Master Global Sourcing of Neuropathy Shoes for Better
Guide to Neuropathy Shoes
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for neuropathy shoes
- Understanding neuropathy shoes Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of neuropathy shoes
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for neuropathy shoes
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for neuropathy shoes
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for neuropathy shoes Sourcing
- Spotlight on Potential neuropathy shoes Manufacturers and Suppliers
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for neuropathy shoes
- Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the neuropathy shoes Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of neuropathy shoes
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for neuropathy shoes
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for neuropathy shoes
In the rapidly evolving landscape of healthcare and mobility solutions, neuropathy shoes have emerged as a vital product for improving quality of life among individuals suffering from peripheral nerve damage. For international B2B buyers—particularly those operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—understanding the nuances of this specialized footwear is essential for meeting rising demand and ensuring optimal patient outcomes. These shoes are not merely footwear; they are a critical component of diabetic and neurological care, combining advanced materials, ergonomic design, and rigorous quality standards.
This comprehensive guide offers an in-depth overview of the neuropathy shoe market, covering key aspects such as product types, innovative materials, manufacturing best practices, quality control measures, and supplier sourcing strategies. It also delves into cost considerations, market trends, and frequently asked questions, equipping buyers with the insights needed to make informed procurement decisions. Whether sourcing from established manufacturing hubs in Europe or exploring emerging suppliers in Africa and South America, this guide aims to streamline your sourcing process.
By leveraging this knowledge, B2B buyers can identify reliable suppliers, assess product quality, and negotiate effectively—ensuring they deliver effective, compliant, and competitively priced neuropathy footwear to their markets. Ultimately, this guide empowers you to navigate the complexities of the global market with confidence, fostering sustainable partnerships and expanding your footprint in this vital healthcare segment.
Understanding neuropathy shoes Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Therapeutic/Medical-Grade Shoes | Designed with specialized insoles, non-slip soles, and extra width options | Healthcare providers, pharmacies, clinics | Pros: Meets medical standards, high customer trust. Cons: Higher cost, limited customization options. |
| Custom-Designed Orthopedic Shoes | Fully customizable with tailored insoles, adjustable fittings, and specific support features | Specialty clinics, orthopedists, custom retailers | Pros: High patient satisfaction, differentiation. Cons: Longer lead times, higher manufacturing complexity. |
| Comfort & Support Shoes | Emphasize cushioning, shock absorption, and ergonomic design | Retailers targeting elderly or diabetic markets | Pros: Broad market appeal, scalable production. Cons: Less specialized, may require frequent updates to keep pace with trends. |
| Slip-Resistant & Safety Shoes | Incorporate anti-slip soles, reinforced toe caps, and durable materials | Industrial and occupational health sectors | Pros: High demand in safety-critical environments, durable. Cons: Niche focus, potentially higher material costs. |
| Eco-Friendly & Sustainable Shoes | Use biodegradable, recycled, or organic materials with eco-conscious manufacturing | Green health markets, eco-conscious retailers | Pros: Growing market segment, aligns with sustainability goals. Cons: Material sourcing can be complex, potentially higher costs. |
Therapeutic/Medical-Grade Shoes
Therapeutic shoes are engineered specifically for patients with neuropathy, diabetes, or other foot conditions. They feature extra depth, non-binding uppers, and specialized insoles to reduce pressure points and improve circulation. B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing from manufacturers compliant with medical standards such as ISO 13485, ensuring product safety and efficacy. These shoes are ideal for clinics, pharmacies, and healthcare distributors aiming to provide high-trust solutions. While they command premium pricing, their high quality reduces return rates and enhances brand reputation, making them a valuable addition to medical product portfolios.
Custom-Designed Orthopedic Shoes
These shoes are tailored to individual patient needs, offering personalized support, adjustable fittings, and bespoke insoles. They are often produced after detailed assessments by orthopedists, enabling precise correction of foot deformities or neuropathy symptoms. For B2B buyers, establishing relationships with manufacturers capable of rapid customization and reliable quality control is critical. Although the production process is more complex and costly, these shoes can command premium margins and foster loyalty among healthcare providers seeking differentiated solutions. They are particularly suitable for markets with high rates of chronic foot conditions, such as Europe and parts of South America.
Comfort & Support Shoes
Focusing on general ergonomic benefits, these shoes incorporate cushioning, shock absorption, and supportive insoles suitable for a broad consumer base, including the elderly and diabetics. They are produced in larger volumes, making them scalable for mass distribution. B2B buyers should look for manufacturers with robust supply chains and compliance with safety standards like EN ISO 20345. While less specialized, they serve as entry points for new markets or retail channels, especially in regions with growing awareness of foot health. Their versatility makes them a staple product line, though staying ahead of ergonomic trends is essential to maintain competitiveness.
Slip-Resistant & Safety Shoes
Designed for industrial, occupational, or hazardous environments, these shoes feature slip-proof soles, reinforced toe caps, and durable materials. They are highly demanded in sectors such as manufacturing, warehousing, and healthcare, where foot safety is paramount. B2B buyers should evaluate certifications like ASTM or EN standards and consider sourcing from manufacturers with proven durability and safety track records. These shoes often require bulk procurement and may involve long-term contracts, making quality assurance and supply reliability key factors. They present lucrative opportunities in regions with expanding industrial sectors or strict workplace safety regulations.
Eco-Friendly & Sustainable Shoes
With increasing consumer demand for sustainability, eco-friendly neuropathy shoes utilize recycled plastics, organic textiles, and biodegradable components. For B2B buyers, sourcing from suppliers committed to transparent supply chains and eco-certifications (e.g., GOTS, FSC) is vital. These shoes appeal to environmentally conscious markets across Europe, South America, and the Middle East, aligning with global sustainability trends. Although sourcing sustainable materials can involve higher costs and supply chain complexities, positioning as a green brand can unlock premium market segments. Investing in partnerships with innovative manufacturers can ensure product quality while supporting environmental goals.
Key Industrial Applications of neuropathy shoes
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of neuropathy shoes | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare & Medical Devices | Custom therapeutic footwear for diabetic and neuropathic patients | Enhances patient outcomes, reduces complications, and lowers liability | Certification standards, material safety, and customization capabilities |
| Rehabilitation & Physiotherapy | Post-surgical and injury recovery footwear | Supports healing, minimizes re-injury, and improves patient compliance | Flexibility in design, durability, and compatibility with orthotic devices |
| Occupational Safety & Industrial Workwear | Anti-fatigue and protective footwear for workers with nerve impairments | Reduces occupational injuries, enhances safety, and boosts productivity | Compliance with safety standards, slip resistance, and ergonomic design |
| Elderly Care & Assisted Living | Comfortable, supportive shoes for seniors with neuropathy | Improves mobility, reduces fall risk, and enhances quality of life | Ease of donning, non-slip soles, and long-term comfort features |
| Sports & Active Lifestyle | Specialized footwear for athletes with nerve conditions | Enables safe participation in physical activities, prevents injury | Breathability, lightweight construction, and impact absorption |
Healthcare & Medical Devices
Neuropathy shoes in the healthcare sector are primarily designed as custom therapeutic footwear tailored for diabetic and neuropathic patients. These shoes address common issues such as foot ulcers, pressure points, and skin breakdown, significantly reducing the risk of complications. For international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America where diabetes prevalence is rising, sourcing high-quality, certified medical footwear is crucial. Suppliers must ensure compliance with medical device standards, use biocompatible materials, and offer customization options to meet diverse patient needs. Reliable supply chains and adherence to local regulatory requirements are essential for success.
Rehabilitation & Physiotherapy
In rehabilitation settings, neuropathy shoes are used post-surgery or after injuries to support healing and prevent re-injury. These shoes often incorporate orthotic compatibility, adjustable features, and enhanced cushioning to accommodate swelling or deformities. For B2B buyers in Europe and the Middle East, sourcing durable, adaptable footwear that aligns with physiotherapy protocols can streamline patient recovery processes. Emphasizing product versatility, long-term wearability, and compliance with health standards can provide a competitive edge, especially when catering to aging populations or chronic conditions.
Occupational Safety & Industrial Workwear
Industrial sectors such as manufacturing, construction, and oil & gas often employ workers with nerve impairments or foot conditions requiring specialized footwear. Neuropathy shoes in this context offer anti-fatigue properties, slip resistance, and reinforced support to prevent workplace accidents. For international buyers, sourcing footwear that complies with regional safety regulations (e.g., PPE standards in Europe or Middle East) and offers durability under harsh conditions is vital. Bulk procurement, cost efficiency, and customization for specific work environments are key considerations to optimize safety and productivity.
Elderly Care & Assisted Living
The elderly care industry demands footwear that promotes mobility and reduces fall risks among seniors with neuropathy. These shoes typically feature non-slip soles, easy fastening mechanisms, and extra cushioning to ensure comfort and stability. B2B buyers in Spain or other European countries can focus on sourcing products that meet strict safety standards, are easy to don and doff, and offer long-lasting comfort. Partnering with manufacturers that provide scalable solutions and comply with healthcare regulations can facilitate supply chain reliability and improve care quality.
Sports & Active Lifestyle
For athletes or active individuals with nerve conditions, specialized neuropathy shoes enable participation in sports while minimizing injury risks. These shoes emphasize lightweight construction, impact absorption, and breathability, supporting active lifestyles without compromising safety. B2B buyers targeting niche markets in regions like South America or the Middle East should seek suppliers offering innovative designs, high-performance materials, and customization options. Ensuring product quality and adherence to sports safety standards can open new market segments and enhance brand reputation.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for neuropathy shoes
Material Analysis for Neuropathy Shoes
Selecting the appropriate materials for neuropathy shoes is critical for ensuring optimal performance, safety, and compliance across diverse international markets. Each material must balance durability, comfort, cost, and regulatory standards, especially considering regional variations in standards and preferences. Below is an in-depth analysis of four common materials used in the manufacturing of neuropathy shoes, focusing on their key properties, advantages, limitations, and considerations for B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Leather (Natural and Synthetic)
Key Properties:
Leather offers excellent breathability, flexibility, and natural moisture-wicking properties, making it suitable for prolonged wear. It also provides moderate resistance to abrasion and can be treated for enhanced water resistance. Synthetic leather, on the other hand, offers more uniformity, lighter weight, and easier manufacturing.
Pros & Cons:
Leather is highly durable and provides a premium feel, which appeals to European and Middle Eastern markets with high standards for quality. Synthetic variants tend to be more cost-effective and easier to produce at scale, suitable for emerging markets. However, genuine leather can be expensive, and its production involves environmental considerations, which may impact compliance with regional standards.
Impact on Application:
Leather’s breathability and flexibility make it ideal for the upper part of neuropathy shoes, providing comfort and reducing pressure points. Synthetic leather can be used where cost or weight is a concern but may compromise some breathability.
International Considerations:
European markets often emphasize sustainability and animal welfare, favoring vegetable-tanned or eco-friendly leather. Compliance with standards like the EU’s REACH regulation is essential. African and South American buyers should consider sourcing from suppliers adhering to local environmental laws, and synthetic options may be preferable where leather import restrictions exist.
EVA (Ethylene Vinyl Acetate)
Key Properties:
EVA is a lightweight, flexible, and shock-absorbing foam material. It exhibits excellent cushioning properties, making it ideal for insoles and midsoles in neuropathy shoes. It also has good chemical resistance and weatherability.
Pros & Cons:
EVA’s primary advantage is its cushioning and shock absorption, reducing pressure on sensitive nerves. It is relatively inexpensive and easy to mold, supporting mass production. However, EVA can degrade over time with exposure to UV light and may compress permanently under heavy loads, affecting longevity.
Impact on Application:
EVA is predominantly used in midsoles and insoles to provide comfort and reduce neuropathic pain. Its lightweight nature benefits users who require less fatigue during prolonged standing or walking.
International Considerations:
EVA’s compliance with international standards (such as ASTM or ISO) is generally straightforward. For regions like Europe, suppliers should ensure the EVA meets REACH regulations. In Africa and South America, sourcing from certified suppliers ensures quality and safety, especially for medical-grade footwear.
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU)
Key Properties:
TPU combines elasticity, transparency, and high abrasion resistance. It offers excellent flexibility, good load-bearing capacity, and resistance to oils, greases, and weathering.
Pros & Cons:
TPU’s durability makes it suitable for outsole components, providing long-lasting wear. It also offers good chemical resistance, which is beneficial in humid or corrosive environments common in tropical regions. However, TPU can be more costly than EVA and may require specialized manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application:
TPU is often used in outsoles and heel counters to enhance durability and traction. Its resistance to environmental factors makes it suitable for outdoor use in diverse climates.
International Considerations:
European and Middle Eastern markets often prefer high-performance, durable materials like TPU due to their standards for safety and longevity. Compliance with DIN or JIS standards for impact and abrasion resistance is vital. African and South American buyers should verify supplier certifications to ensure material safety and environmental compliance.
Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE)
Key Properties:
TPEs are versatile, rubber-like materials that combine the processing advantages of plastics with the flexibility of elastomers. They are resistant to cracking, UV exposure, and various chemicals.
Pros & Cons:
TPEs are highly adaptable, allowing for customization in hardness and flexibility, which is advantageous for custom-fit neuropathy shoes. They are also environmentally friendlier than some traditional rubbers. However, TPEs may be more expensive than EVA and require precise manufacturing controls.
Impact on Application:
TPEs are suitable for flexible components, such as heel pads, straps, or custom insoles, providing comfort and adaptability for neuropathic conditions.
International Considerations:
European markets favor TPEs for their eco-friendly profile and compliance with strict chemical safety standards. Buyers should ensure TPEs meet REACH or similar certifications. In emerging markets, cost considerations might lead to selecting specific grades, so supplier transparency is crucial.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for neuropathy shoes | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leather (Natural/Synthetic) | Uppers, overlays | Breathability, flexibility, premium feel | Costly, environmental concerns, supply variability | Med |
| EVA | Midsoles, insoles | Lightweight, cushioning, shock absorption | UV degradation, compression over time | Low |
| TPU | Outsoles, heel counters | Durability, chemical resistance, long-lasting | Higher cost, requires specialized manufacturing | Med |
| TPE | Flexible components, insoles, heel pads | Customizable, eco-friendly, chemical resistance | More expensive, requires precise processing | Med |
This comprehensive material analysis equips B2B buyers with the insights needed to select appropriate materials tailored to regional standards, cost considerations, and end-user needs. Ensuring compliance and sourcing from reputable suppliers will facilitate the successful manufacturing and distribution of high-quality neuropathy shoes across global markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for neuropathy shoes
Manufacturing Processes for Neuropathy Shoes
The production of neuropathy shoes involves a meticulous combination of specialized materials, precise manufacturing techniques, and rigorous assembly processes to ensure both comfort and safety for end-users. For B2B buyers, understanding these stages helps in assessing supplier capabilities and product quality.
Material Preparation and Selection
The foundation of high-quality neuropathy shoes lies in the careful selection of materials. Typically, suppliers use medical-grade, breathable, and hypoallergenic materials such as soft leathers, advanced synthetic fabrics, and memory foams. These materials must meet international standards for biocompatibility and durability. Raw materials undergo thorough inspection upon receipt, including visual checks and basic testing for contaminants or defects.
Forming and Component Manufacturing
The shoe manufacturing process begins with cutting, molding, and forming components. Automated cutting machines, often with CAD/CAM integration, ensure precision and consistency in fabric and leather pieces. For the insole and cushioning, foam molding is performed under controlled temperature and humidity conditions to achieve uniform density and comfort. Some manufacturers employ computer-controlled injection molding for durable, customized insoles.
Assembly and Construction
Assembly involves stitching, bonding, and attaching various components like uppers, insoles, midsoles, and outsoles. High-frequency welding and ultrasonic bonding are common for seamless, durable joins, especially for waterproof or seamless designs critical for neuropathy shoes. The assembly process emphasizes ergonomic fit, ensuring the shoes conform to prescribed orthopedic specifications. Quality control at this stage includes checking for alignment, stitching integrity, and proper attachment of components.
Finishing and Packaging
The finishing phase involves trimming excess material, applying protective coatings, and adding features such as non-slip outsoles, reflective elements, or adjustable straps. Surface treatments like anti-bacterial coatings or anti-slip soles are applied to enhance safety. Final inspections verify that the shoes meet dimensional tolerances and aesthetic standards before packaging in materials compliant with export regulations.
Quality Assurance (QA) and Control in Manufacturing
Ensuring consistent quality in neuropathy shoes is vital, especially for international markets where regulatory and safety standards vary. Suppliers typically adopt comprehensive QA protocols aligned with international standards such as ISO 9001, while also complying with industry-specific certifications like CE marking or API standards for medical devices.
International and Industry-Specific Standards
- ISO 9001: The cornerstone for quality management systems, ISO 9001 certification indicates that a manufacturer has a systematic approach to quality, including risk management, process control, and continuous improvement.
- CE Marking (Europe): Essential for products marketed within the European Economic Area (EEA), indicating compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection directives.
- API Standards: For certain medical-grade footwear, adherence to API standards ensures the shoes meet specific safety and durability criteria.
Key Quality Control Checkpoints
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC):
Raw materials undergo inspection for compliance with specifications, including physical properties, chemical composition, and cleanliness. Suppliers often require certificates of analysis (CoA) from certified vendors. -
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC):
During manufacturing, critical parameters such as stitching tension, foam density, and component fit are monitored. Statistical process control (SPC) tools are employed to detect deviations early, reducing waste and rework. -
Final Quality Control (FQC):
Before shipment, finished shoes are subjected to comprehensive testing, including dimensional checks, visual inspections, and functional tests like slip resistance and pressure distribution. Samples may undergo simulated wear tests to assess durability.
Testing Methods and Certification
- Biomechanical and Comfort Testing: Ensures the shoes provide adequate support and reduce pressure points, crucial for neuropathy patients.
- Slip Resistance Testing: Conducted per standards like ASTM or EN, ensuring soles meet anti-slip requirements.
- Durability and Wear Testing: Accelerated aging tests simulate long-term use to verify component integrity.
- Chemical Safety Tests: Confirm that materials do not emit harmful substances, aligning with REACH or FDA regulations.
Verifying Supplier Quality for International B2B Buyers
B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should implement robust verification strategies to ensure supplier compliance and product integrity.
Audits and Inspections
- Factory Audits: Conduct comprehensive audits focusing on quality management systems, production capabilities, and adherence to certifications like ISO 9001. Preferably, audits are performed by third-party inspectors familiar with local and international standards.
- Product Inspections: Engage third-party inspection agencies (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas) to perform pre-shipment inspections, sampling, and testing, especially for high-volume orders or new suppliers.
- Documentation Review: Verify CoA, test reports, certification credentials, and compliance documents for authenticity and relevance.
Ongoing Quality Monitoring
- Sample Testing: Regularly request samples for testing based on international standards to verify ongoing product quality.
- Supplier Performance Reviews: Maintain open communication channels and establish KPIs related to defect rates, delivery timelines, and compliance.
- Third-party Certification: Encourage or require suppliers to obtain and maintain internationally recognized certifications to mitigate risks.
Nuances for International B2B Buyers
Different regions have specific regulatory and market expectations that influence manufacturing and QC strategies:
- Africa & South America: Suppliers should demonstrate compliance with local import regulations, such as customs certifications, and be prepared for customs audits. Emphasize certifications like ISO 13485 if the shoes are marketed as medical devices.
- Middle East: Given regional standards such as Gulf Standards (GSO), verify that suppliers have GSO certifications or equivalent. Also, consider climate-specific features like UV resistance and heat durability.
- Europe (e.g., Germany, Spain): Strict adherence to CE marking, REACH compliance, and EN standards is essential. Buyers should prioritize suppliers with documented compliance and proactive testing regimes.
Final Recommendations for B2B Buyers
- Due Diligence: Conduct detailed supplier assessments, including factory visits where feasible.
- Quality Agreements: Establish clear quality agreements specifying standards, testing requirements, and documentation.
- Continuous Improvement: Foster partnerships with suppliers committed to ongoing quality enhancement and regulatory compliance.
- Leverage Technology: Utilize digital QC tools such as real-time inspection reports and supply chain traceability platforms to enhance transparency and accountability.
By understanding these manufacturing and quality assurance intricacies, B2B buyers can better evaluate supplier capabilities, ensure product safety and compliance, and foster long-term, reliable partnerships in the neuropathy shoe market.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for neuropathy shoes Sourcing
Cost Structure Breakdown for Neuropathy Shoes
Understanding the cost components involved in sourcing neuropathy shoes is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost elements include:
-
Materials: High-quality, medical-grade materials such as specialized cushioning, breathable fabrics, and supportive insoles significantly influence the base price. Premium materials that meet medical standards or certifications tend to increase costs but are vital for product efficacy and compliance.
-
Labor: Manufacturing labor costs vary widely depending on the country of origin. Countries like China, Vietnam, and India generally offer lower labor costs, whereas European countries such as Germany and Spain have higher wages but potentially higher craftsmanship quality.
-
Manufacturing Overheads: These include factory expenses, equipment depreciation, and energy costs. Overheads are typically lower in developing countries but may be offset by longer lead times or quality control challenges.
-
Tooling & Development: For custom designs or specific features (e.g., orthotic accommodations), upfront tooling costs can be significant. These are usually amortized over larger production runs, reducing per-unit costs.
-
Quality Control & Certifications: Ensuring compliance with medical and safety standards (e.g., CE marking in Europe, ISO certifications) can add to costs but are crucial for market acceptance, especially in regulated regions.
-
Logistics & Shipping: Freight costs depend on shipment volume, destination, and mode (air vs. sea). For bulk orders to Europe or South America, sea freight is economical but slower; air freight offers speed at a premium.
-
Profit Margin: Suppliers typically add a markup to cover risks and ensure profitability. Margins vary depending on the supplier’s market positioning and relationship with buyers.
Price Influencers and Their Impact
Several factors directly influence the final pricing of neuropathy shoes:
-
Order Volume & MOQ: Larger orders typically unlock volume discounts, reducing per-unit costs. Many suppliers prefer minimum order quantities (MOQs) ranging from 500 to 2000 pairs, especially for customized products.
-
Specifications & Customization: Customized features, such as specific orthotic supports, branding, or sizing, increase manufacturing complexity and cost. Standard models are more economical, while tailored solutions command higher prices.
-
Material Selection: Opting for medical-grade, eco-friendly, or innovative materials will influence costs. Suppliers often offer tiered pricing based on material quality.
-
Quality & Certifications: Higher quality standards and certifications (e.g., CE, FDA, ISO) not only increase costs but are often prerequisites for entry into certain markets, notably Europe and the Middle East.
-
Supplier Location & Capabilities: Suppliers in regions with advanced manufacturing infrastructure may charge more but can offer higher quality and faster lead times. Conversely, suppliers in emerging markets might offer competitive prices but may require rigorous quality assurance.
-
Incoterms & Shipping Terms: The choice of Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF, DDP) impacts who bears shipping costs, customs duties, and risks. DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) simplifies logistics for buyers but typically adds to the cost.
Strategic Tips for International B2B Buyers
-
Negotiate for Volume Discounts & Long-Term Contracts: Building ongoing relationships can unlock better pricing, favorable payment terms, and priority production scheduling.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Don’t focus solely on unit price. Consider logistics, customs, tariffs, and potential quality-related costs that may arise post-purchase.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Prices can vary due to currency fluctuations, geopolitical factors, and regional economic conditions. Regular market monitoring and currency hedging strategies can mitigate risks.
-
Leverage Local Expertise & Certification Requirements: For markets like Europe and the Middle East, ensure suppliers are familiar with regional standards, which can prevent costly delays or rejections.
-
Request Detailed Quotations: Ask for comprehensive quotes that specify costs for materials, tooling, QC, shipping, and taxes to avoid hidden charges.
Price Range Estimates (Indicative Only)
- Basic neuropathy shoes: $10–$20 per pair (manufactured in Asia, bulk orders, standard features).
- Mid-range models with certifications: $20–$40 per pair (European or certified suppliers, some customization).
-
Premium, customized orthotic models: $40–$70+ per pair (specialized materials, advanced features, smaller MOQ).
-
Note:* Prices are indicative and subject to change based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific product requirements.
By comprehensively understanding these cost and pricing factors, international B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can strategically plan their sourcing, negotiate effectively, and optimize their total investment in neuropathy shoes.
Spotlight on Potential neuropathy shoes Manufacturers and Suppliers
- (No specific manufacturer data was available or requested for detailed profiling in this section for neuropathy shoes.)*
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for neuropathy shoes
Critical Technical Properties for Neuropathy Shoes
1. Material Grade and Composition
The choice of materials directly impacts durability, comfort, and safety. High-quality, medical-grade leathers or synthetic leathers are preferred for their breathability and flexibility, reducing skin irritation. For insoles and linings, hypoallergenic and antimicrobial fabrics are essential to prevent infections. B2B buyers should specify material standards (e.g., ISO certifications) to ensure consistent quality across batches, especially when sourcing from different regions.
2. Cushioning and Shock Absorption
Effective neuropathy shoes require advanced cushioning systems that absorb impact and reduce pressure points. This includes gel inserts, memory foam layers, or specialized midsole compounds. Proper cushioning minimizes pain and prevents further nerve damage. When evaluating suppliers, request detailed technical data sheets demonstrating the shock absorption capabilities and longevity of these materials.
3. Tolerance and Fit Precision
Manufacturing tolerances—acceptable deviations during production—are vital for ensuring a perfect fit. Tight tolerances (e.g., ±1 mm) indicate high manufacturing precision, which is critical for footwear designed for sensitive feet. Accurate sizing reduces the risk of blisters, ulcers, or discomfort, especially in diabetic or neuropathic patients. B2B buyers should verify the production standards and quality control processes of potential suppliers.
4. Flexibility and Support Structure
The shoe’s flexibility influences gait and comfort, while support features (arch support, heel counters) stabilize the foot. Balancing flexibility with stability helps in reducing nerve strain. Technical specifications should include bend tests and support ratings, ensuring the shoes accommodate different foot deformities common among neuropathy sufferers.
5. Durability and Wear Resistance
Neuropathy shoes often need to withstand daily use without degradation. Features such as reinforced toe caps, abrasion-resistant outsoles, and high-quality stitching extend lifespan. Suppliers should provide data on material wear resistance (e.g., Taber abrasion testing results) to confirm product longevity, which is crucial for cost-effective procurement.
6. Breathability and Moisture Control
Proper ventilation prevents moisture buildup, which can lead to skin issues. Materials with moisture-wicking properties and breathable meshes are preferred. B2B buyers should specify standards for moisture management, especially when sourcing for humid climates or regions with high temperatures.
Essential Industry and Trade Terms
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to companies that produce neuropathy shoes based on a buyer’s design and specifications. Understanding OEM capabilities is crucial for customizing products to regional preferences or specific medical standards, especially when entering new markets.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
The smallest number of units a supplier is willing to produce or sell in one order. Awareness of MOQ helps buyers plan inventory and budget, particularly when testing new suppliers or launching customized lines for different markets.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
A formal document sent to suppliers requesting price, lead time, and terms for a specific order. Efficient RFQ processes streamline procurement, enable comparison across multiple vendors, and clarify technical requirements, which is essential for international sourcing.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Standardized trade terms defining the responsibilities of buyers and sellers for delivery, risk transfer, and costs. Familiarity with Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF, DDP) ensures clarity in logistics planning and cost calculation, especially across different countries with varying import regulations.
5. Certification and Compliance Terms
References to standards such as ISO, CE (European Conformity), or FDA approval indicate adherence to safety, quality, and health standards. Confirming these certifications during sourcing ensures the shoes meet regional regulations, reducing legal and compliance risks.
6. Lead Time
The duration from order placement to product delivery. Accurate knowledge of lead times is vital for inventory planning and meeting regional demand cycles, especially in markets with seasonal fluctuations or logistical constraints.
By mastering these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can make informed decisions, negotiate effectively, and ensure the procurement of high-quality neuropathy shoes tailored to their regional needs and regulatory requirements.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the neuropathy shoes Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global neuropathy shoes sector is experiencing significant growth driven by demographic shifts, increasing awareness of diabetic and neuropathy-related foot care, and advancements in footwear technology. Emerging markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are becoming pivotal players in sourcing and distribution, driven by expanding healthcare infrastructure and rising consumer demand for specialized footwear.
For international B2B buyers, understanding regional market dynamics is crucial. European markets, especially Germany and Spain, are characterized by stringent quality standards and a preference for innovative, medical-grade footwear. Conversely, markets in Africa and South America often prioritize cost-effective solutions, but are increasingly shifting towards higher-quality, durable products due to rising health awareness.
Current sourcing trends include a move towards modular, customizable shoes that accommodate various neuropathic conditions, leveraging advances in 3D printing and smart materials. Digital supply chain platforms and direct-to-manufacturer procurement models are gaining traction, reducing lead times and enhancing traceability. Moreover, there’s a notable shift toward sourcing from regions with emerging manufacturing capabilities, such as Southeast Asia and Eastern Europe, balancing quality and cost efficiency.
For B2B buyers, strategic sourcing involves evaluating supplier certifications, compliance with regional medical device regulations, and capacity for innovation. Establishing strong, transparent supplier relationships and leveraging trade agreements can mitigate risks associated with geopolitical fluctuations and supply chain disruptions. Staying attuned to local market preferences and regulatory landscapes is essential for successful market entry and sustained growth.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is increasingly a critical factor in sourcing neuropathy shoes, driven by both regulatory pressures and consumer preferences. Environmentally conscious buyers in Europe and parts of South America are demanding products made with eco-friendly materials and transparent supply chains. Using sustainably sourced, biodegradable, or recycled materials—such as natural rubber, organic cotton, or plant-based leathers—can significantly enhance brand reputation and market acceptance.
Ethical sourcing practices are equally vital, particularly in regions like Africa and South America where supply chain transparency may be challenged by complex local regulations. Ensuring fair labor practices, safe working conditions, and compliance with international standards such as Fair Trade or SA8000 can reduce reputational risks and foster long-term supplier relationships. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers with verifiable certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management or B Corp certification for social responsibility.
Investing in green certifications and eco-labels not only aligns with global sustainability goals but also opens access to premium markets willing to pay a higher price for ethically produced goods. Additionally, integrating sustainability into sourcing strategies can contribute to regulatory compliance, especially in Europe where legislation like the EU Green Deal emphasizes environmental accountability. Building a resilient, sustainable supply chain involves continuous monitoring, supplier audits, and adopting innovative eco-friendly materials to meet evolving standards.
Brief Evolution/History (Optional)
The neuropathy shoes sector has evolved from basic therapeutic footwear to a highly specialized, technology-driven industry. Early products focused primarily on comfort and basic support, but recent decades have seen significant innovation driven by medical research, material science, and digital manufacturing. The adoption of smart materials, 3D printing, and IoT-enabled products has transformed the landscape, enabling customization and improved patient outcomes.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
This evolution has been fueled by increasing global prevalence of diabetes and neuropathic conditions, prompting manufacturers to develop more effective, comfortable, and sustainable solutions. For B2B buyers, understanding this history highlights the importance of partnering with innovative suppliers who can adapt to technological advances and shifting regulatory requirements. It also underscores the need for continuous market intelligence to stay ahead of industry trends and meet the evolving needs of healthcare providers and end-users worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of neuropathy shoes
1. How can I effectively vet neuropathy shoe suppliers to ensure product quality and reliability?
Vetting international suppliers requires a multi-step approach. Start by requesting comprehensive company credentials, including business licenses, quality certifications (ISO, CE, FDA), and factory audits. Review their production capacity, lead times, and client references, especially from regions similar to yours. Conduct virtual factory visits or third-party inspections when possible. Additionally, assess their compliance with safety standards relevant to your target market. Engaging with verified trade platforms or industry associations can also help verify legitimacy. A thorough vetting process minimizes risks and ensures you partner with reputable manufacturers capable of meeting your quality expectations.
2. What customization options are typically available for neuropathy shoes, and how can I communicate my requirements effectively?
Most suppliers offer customization such as sizing, color, branding (logos), and specific orthotic features. Advanced customization may include material choices, sole design, and specialized cushioning. To communicate your needs clearly, provide detailed specifications, including technical drawings, material samples, and desired certifications. Establish clear communication channels with the supplier, preferably in writing, to avoid misunderstandings. Discuss lead times for customization and request prototypes or samples before bulk production. This proactive approach ensures the final product aligns with your market demands and customer preferences, reducing costly revisions later.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
3. What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs), lead times, and payment terms for neuropathy shoes in international trade?
MOQs for neuropathy shoes generally range from 500 to 2,000 pairs, depending on the manufacturer’s capacity and customization level. Lead times are typically between 4 to 12 weeks, influenced by order size and complexity. Common payment terms include 30% upfront deposit with the balance payable before shipment, or letters of credit for larger orders. Some suppliers may offer flexible terms for repeat buyers or large volume orders. Negotiating payment terms upfront and securing clear delivery timelines help manage cash flow and inventory planning effectively across borders.
4. What certifications and quality assurances should I look for in neuropathy shoe suppliers to meet international standards?
Key certifications include ISO 9001 (quality management), CE marking (European conformity), FDA approval (for U.S. markets), and relevant safety standards like EN 14683 for medical devices. Suppliers should provide test reports for slip resistance, durability, and biocompatibility of materials. Request evidence of compliance with specific regional regulations, especially if selling in Europe, Africa, or Latin America. Additionally, suppliers with GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) certifications demonstrate adherence to high-quality manufacturing protocols. Verifying these certifications ensures your products meet legal and safety standards, reducing liability and enhancing consumer trust.
5. How should I plan logistics and shipping when importing neuropathy shoes from overseas suppliers?
Effective logistics planning involves selecting reliable freight forwarders experienced in medical or footwear products. Consider incoterms like FOB or CIF to clarify responsibilities and costs. Evaluate shipping options—air freight offers faster delivery but at higher costs, while sea freight is more economical for large volumes but slower. Customs clearance processes vary by country; ensure supplier provides all necessary documentation, including invoices, certificates, and certificates of origin. Collaborate with local customs brokers to streamline clearance. Establishing transparent communication with logistics partners reduces delays, minimizes costs, and ensures timely delivery to your market.
6. How do I handle potential disputes or quality issues with overseas neuropathy shoe suppliers?
Preemptively, include clear terms in your purchase agreement covering quality standards, inspection rights, and dispute resolution procedures. Regularly conduct quality inspections during production, either via third-party inspectors or virtual audits. If issues arise, communicate promptly and document discrepancies with photos and detailed reports. Negotiating arbitration clauses or choosing dispute resolution centers can streamline conflict resolution. Building strong relationships and maintaining open communication channels often prevent misunderstandings. If necessary, leverage trade protections or local legal counsel familiar with international trade laws to enforce contractual obligations and resolve disputes efficiently.
7. What are the best practices for ensuring product compliance with regional health and safety regulations?
Stay informed about specific regional requirements—European markets may demand CE marking, while South American or Middle Eastern countries may have local standards. Collaborate with suppliers who understand these regulations and can provide compliance documentation. Conduct independent testing or certification if necessary, especially for medical-grade footwear. Incorporate quality control checks at multiple production stages to ensure ongoing compliance. Regularly update yourself on regulatory changes in your target markets. This proactive approach reduces the risk of product recalls, legal penalties, and market entry delays, safeguarding your brand reputation.
8. How can I build long-term relationships with neuropathy shoe suppliers to ensure consistent supply and quality?
Establish clear communication and mutual understanding from the outset, including quality expectations, lead times, and payment terms. Visit suppliers when possible and foster transparent, professional relationships. Consider signing long-term agreements or contracts that provide benefits such as better pricing, priority production, and flexible terms. Regularly review supplier performance based on quality, delivery, and responsiveness, and provide constructive feedback. Building trust through consistent orders, prompt payments, and collaborative problem-solving encourages suppliers to prioritize your needs. This strategic partnership approach ensures reliable supply chains, product quality, and competitive advantage in your target markets.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for neuropathy shoes
Conclusion and Future Outlook
Effective strategic sourcing is essential for international B2B buyers aiming to secure high-quality neuropathy shoes that meet both clinical standards and market demands. Prioritizing supplier reliability, product innovation, and compliance with regional regulations will ensure a competitive advantage in this specialized sector. Engaging with reputable manufacturers across Europe, Asia, and emerging markets can also facilitate access to advanced materials and cost efficiencies, while maintaining product integrity.
For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, adopting a proactive sourcing strategy will enable better risk management and supply chain resilience amid fluctuating global markets. Building strong supplier relationships and leveraging trade partnerships can lead to more favorable terms and faster time-to-market.
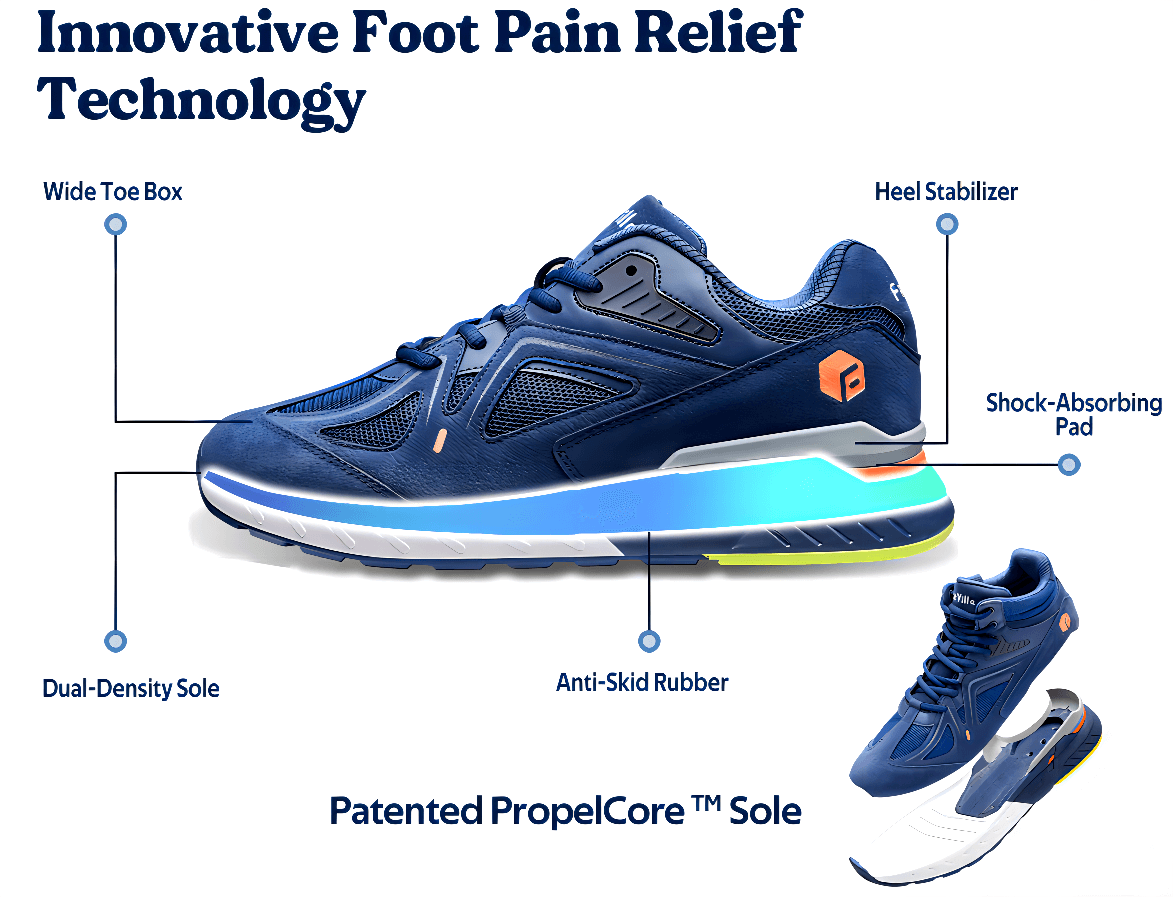
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Looking ahead, technological advancements such as smart insoles and customized fit solutions will redefine the neuropathy shoe landscape. International buyers should stay informed on industry innovations and evolving regulatory frameworks to capitalize on emerging opportunities. A strategic, forward-thinking approach will be vital in delivering value to end-users and strengthening your position within this growing healthcare niche.