Suppliers often offer customization in size, shape, firmness, color, branding (logos or packaging), and specific therapeutic features (e.g., arch support, odor control). Customization may increase lead times by 2-4 weeks depending on complexity and production capacity. Costs vary based on volume, complexity, and tooling requirements; larger orders usually benefit from lower unit costs. Clearly communicate your specifications early, and request detailed quotes and sample approvals to avoid delays or unexpected expenses. Establishing a long-term partnership can also streamline customization processes and reduce costs over time. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs), lead times, and payment terms for international B2B purchases of gel shoe inserts?
Most suppliers have MOQs ranging from 1,000 to 10,000 pairs, depending on product complexity and manufacturing scale. Lead times typically range from 4 to 8 weeks after order confirmation, influenced by customization and stock availability. Common payment terms include 30% upfront with the balance before shipment or upon delivery, often via bank transfer or letter of credit for larger orders. Negotiating flexible terms, especially for recurring orders, can improve cash flow. Always confirm lead times and payment conditions before finalizing agreements to align with your distribution schedules. -
What quality assurance measures and certifications should I look for in gel shoe insert suppliers?
Seek suppliers with ISO 9001 certification for quality management and product-specific standards like CE marking or SGS testing reports, which ensure safety and compliance with regional regulations. Request detailed QA procedures, including raw material testing, in-process inspections, and final product testing. Suppliers should provide Certificates of Analysis (CoA) and compliance documents. Conduct or commission third-party testing if necessary, especially for markets with strict standards. Verifying these credentials minimizes product recalls, legal issues, and enhances consumer confidence in your brand. -
How can I manage logistics effectively when importing gel shoe inserts to my country?
Establish clear logistics plans by choosing reliable freight forwarders experienced in international trade, especially for your target regions. Decide on Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) that specify responsibilities and costs between buyer and seller. Consider shipping modes—air freight for faster delivery or sea freight for cost efficiency—based on order volume and urgency. Ensure suppliers can provide accurate documentation (commercial invoice, packing list, bill of lading) for customs clearance. Building relationships with local customs brokers can expedite clearance processes and reduce delays or unexpected costs. -
What are common dispute resolution mechanisms for international B2B transactions in this industry?
Disputes often arise over quality, delivery delays, or payment issues. To mitigate risks, include clear terms in your contract, such as arbitration clauses under recognized bodies like ICC or LCIA, to resolve disputes efficiently. Maintain detailed documentation of all communications, orders, and inspection reports. Using escrow services or letters of credit can secure payments. If disagreements occur, negotiate in good faith and consider involving third-party mediators before escalating to legal action. Proper contractual safeguards and transparent communication are key to minimizing and resolving conflicts. -
How do I ensure compliance with regional regulations and standards for gel shoe inserts in my target markets?
Research specific regulations, such as the EU’s CE standards, South America’s local certifications, or Middle Eastern import requirements. Request suppliers to provide compliance documentation and test reports relevant to your market. Consider engaging local compliance consultants or third-party testing labs for verification. Adjust product labeling, packaging, and safety information to meet regional language and regulatory demands. Regularly monitor changes in standards and maintain open communication with suppliers to ensure ongoing compliance, reducing the risk of shipment delays or legal penalties. -
What strategies can I adopt to build long-term relationships with reliable gel shoe insert suppliers?
Prioritize transparent communication, timely payments, and consistent order volumes to foster trust. Offer feedback on product quality and share market insights to deepen collaboration. Consider volume discounts or exclusive agreements for loyalty. Visit suppliers’ facilities when possible or conduct virtual audits to assess their capabilities. Developing a partnership mindset, including joint development of new products or customization, can lead to better pricing, priority service, and innovation. Long-term relationships reduce sourcing risks, improve supply chain stability, and support mutual growth in competitive markets.
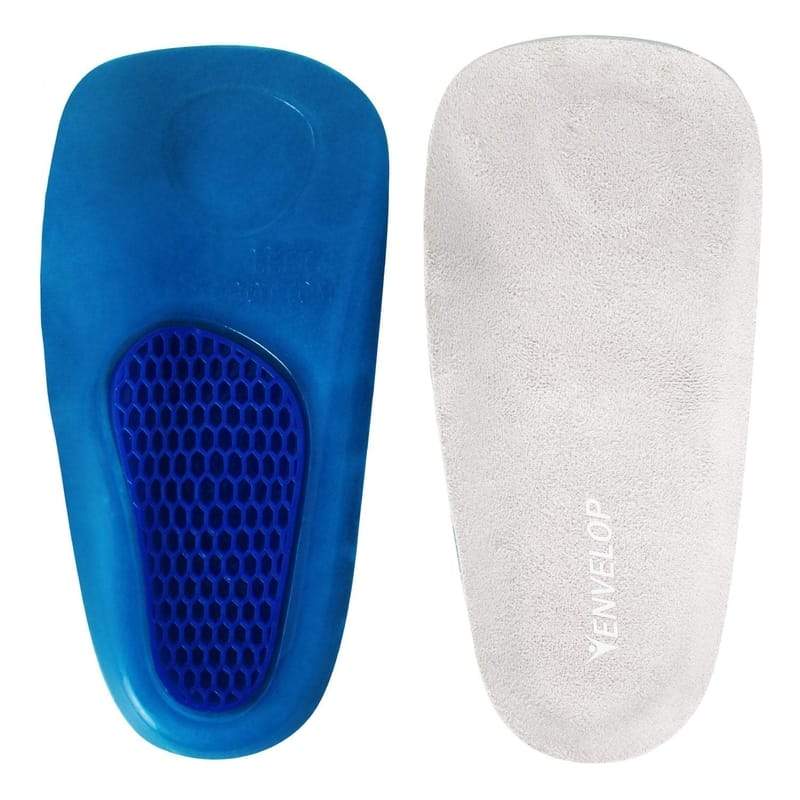

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for gel shoe inserts
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for gel shoe inserts
Effective strategic sourcing is essential for B2B buyers aiming to capitalize on the growing demand for gel shoe inserts worldwide. By prioritizing supplier reliability, quality assurance, and cost competitiveness, organizations can build resilient supply chains capable of adapting to market fluctuations. Diversifying sourcing regions—such as exploring manufacturers in Asia, Europe, or emerging markets—can mitigate risks and unlock innovative product offerings tailored to diverse consumer preferences.
For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, establishing strong supplier relationships and leveraging regional trade agreements can enhance procurement efficiency and reduce lead times. Staying informed about technological advancements and sustainability trends will also position buyers at the forefront of industry innovation.
Looking ahead, the market for gel shoe inserts is poised for continued growth driven by increasing health awareness and footwear customization trends. International B2B buyers should adopt a proactive approach, continuously evaluating suppliers and fostering collaborative partnerships. By doing so, they can ensure a competitive edge in this dynamic sector and meet evolving consumer demands with quality, affordability, and innovation.