Master Sourcing and Selling Vegan Shoes: The Ultimate B2B
Guide to Vegan Shoes
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for vegan shoes
- Understanding vegan shoes Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of vegan shoes
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for vegan shoes
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for vegan shoes
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for vegan shoes Sourcing
- Spotlight on Potential vegan shoes Manufacturers and Suppliers
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for vegan shoes
- Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the vegan shoes Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of vegan shoes
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for vegan shoes
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for vegan shoes
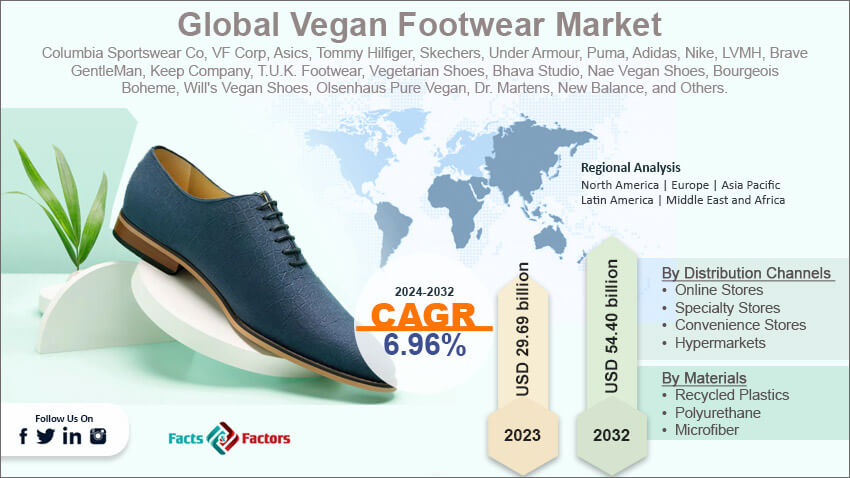
In today’s rapidly evolving footwear industry, vegan shoes have emerged as a vital sector driven by increasing consumer demand for sustainable, cruelty-free, and ethically produced products. For international B2B buyers—particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—understanding this dynamic market is crucial to capitalize on emerging opportunities and meet shifting market expectations. As more brands and retailers prioritize eco-conscious sourcing, the ability to identify reliable suppliers and navigate complex global supply chains becomes a competitive advantage.
This comprehensive guide offers strategic insights into the vegan shoe market, covering essential topics such as product types, innovative plant-based materials, manufacturing and quality control standards, sourcing options, and cost considerations. It also explores market trends, regulatory landscapes, and consumer preferences across diverse regions, empowering buyers to make informed, sustainable sourcing decisions.
For B2B buyers operating across continents, this resource serves as a critical tool to streamline procurement processes, identify trustworthy suppliers, and negotiate effectively in a competitive global landscape. Whether expanding product lines or entering new markets, understanding the nuances of vegan footwear will enable you to meet increasing demand while aligning with global sustainability goals. This guide aims to equip you with the knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of the vegan shoe market confidently and successfully.
Understanding vegan shoes Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Classic Vegan Sneakers | Made from synthetic leather, canvas, or knit fabrics, often with minimal embellishments | Fashion retail, casual wear | Pros: Widely accepted, versatile, high consumer demand; Cons: Price variability based on material quality |
| Vegan Dress Shoes | Formal styles crafted from faux leather, microfiber, or sustainable alternatives | Formal wear, corporate gifting | Pros: Growing market in professional sectors; Cons: Limited options in high-end segments |
| Eco-Friendly Outdoor Shoes | Constructed with recycled or biodegradable materials, often with rugged soles | Outdoor, sports, eco-conscious markets | Pros: Appeals to sustainability-focused buyers; Cons: Durability and performance standards vary |
| Slip-On & Loafers | Simplified designs using flexible, synthetic materials for easy wear | Casual, office, travel accessories | Pros: Easy to produce at scale, high margin potential; Cons: Limited design complexity may restrict premium positioning |
| Specialized Vegan Boots | Heavy-duty, weather-resistant, often with vegan leather or rubber components | Workwear, fashion, niche markets | Pros: High durability and niche appeal; Cons: Higher production costs and limited mass-market appeal |
Classic Vegan Sneakers
This category encompasses casual, everyday footwear made from synthetic or natural fibers that mimic traditional leather. They are characterized by simple construction, often with breathable uppers and flexible soles, making them highly versatile. B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing from manufacturers that offer consistent quality, as consumer demand for stylish yet affordable vegan sneakers continues to rise globally, especially in markets like Europe and South America. Consider suppliers with scalable production capabilities to meet fluctuating demand while maintaining quality standards.
Vegan Dress Shoes
Designed to emulate formal leather footwear, vegan dress shoes use innovative faux leathers, microfiber, or plant-based materials to achieve a polished appearance. These shoes are increasingly sought after in corporate gifting and professional markets, especially in regions with a growing vegan or eco-conscious demographic such as Europe and Brazil. B2B buyers should evaluate suppliers for material authenticity and durability, ensuring the shoes meet formal wear expectations. Cost and lead time are critical factors, especially when fulfilling bulk orders for retail or corporate clients.
Eco-Friendly Outdoor Shoes
These shoes leverage recycled plastics, natural rubber, and biodegradable materials to create durable footwear suitable for outdoor activities. They appeal strongly to eco-conscious consumers across Africa, South America, and the Middle East, where outdoor lifestyles are prevalent. B2B buyers should assess the performance metrics—such as grip, waterproofing, and breathability—and verify suppliers’ sustainability credentials. These shoes often command higher price points, so quality assurance and certification are vital for successful market entry.
Slip-On & Loafers
Known for their minimalistic design and ease of wear, slip-ons and loafers are produced using synthetic leathers or knitted fabrics. Their simplicity makes them ideal for mass production, offering high margins and quick turnaround times. They are suitable for casual, office, and travel markets, especially in regions with a preference for comfort and convenience. B2B buyers should focus on suppliers offering consistent sizing, reliable supply chains, and scalable customization options to meet diverse retail needs.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Specialized Vegan Boots
Constructed with vegan leather alternatives and robust rubber soles, these boots are designed for durability and weather resistance. They serve niche markets like workwear, fashion-forward consumers, or outdoor enthusiasts. While they often involve higher manufacturing costs, they can command premium pricing in specialized sectors. B2B buyers should evaluate the durability, material sourcing transparency, and certifications for waterproofing and eco-friendliness to ensure alignment with market expectations and brand positioning.
Key Industrial Applications of vegan shoes
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of vegan shoes | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction & Industrial Safety | Safety footwear for construction workers and industrial environments | Eco-friendly, non-allergenic, and compliant with safety standards; appeals to sustainability commitments | Certification for safety standards (e.g., EN, ASTM), durability, availability of bulk supply, and compliance with local safety regulations |
| Hospitality & Tourism | Uniform footwear for hotel staff, tour guides, and hospitality personnel | Sustainable branding, allergen-free, easy to clean, and comfortable for long shifts | Consistent quality, customization options (branding), and reliable supply chains across regions |
| Healthcare & Medical | Staff footwear in clinics, laboratories, and healthcare facilities | Hygienic, antimicrobial properties, allergen-free, and compliant with health regulations | Certifications for medical use, antimicrobial treatment, and ease of cleaning/disinfection |
| Fashion & Retail | Eco-conscious footwear collections for retail markets | Aligns with global sustainability trends, enhances brand image, and appeals to ethically conscious consumers | Trend alignment, design flexibility, quality consistency, and regional distribution capabilities |
| Corporate & Uniforms | Employee footwear for corporate offices and uniformed services | Promotes corporate social responsibility, reduces environmental impact, and supports branding | Large volume sourcing, consistent quality, and customization options for corporate branding |
Construction & Industrial Safety
Vegan shoes designed for construction and industrial use serve as a sustainable alternative to traditional safety footwear. These shoes meet rigorous safety standards such as slip resistance, impact protection, and electrical hazard resistance while eliminating animal-derived materials. For international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, sourcing vegan safety shoes ensures compliance with local safety regulations and aligns with growing environmental and ethical standards. Bulk procurement from reputable suppliers with certifications guarantees durability and consistent quality, reducing long-term costs and enhancing worker safety.
Hospitality & Tourism
In the hospitality sector, vegan shoes are increasingly adopted as part of staff uniforms, especially in eco-conscious establishments. These shoes offer comfort for long shifts, are easy to maintain, and support the hotel’s sustainability credentials. For European and South American markets, where eco-tourism and responsible hospitality are expanding, sourcing stylish yet durable vegan footwear can strengthen brand differentiation. Ensuring reliable supply chains and customization options for branding helps hospitality companies meet regional preferences and operational demands efficiently.
Healthcare & Medical
Vegan footwear in healthcare settings emphasizes hygiene, allergen-free materials, and antimicrobial properties. These shoes are suitable for clinics, laboratories, and hospitals aiming to reduce animal-derived materials while maintaining high standards of cleanliness and safety. International buyers from regions like the Middle East and Africa benefit from sourcing certified medical-grade vegan shoes that adhere to local health regulations. Prioritizing certifications and antimicrobial features ensures the shoes support infection control, staff comfort, and environmental sustainability, aligning with global healthcare standards.
Fashion & Retail
The fashion industry’s shift towards sustainability drives demand for vegan shoes as part of eco-friendly collections. These shoes appeal to ethically conscious consumers across Europe, Brazil, and other markets, offering stylish designs without animal products. B2B buyers should focus on sourcing high-quality, trend-aligned vegan footwear that can be produced at scale while maintaining design flexibility. Establishing reliable partnerships with regional suppliers ensures timely delivery, consistent quality, and the ability to adapt to regional fashion preferences.
Corporate & Uniforms
Many corporations and public service organizations are incorporating vegan shoes into their uniform policies to demonstrate social responsibility. These shoes provide a sustainable, allergen-free alternative that supports branding efforts centered on environmental values. For international B2B buyers, sourcing large volumes of customizable vegan footwear from regional manufacturers ensures cost-effectiveness, consistent quality, and timely delivery. This approach helps build a positive corporate image while meeting regional employment and sustainability standards.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for vegan shoes
Analysis of Common Materials for Vegan Shoes
1. Polyurethane (PU)
Key Properties:
Polyurethane is a versatile synthetic polymer widely used in footwear due to its excellent flexibility, lightweight nature, and ease of manufacturing. It offers good abrasion resistance and can be formulated to mimic leather’s appearance and texture. PU performs well across a range of temperatures, typically from -20°C to 80°C, making it suitable for various climates.
Pros & Cons:
PU is generally more affordable than natural leather alternatives, with moderate durability suitable for daily wear. It can be produced in a variety of finishes, including matte and glossy, allowing for diverse aesthetic options. However, PU’s environmental footprint is significant, as it is derived from petrochemicals and is not biodegradable. Durability can vary depending on formulation; some PU materials may crack or degrade over time, especially under UV exposure.
Impact on Application:
PU’s compatibility with adhesives and stitching makes it suitable for upper materials in vegan shoes. Its water-resistant properties are advantageous in humid or rainy environments, common in regions like Brazil or parts of Africa. However, PU’s breathability is limited, which could affect comfort in hot climates typical of the Middle East or tropical South America.
International Buyer Considerations:
Regulatory standards such as REACH in Europe and ASTM in the US may scrutinize chemical compositions of PU, especially for imports. Buyers should prioritize suppliers adhering to eco-friendly formulations and certifications. Additionally, consumers increasingly favor sustainable products, so sourcing bio-based or recycled PU can enhance market acceptance.
2. Microfiber (Polyester or Nylon-based)
Key Properties:
Microfiber fabrics are made from finely woven polyester or nylon fibers, offering a soft, suede-like appearance. They are lightweight, resistant to water and stains, and have good tensile strength. Microfiber can be engineered for enhanced breathability and flexibility, suitable for various shoe designs.
Pros & Cons:
Microfiber is generally cost-effective and easy to manufacture at scale, with consistent quality. Its resistance to water and stains makes it ideal for outdoor or active footwear. However, microfiber’s environmental impact is notable, as it is derived from synthetic polymers that shed microplastics during washing. Durability is high, but prolonged UV exposure can cause degradation.
Impact on Application:
Microfiber’s water resistance and ease of cleaning are advantageous in humid or rainy regions like Brazil or parts of Africa. Its flexibility supports ergonomic shoe designs. However, its limited biodegradability and microplastic shedding may pose environmental concerns, especially in markets with strict regulations or eco-conscious consumers.
International Buyer Considerations:
Buyers should verify microfiber’s compliance with environmental standards such as OEKO-TEX or GOTS, especially for European markets. Transparency regarding the source of fibers (recycled vs. virgin) can influence consumer acceptance. Additionally, microfiber’s manufacturing process should align with fair labor practices and sustainability standards.
3. Cork
Key Properties:
Cork is a natural, renewable material harvested from the bark of cork oak trees. It is lightweight, elastic, and exhibits excellent thermal and acoustic insulation. Cork is naturally resistant to water, mold, and pests, making it highly durable in various conditions.
Pros & Cons:
Cork’s sustainability credentials are high, as harvesting does not harm the tree, and it is biodegradable. It provides a unique aesthetic and tactile experience, often associated with premium products. Its limitations include higher cost and variability in supply, which can impact consistency and scalability. Mechanical strength is moderate, so it is often used as an accent or in combination with other materials rather than as the primary upper.
Impact on Application:
Cork’s natural properties make it suitable for eco-luxury vegan shoes, especially in markets like Europe and South America where sustainability is valued. Its water resistance is sufficient for most applications, but it may require sealing treatments for prolonged exposure to moisture. Cork’s thermal insulation benefits wearers in colder climates, but it may be less suitable for very hot, humid environments unless properly treated.
International Buyer Considerations:
Cork’s compliance with environmental standards such as FSC certification is crucial for European and South American markets. Importers should verify the supply chain’s sustainability claims and consider certifications to meet regional eco-label requirements. Cost considerations are also vital, as cork tends to be more expensive than synthetic alternatives.
4. Mushroom Leather (Mycelium-based)
Key Properties:
Mushroom leather, derived from mycelium, is an innovative, biodegradable material that mimics the look and feel of traditional leather. It offers good flexibility, breathability, and a soft texture. Its production process is relatively eco-friendly, utilizing agricultural waste and requiring less water and energy.
Pros & Cons:
Mushroom leather is highly sustainable, biodegradable, and has a lower environmental footprint than synthetic or animal leather. It can be engineered for durability, though it still faces challenges with long-term wear and water resistance. Its novelty means limited mass production experience, which can influence consistency and cost.
Impact on Application:
Ideal for high-end vegan footwear targeting eco-conscious consumers in Europe and emerging markets in South America and Africa. Its breathability enhances comfort, especially in warmer climates. However, it may require protective coatings to improve water resistance, adding to manufacturing complexity.
International Buyer Considerations:
Regulatory acceptance is growing as mushroom leather gains recognition as a sustainable material. Buyers should seek suppliers with transparent production processes and relevant eco-certifications. Cost remains higher than synthetic options, but economies of scale are improving as the technology matures.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for vegan shoes | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyurethane (PU) | Upper material, insoles, decorative elements | Cost-effective, versatile, water-resistant | Environmental impact, durability varies | Med |
| Microfiber | Uppers, linings, outdoor footwear | Affordable, stain-resistant, lightweight | Microplastic shedding, limited biodegradability | Low |
| Cork | Insoles, accents, eco-luxury designs | Sustainable, lightweight, insulating | Higher cost, supply variability | High |
| Mushroom Leather | Premium uppers, fashion-forward footwear | Eco-friendly, biodegradable, breathable | Costly, limited long-term durability | High |
This comprehensive analysis provides B2B buyers with critical insights into material selection, emphasizing sustainability, performance, cost, and regional considerations. By aligning material choices with market demands and compliance standards, buyers can optimize their product offerings
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for vegan shoes
Manufacturing Processes of Vegan Shoes
The production of vegan shoes involves a series of carefully orchestrated stages designed to ensure durability, comfort, and ethical compliance. Understanding these stages enables B2B buyers to assess supplier capabilities and ensure product quality aligns with market expectations.
Material Preparation
The foundation of vegan footwear is the selection and preparation of sustainable, cruelty-free materials. Common materials include:
- Synthetic leathers: Polyurethane (PU), microfiber, and other innovative textiles that mimic traditional leather.
- Plant-based materials: Cork, mushroom leather (mycelium), pineapple leaf fiber (Piñatex), and other biodegradable options.
- Recycled fabrics: PET-based textiles, recycled rubber, and other eco-friendly textiles.
Material suppliers should provide detailed documentation on sourcing, processing methods, and compliance with environmental standards. B2B buyers should verify that materials meet international standards such as ISO 14001 for environmental management.
Forming and Cutting
Once materials are prepared, they are cut into the required shapes using automated or manual cutting machines. Precision in this stage is crucial to minimize waste and ensure consistency. Advanced techniques like computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) are increasingly used for accuracy and efficiency.
For synthetic materials, heat pressing and embossing are common to achieve desired textures and branding. Plant-based leathers may undergo additional treatments to improve flexibility and durability.
Assembly and Construction
The assembled components—uppers, insoles, outsoles—are stitched, glued, or heat-bonded together. Key techniques include:
- Bonding: Use of eco-friendly adhesives with strong adhesion properties suitable for flexible, synthetic materials.
- Stitching: Reinforced stitching techniques that prevent separation, especially in stress points like seams and heel counters.
- Sole attachment: Methods such as direct injection, cementing, or vulcanization, depending on the outsole material.
Manufacturers employing automation can ensure consistency, while artisanal processes may be preferred for high-end or bespoke vegan shoes. Attention to detail during assembly impacts overall durability and customer satisfaction.
Finishing
Final steps include quality checks, polishing, branding, and packaging. Finishing processes should aim to enhance aesthetics while maintaining eco-friendly practices. For instance, water-based dyes and finishes are preferred over solvent-based options.
Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC) in Vegan Shoe Manufacturing
Ensuring consistent quality in vegan shoes requires a robust QA/QC framework aligned with international standards and industry-specific certifications.
International Standards and Certifications
- ISO 9001: The cornerstone of quality management systems, ISO 9001 certification indicates that a manufacturer adheres to internationally recognized processes ensuring consistent product quality.
- ISO 14001: Focuses on environmental management, essential for sustainable vegan footwear production.
- CE Marking (Europe): Demonstrates compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental requirements, crucial for European markets.
- API or ASTM Standards: For certain functional aspects like slip resistance or chemical safety, relevant especially in markets like South America or the Middle East.
Manufacturers should maintain documentation demonstrating compliance and continuous improvement aligned with these standards.
QC Checkpoints and Testing Methods
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon receipt for defects, consistency, and compliance with specifications. Tests include visual inspection, dimensional checks, and material property assessments.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, checkpoints verify adherence to process parameters, such as stitching tension, adhesive application, and assembly accuracy. Regular sampling and inspection are critical.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): The finished product undergoes comprehensive testing, including:
-
Durability tests: Flex testing, abrasion resistance (ASTM D4157), and tensile strength.
- Chemical safety tests: Ensuring no harmful substances (e.g., phthalates, formaldehyde) are present, complying with OEKO-TEX standards.
- Environmental resistance: Water resistance, UV stability, and color fastness.
Third-Party Inspection and Certification
B2B buyers should consider engaging third-party inspection agencies (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas, Intertek) to verify supplier claims and ensure compliance before placing large orders. These audits evaluate:
- Manufacturing facilities
- Quality management systems
- Product testing reports
- Supply chain transparency
Request recent inspection reports and certifications as part of supplier due diligence.
Nuances for International B2B Buyers
Different regions have specific expectations and regulatory requirements that influence manufacturing and QC processes.
Africa and South America
- Focus on cost-effective yet compliant manufacturing: Suppliers often operate in regions with emerging quality infrastructure. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers with ISO 9001 and environmental certifications, and consider third-party audits to verify adherence.
- Customization and flexibility: Local manufacturers may offer more adaptable processes but require thorough QC oversight to meet international standards.
Middle East
- Compliance with regional standards: Emphasize adherence to Gulf Standards (GSO) and chemical safety regulations. Verify that suppliers conduct rigorous chemical and safety testing.
- Certifications: CE marking for European markets, along with GSO compliance, are often mandatory.
Europe (e.g., Spain)
- Strict regulatory environment: High expectations for chemical safety, environmental sustainability, and ethical practices.
- Third-party certification: OEKO-TEX Standard 100, REACH compliance, and ISO 9001 are highly valued.
- Transparency: B2B buyers should demand comprehensive documentation, including material origin, manufacturing processes, and testing reports.
Brazil
- Certification compliance: Ensure adherence to ANVISA regulations concerning chemical safety.
- Sustainability claims: Verification of eco-labels and sustainability certifications enhances credibility.
Practical Recommendations for B2B Buyers
- Supplier Audits: Conduct on-site inspections or engage third-party auditors to verify manufacturing processes, QC procedures, and certification validity.
- Sample Testing: Request product samples for independent testing, particularly chemical safety and durability, before large-scale orders.
- Documentation Verification: Review certificates, material safety data sheets (MSDS), and compliance reports meticulously.
- Continuous Monitoring: Establish ongoing quality monitoring through periodic audits, QC reports, and supplier scorecards to ensure sustained compliance.
Conclusion
For international B2B buyers, especially from diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the intricacies of vegan shoe manufacturing and quality assurance is vital. A combination of rigorous supplier vetting, adherence to international standards, and transparent communication ensures the delivery of high-quality, sustainable vegan footwear that meets regional market expectations.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for vegan shoes Sourcing
Understanding Cost Components in Vegan Shoe Production
Effective sourcing begins with a clear grasp of the key cost components involved in manufacturing vegan shoes. The primary expense categories include:
- Materials: Vegan leathers (such as PU, PVC, or plant-based alternatives), recycled fabrics, and eco-friendly adhesives. Material costs vary significantly based on quality, sourcing region, and certification standards.
- Labor: Wages differ across regions, with Asian countries like China and Vietnam typically offering lower labor costs compared to European or Middle Eastern manufacturers. Ethical labor practices and certifications can influence costs.
- Manufacturing Overhead: Factory utilities, machinery maintenance, and administrative expenses. Overhead costs are often embedded within the per-unit price but can fluctuate based on factory size and technology.
- Tooling and Development: Initial mold and pattern creation are fixed costs that impact batch pricing. Larger orders amortize these costs more effectively.
- Quality Control (QC): Ensuring vegan and ethical standards are met involves inspection processes, which may add to costs, especially for brands requiring certifications like PETA-approved or B Corp.
- Logistics and Shipping: Freight costs depend on order volume, destination, and chosen incoterms. Shipping from Asia to Africa, South America, or Europe typically constitutes a significant portion of total costs.
Price Influencers and Variations
Several factors influence the final FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) prices for vegan shoes:
- Order Volume and MOQ: Higher volumes generally lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) can range from 500 to 5,000 pairs, with larger orders offering better pricing incentives.
- Customization and Specs: Tailored designs, unique materials, or specific certifications increase costs. Custom molds and special packaging also add to initial expenses.
- Material Choices: Premium vegan leathers or innovative eco-friendly materials command higher prices but can justify premium retail positioning.
- Quality and Certifications: Strict adherence to vegan and ethical standards, along with certifications like Fair Trade or cruelty-free labels, can elevate costs but enhance market appeal.
- Supplier Factors: Established, reputable suppliers with reliable quality control and faster lead times may charge premium prices, but reduce risks of delays or non-compliance.
- Incoterms: The choice between FOB, CIF, or DDP impacts total landed costs. Buyers should evaluate additional costs like insurance, duties, and local taxes.
Strategic Tips for International B2B Buyers
- Negotiate for Better Terms: Leverage order volume, long-term partnership potential, and upfront payments to secure discounts. Clarify inclusion of QC and certification costs in the quoted price.
- Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Consider sourcing from regions with favorable labor and material costs, such as Vietnam or India, but balance this with quality standards and logistical considerations.
- Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond unit price, account for shipping, customs duties, taxes, and potential delays. European buyers should consider import tariffs and compliance costs.
- Pricing Nuances for Different Markets: Buyers from Africa and South America should be aware of customs duties and local taxes that can significantly impact landed costs. Middle Eastern buyers should factor in import regulations and potential VAT charges, while European buyers should consider the impact of EU tariffs and certification requirements.
Indicative Price Ranges (Disclaimer)
While prices fluctuate based on specifications and market conditions, typical FOB prices for vegan shoes can range from $15 to $40 per pair for standard models in moderate volumes. Premium or highly customized shoes may command $50 or more per pair. These figures serve as a guideline; actual prices should be obtained through direct supplier quotes considering current market dynamics.
Final Considerations
For international B2B buyers, understanding the nuanced cost structure and influencing factors is essential for making informed sourcing decisions. Prioritize building relationships with transparent suppliers, clarify all cost elements upfront, and consider the broader logistics and compliance landscape to optimize your total cost and ensure a competitive market position.
Spotlight on Potential vegan shoes Manufacturers and Suppliers
- (No specific manufacturer data was available or requested for detailed profiling in this section for vegan shoes.)*
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for vegan shoes
Critical Technical Properties for Vegan Shoes
1. Material Grade and Certification
The quality of vegan shoe materials, such as synthetic leathers, textiles, and adhesives, is pivotal. High-grade materials ensure durability, comfort, and aesthetic appeal, reducing product returns and enhancing brand reputation. Certifications like PETA-Approved Vegan or Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) add credibility, assuring buyers that no animal products or harmful chemicals are involved.
2. Material Composition and Thickness
Understanding the precise composition—such as the percentage of bio-based polymers versus synthetic compounds—helps in assessing product performance and compliance with regional standards. Thickness specifications, especially for uppers and soles, impact flexibility, wear resistance, and overall shoe longevity. Consistent specifications are vital for maintaining quality across production batches.
3. Tolerance and Dimensional Accuracy
Tolerance levels specify how much variation is acceptable in shoe size, shape, and component dimensions. Tight tolerances ensure consistent fit and manufacturing quality, which is essential for international markets where sizing standards may differ. Clear tolerance specifications facilitate smoother logistics and reduce rejection rates.
4. Sole and Midsole Properties
The sole material’s hardness, slip resistance, and flexibility influence safety and comfort. Eco-friendly options like recycled rubber or bio-based polyurethane are increasingly in demand. Specifications should include abrasion resistance and grip performance to meet diverse market requirements, especially in regions with varied terrains.
5. Environmental and Chemical Compliance
Vegan shoes must adhere to environmental regulations, such as REACH in Europe or EPA standards in the US. Materials free from hazardous substances reduce legal risks and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers. Certification documentation verifying compliance is often necessary for market entry.
6. Tolerance in Manufacturing Processes
Manufacturing tolerances, including stitching, bonding, and assembly precision, directly impact product quality. Strict tolerances help ensure consistent aesthetics and durability, especially important when scaling production for large orders in markets like Brazil or South Africa.
Common Industry and Trade Terminology
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to factories that produce shoes based on the buyer’s design and specifications. Understanding OEM relationships helps B2B buyers control quality, lead times, and intellectual property rights, especially when sourcing from new suppliers or regions like the Middle East.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
The smallest quantity a manufacturer will accept for a production run. Knowledge of MOQ helps buyers plan inventory and budget effectively, particularly crucial for smaller brands or emerging markets in Latin America and Africa seeking flexible order sizes.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
A formal request sent to suppliers to obtain price estimates, lead times, and terms for specific products. Issuing RFQs is essential for comparing suppliers, negotiating prices, and ensuring transparency in international transactions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Standardized trade terms defining responsibilities, costs, and risks during shipping. Common Incoterms like FOB (Free on Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) determine who handles shipping, insurance, and customs clearance, vital for smooth cross-border transactions across Europe, South America, and Africa.
5. Lead Time
The period from order confirmation to product delivery. Accurate knowledge of lead times helps manage supply chain risks, especially when dealing with overseas suppliers who may face logistical delays or customs procedures.
6. Specification Sheet (Spec Sheet)
A detailed document outlining material properties, dimensions, colors, and performance standards. Providing clear spec sheets reduces misunderstandings, accelerates approval processes, and ensures product consistency across diverse markets.
Strategic Insights for B2B Buyers
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms empowers buyers to make informed decisions, negotiate effectively, and mitigate risks associated with international sourcing. Emphasizing quality specifications aligned with regional standards—such as compliance certifications—can enhance market acceptance. Additionally, familiarizing oneself with trade terminology streamlines communication, expedites procurement processes, and fosters strong supplier relationships, especially in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the vegan shoes Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global vegan footwear market is experiencing rapid growth, driven by increasing consumer awareness of ethical, environmental, and health issues. For B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, this presents both opportunities and challenges. Europe, especially countries like Spain, is at the forefront, with a strong demand for sustainable products and established supply chains. Brazil and other South American nations are emerging as key sourcing hubs due to their rich biodiversity and access to innovative plant-based materials.
Emerging sourcing trends include the adoption of advanced biotechnologies and alternative materials such as mushroom leather, pineapple fibers (Piñatex), and recycled ocean plastics. These materials are gaining popularity not only for their eco-friendly credentials but also for their durability and aesthetic appeal. B2B buyers should monitor innovations in material science that enable scalable, cost-effective production while maintaining high quality standards.
Technological advancements like automation, 3D printing, and blockchain traceability are transforming supply chains, allowing for greater transparency and efficiency. For example, blockchain enables verified ethical sourcing and material authenticity, which is crucial for brands targeting eco-conscious consumers. Market dynamics are also influenced by regulatory shifts, such as stricter environmental standards in Europe and evolving import/export policies in emerging markets, which require proactive compliance strategies from international buyers.
Furthermore, the rise of niche and premium segments—such as luxury vegan shoes—creates opportunities for high-margin products. To stay competitive, B2B buyers should forge partnerships with innovative suppliers, leverage regional trade agreements, and adapt to shifting consumer preferences toward transparency and sustainability.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are pivotal in the vegan shoes sector, influencing purchasing decisions across all regions. Environmentally, vegan shoes reduce reliance on animal products, lowering greenhouse gas emissions, water use, and land degradation. Materials like cork, recycled plastics, and plant-based leathers contribute to a smaller ecological footprint, aligning with global climate commitments.
For B2B buyers, prioritizing suppliers with verified sustainability credentials is essential. Certifications such as Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS), Forest Stewardship Council (FSC), and Cradle to Cradle demonstrate adherence to environmental standards and ethical practices. These certifications not only reinforce brand credibility but also facilitate compliance with international regulations, especially in Europe where eco-labeling is increasingly mandated.
Ethical sourcing extends beyond environmental considerations to fair labor practices and supply chain transparency. Buyers should seek suppliers with transparent traceability systems, ensuring that raw materials are sourced responsibly and workers are protected under fair labor standards. Collaborating with suppliers who implement eco-friendly manufacturing processes—like low-impact dyeing or water recycling—can significantly enhance sustainability profiles.
Incorporating “green” materials and sustainable production techniques is vital for differentiation in a competitive market. Building long-term relationships with certified suppliers supports continuous improvement and innovation in eco-friendly footwear solutions. Ultimately, a commitment to sustainability in sourcing not only meets regulatory and consumer demands but also positions B2B buyers as leaders in the transition toward a more ethical and environmentally conscious industry.
Brief Evolution/History (Optional)
The vegan shoes sector has evolved significantly over the past two decades, transitioning from niche alternative products to mainstream sustainable footwear. Initially driven by animal rights activism, the movement gained momentum with technological advancements in material science, enabling the development of durable, aesthetically appealing vegan leathers and textiles.
Major footwear brands began integrating vegan options into their collections, prompting a surge in specialized manufacturers. This evolution has been supported by increasing consumer demand for transparency and sustainability, especially in Europe and North America. Emerging markets like Brazil and South Africa are now exploring local plant-based resources, fostering regional innovation.
Understanding this historical progression helps B2B buyers anticipate future trends, such as the integration of regenerative agriculture practices and circular economy models. Recognizing the sector’s trajectory allows for strategic sourcing decisions that align with ongoing innovations and market expectations, ensuring long-term competitiveness and sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of vegan shoes
1. How can I effectively vet vegan shoe suppliers to ensure product quality and reliability?
Vetting suppliers requires a multi-step approach. Start by requesting comprehensive company profiles, including certifications, manufacturing credentials, and client references. Verify their compliance with international standards such as ISO or vegan-specific certifications (e.g., PETA-Approved). Conduct virtual audits or visit manufacturing facilities if feasible, especially for large orders. Review sample products for quality, durability, and finish. Additionally, seek transparency regarding their supply chain, raw material sources, and ethical practices. Building relationships with verified, reputable suppliers reduces risks and ensures consistent product quality for your market.
2. What customization options are typically available for vegan shoes, and how can I communicate my specific requirements?
Most vegan shoe manufacturers offer customization in design, color, branding, and packaging. Clearly define your specifications—such as materials, sole type, branding placements, and packaging preferences—early in negotiations. Use detailed sketches, technical specifications, and sample references to communicate your needs precisely. Consider requesting prototypes before bulk production to verify adherence to your standards. Establish a clear timeline for revisions and approvals. Open communication and detailed documentation streamline the process, ensuring the final product aligns with your brand identity and market expectations.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
3. What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for importing vegan shoes internationally?
MOQs for vegan shoes vary widely but generally range from 300 to 1,000 pairs per style, depending on the manufacturer’s scale and customization level. Lead times typically span 4 to 12 weeks, including production, quality checks, and shipping. For smaller orders or new suppliers, negotiate flexible MOQs or sample batches to test market response. Always factor in potential delays due to customs, holidays, or unforeseen disruptions. Establish clear timelines with your supplier and plan your inventory accordingly to avoid stockouts or excess inventory.
4. Which certifications and quality assurance measures should I look for in vegan shoe suppliers?
Prioritize suppliers with certifications such as PETA-Approved Vegan, Leaping Bunny, or equivalent ethical standards. Additionally, look for ISO 9001 or ISO 14001 certifications indicating quality management and environmental responsibility. Request detailed Quality Assurance (QA) reports, inspection protocols, and third-party testing results for durability, color fastness, and non-toxicity. Conduct pre-shipment inspections or hire third-party inspection agencies to verify product compliance before shipment. These measures help mitigate risks related to product recalls, legal compliance, and brand reputation in diverse international markets.
5. How can I manage logistics and shipping to ensure timely delivery across different regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe?
Partner with experienced freight forwarders familiar with your target regions. Opt for Incoterms like FOB or CIF to clearly define responsibilities and costs. Consider shipping methods—air freight for urgent needs or sea freight for cost efficiency—based on order size and urgency. Track shipments via reliable logistics platforms and maintain regular communication with your supplier and logistics providers. Account for customs clearance procedures, import duties, and local regulations in each region. Building strong logistics partnerships minimizes delays and ensures your vegan shoes reach markets on schedule.
6. How should I handle disputes or quality issues with international vegan shoe suppliers?
Establish clear contractual terms covering quality standards, inspection procedures, and dispute resolution mechanisms before order confirmation. In case of disputes, document issues with detailed photos, samples, and correspondence. Engage in direct negotiation to resolve minor disagreements swiftly; for persistent issues, consider mediation or arbitration under internationally recognized frameworks like ICC or UNCITRAL. Maintain open communication and foster collaborative problem-solving. Building a solid relationship and clear contractual clauses helps protect your interests and facilitates prompt resolution, minimizing disruptions to your supply chain.
7. What payment terms are common in international B2B transactions for vegan shoes, and how can I mitigate financial risks?
Common payment terms include 30% deposit upfront with the balance paid before shipment, or letters of credit for added security. For trusted suppliers, net terms of 60 or 90 days may be negotiated. To mitigate risks, perform due diligence on the supplier’s financial stability, and consider using escrow services or trade finance options. Always document payment terms clearly in the contract, including penalties for late payments or non-compliance. Establishing reliable payment processes fosters trust and ensures smooth transactions, especially when dealing with new or distant suppliers.
8. What are key considerations for ensuring compliance with regional import regulations and market standards?
Research import regulations, product standards, and labeling requirements specific to each target market—such as the EU’s CE marking, Brazil’s INMETRO standards, or Middle Eastern customs. Ensure your supplier provides necessary documentation, such as Certificates of Origin, Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS), and compliance certificates. Incorporate local legal advice or consult trade associations for updated regulations. Regularly review changes in standards and maintain compliance documentation to avoid delays or penalties. Proactive regulatory management ensures seamless market entry and protects your brand reputation across diverse regions.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for vegan shoes
Final Thoughts and Future Outlook
Effective strategic sourcing is essential for international B2B buyers aiming to capitalize on the growing demand for vegan shoes. By forging strong partnerships with reliable suppliers—especially those specializing in sustainable, cruelty-free materials—businesses can ensure product quality, reduce supply chain risks, and enhance brand reputation. Diversifying sourcing regions, including emerging markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and established hubs in Europe, offers opportunities for cost optimization and innovation.
As consumer awareness around ethical and eco-friendly footwear continues to expand globally, staying ahead of trends requires proactive engagement with suppliers who prioritize transparency and sustainability. Leveraging technological advancements such as digital procurement platforms and supply chain traceability tools can further streamline sourcing processes.
Looking ahead, B2B buyers should view strategic sourcing not just as a procurement activity but as a competitive advantage. Embracing sustainable supply chains will be critical in meeting evolving consumer expectations and regulatory standards. Now is the time for international buyers to build resilient, responsible sourcing networks—positioning themselves at the forefront of the vegan footwear market’s future growth.