Mastering Mens vs Womens Shoe Size for International B2B
Guide to Mens Vs Womens Shoe Size
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for mens vs womens shoe size
- Understanding mens vs womens shoe size Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of mens vs womens shoe size
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for mens vs womens shoe size
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for mens vs womens shoe size
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for mens vs womens shoe size Sourcing
- Spotlight on Potential mens vs womens shoe size Manufacturers and Suppliers
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for mens vs womens shoe size
- Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the mens vs womens shoe size Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of mens vs womens shoe size
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for mens vs womens shoe size
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for mens vs womens shoe size
Understanding the nuances of men’s versus women’s shoe sizing is fundamental for any B2B buyer engaged in international footwear sourcing. Accurate sizing not only ensures customer satisfaction but also minimizes costly returns and inventory mismatches, making it a critical factor in global trade success. As markets become increasingly interconnected—particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—navigating these differences becomes essential for effective procurement and competitive positioning.
This comprehensive guide covers vital aspects of the shoe industry, including diverse types, materials, manufacturing processes, quality control, supplier evaluation, cost considerations, and market trends. By equipping buyers with detailed insights into sizing standards and regional variations, it enables more precise sourcing decisions that align with local consumer preferences and standards.
For international B2B buyers, especially from diverse markets like Egypt, France, or Brazil, understanding how men’s and women’s shoe sizes differ across regions is crucial for establishing reliable supply chains. This guide aims to empower you with actionable knowledge—helping you select the right suppliers, optimize product offerings, and navigate complex global markets confidently. Ultimately, mastering the intricacies of shoe sizing enhances your ability to meet customer expectations and strengthen your competitive edge worldwide.
Understanding mens vs womens shoe size Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Men’s Shoe Sizing System | Numeric sizes typically 6-16 (US), EU 39-46; standardized width | Footwear manufacturing, wholesale distribution | Pros: Widely recognized, consistent sizing; Cons: Variations across regions can cause misfit |
| Women’s Shoe Sizing System | Numeric sizes generally 4-12 (US), EU 35-42; narrower fit | Retail, bulk imports, custom orders | Pros: Clear, detailed sizing; Cons: Less standardized internationally, potential sizing confusion |
| Unisex Shoe Sizing | Shared sizing scales, often based on men’s measurements | Unisex footwear lines, wholesale imports | Pros: Simplifies inventory management; Cons: Fit may vary, requiring detailed size charts |
| Regional Sizing Variations | Differences between US, EU, UK, and Asian sizing standards | International trade, cross-border sourcing | Pros: Broader market reach; Cons: Increased complexity, need for precise conversion tools |
| Width and Fit Variations | Standard vs. wide/narrow widths, adjustable fits | Specialty footwear, custom manufacturing | Pros: Better fit options, caters to diverse customer needs; Cons: Higher inventory complexity |
Characteristics, Suitability, and B2B Considerations
Men’s Shoe Sizing System:
This system primarily uses numeric scales, such as US sizes 6-16 and European EU sizes 39-46. It provides a straightforward, standardized approach that is widely adopted by manufacturers globally. For B2B buyers, especially those importing large quantities of men’s footwear into Africa, South America, or Europe, understanding these size standards ensures accurate inventory planning and reduces returns due to sizing mismatches. Regional variations, however, may require conversion charts or local expertise to avoid misfit issues.
Women’s Shoe Sizing System:
Women’s sizes tend to be slightly more detailed, with US sizes 4-12 and EU sizes 35-42. While generally consistent within regions, international buyers must be cautious of differences in sizing standards. For instance, European sizing might differ slightly from US sizing, impacting order accuracy. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers that provide comprehensive size charts and conversion information, especially when dealing with bulk orders or custom designs tailored to specific markets like Egypt or France.
Unisex Shoe Sizing:
Unisex sizing simplifies inventory management by using a single size scale that often aligns with men’s measurements. This approach is increasingly popular in casual and athletic footwear lines, appealing to a broad demographic. For international buyers, unisex sizing reduces complexity but necessitates clear communication of sizing charts to retailers and distributors. It is especially advantageous for bulk imports aiming for versatile product lines, but buyers must verify fit consistency across different markets.
Regional Sizing Variations:
Different markets adopt varying standards—US, UK, EU, and Asian sizing systems—creating potential confusion in international trade. B2B buyers engaging in cross-border sourcing should invest in reliable conversion tools or partner with suppliers familiar with regional differences. Accurate sizing translation minimizes the risk of overstocking or understocking, and enhances customer satisfaction in diverse markets like Egypt or South America, where local sizing norms may differ significantly.
Width and Fit Variations:
Beyond length, widths such as standard, wide, or narrow, are critical for ensuring customer satisfaction. Some markets demand specific fit options, and suppliers offering adjustable or multiple width options can command higher margins. B2B buyers should consider stocking a range of widths if targeting niche segments or health-related footwear markets. Managing inventory with varied fit options requires careful planning but can significantly improve market competitiveness by addressing diverse consumer needs.
In summary, understanding these variations enables B2B buyers to streamline procurement, reduce return rates, and tailor their offerings to the specific needs of each regional market. Accurate sizing data and supplier transparency are essential for successful international footwear trade.
Key Industrial Applications of mens vs womens shoe size
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of mens vs womens shoe size | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Footwear Manufacturing | Custom sizing for gender-specific shoe lines | Ensures product accuracy, reduces returns, and enhances customer satisfaction | Access to precise sizing data, reliable measurement standards, and flexible production capabilities |
| Medical & Orthopedic Devices | Custom orthotics and prosthetics tailored to gender-specific foot dimensions | Improves fit, comfort, and efficacy of medical devices, reducing patient complaints | Accurate sizing metrics, gender-specific anatomical data, and quality control standards |
| Safety & Workwear | Gender-specific safety shoes for industrial workers | Enhances safety compliance, comfort, and productivity in diverse work environments | Sourcing gender-appropriate shoe sizing, durable materials, and compliance with safety standards |
| Sports & Performance Gear | Gender-specific athletic footwear for professional and amateur sports | Boosts performance and reduces injury risk through precise fit | Access to detailed sizing charts, high-quality materials, and customization options |
| Retail & Wholesale Distribution | Bulk procurement of men’s and women’s shoe sizes for diverse markets | Enables inventory optimization, targeted marketing, and market segmentation | Reliable suppliers with scalable production, diverse size ranges, and export capabilities |
Footwear Manufacturing
In the footwear industry, precise understanding of men’s versus women’s shoe sizes is critical for producing gender-specific lines. Accurate sizing data ensures that products fit correctly, reducing costly returns and enhancing brand reputation. For international B2B buyers, especially from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, sourcing manufacturers with detailed gender-specific sizing standards and flexible production capabilities is essential to meet diverse market demands efficiently.
Medical & Orthopedic Devices
Custom orthotics and prosthetics rely heavily on gender-specific foot measurements to ensure proper fit and function. Women’s feet tend to differ in shape and arch structure from men’s, necessitating tailored solutions. B2B buyers in healthcare sectors must prioritize suppliers with access to comprehensive anatomical data and high-quality materials, ensuring devices provide optimal comfort and durability across different populations.
Safety & Workwear
Industrial safety footwear must accommodate gender differences to ensure maximum protection and comfort. Women’s safety shoes often require different sizing and ergonomic considerations compared to men’s to prevent injuries and improve worker compliance. Buyers should source from suppliers experienced in gender-specific safety standards, with an emphasis on durable, high-performance materials suitable for harsh working conditions prevalent in regions like Egypt, France, and South America.
Sports & Performance Gear
Athletic footwear designed with gender-specific sizing enhances athletic performance and reduces injury risks. Proper fit is crucial for both professional athletes and casual users, especially in markets with diverse sports cultures. International buyers should seek suppliers that offer detailed sizing charts, customization options, and high-quality, breathable materials to meet the needs of different demographics across continents.
Retail & Wholesale Distribution
Understanding the nuances of men’s versus women’s shoe sizes allows distributors to optimize inventory and tailor marketing strategies for varied markets. Bulk procurement of gender-specific sizes requires reliable sourcing partners capable of scalable production and consistent quality. This approach helps businesses adapt quickly to regional preferences, ensuring better market penetration in diverse regions such as Egypt, France, and South America.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for mens vs womens shoe size
Material Analysis for Shoe Size Manufacturing: Strategic Insights for International Buyers
When selecting materials for manufacturing men’s and women’s shoes, understanding their properties and implications across different markets is crucial. Different regions—such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—have varying standards, climate conditions, and consumer preferences, all of which influence material choice. Below is a detailed analysis of common materials used in shoe manufacturing, focusing on their key properties, advantages, limitations, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
Leather (Full-Grain and Top-Grain)
Key Properties:
Leather remains a premium material in footwear, valued for its durability, breathability, and aesthetic appeal. It offers moderate flexibility, excellent abrasion resistance, and natural moisture-wicking capabilities. Leather’s performance can vary depending on tanning methods—vegetable-tanned leather tends to be stiffer initially, while chrome-tanned leather offers softer, more pliable options.
Pros & Cons:
Advantages include high durability, a premium feel, and ease of repair or customization. However, leather is often costly, requires specialized manufacturing processes, and is sensitive to environmental conditions—particularly humidity and temperature. It can also be susceptible to cracking if not properly maintained.
Impact on Application:
Leather is suitable for both formal and casual shoes, especially in markets where quality perception is high. It performs well across diverse climates but may require additional treatments (e.g., waterproofing) for humid or rainy regions.
International Buyer Considerations:
Compliance with standards such as ISO 9001 (quality management) and adherence to environmental regulations (e.g., REACH in Europe) are critical. Buyers from Africa and South America should consider sourcing from tanneries with sustainable practices to meet local consumer expectations and avoid import restrictions. Leather’s weight and manufacturing complexity may influence logistics and costs, especially in regions with limited skilled labor.
Synthetic Polymers (Polyurethane, PVC)
Key Properties:
Synthetic materials like polyurethane (PU) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) are popular due to their versatility, lower cost, and ease of manufacturing. PU offers good flexibility, moderate breathability, and can mimic leather’s appearance. PVC is highly resistant to water and chemicals but tends to be less breathable.
Pros & Cons:
These materials are cost-effective, lightweight, and suitable for mass production. They also allow for a wide range of finishes and colors. However, synthetic polymers may degrade faster under UV exposure, and some (especially PVC) can emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs), raising environmental and health concerns.
Impact on Application:
Synthetic materials are ideal for casual, athletic, and fashion footwear, especially in price-sensitive markets. They perform well in humid climates but may lack the longevity of natural leather, requiring more frequent replacement.
International Buyer Considerations:
Buyers should verify compliance with local environmental standards, such as REACH in Europe or similar regulations in South America and Africa. Cost savings must be balanced against potential quality perceptions, especially in markets where consumers favor natural materials. Supply chain stability for synthetic materials is generally good, but fluctuations in raw material prices can impact costs.
Thermoplastics (TPU, EVA)
Key Properties:
Thermoplastics like Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) and Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) are commonly used in shoe soles and midsoles. TPU offers excellent elasticity, abrasion resistance, and UV stability, while EVA provides lightweight cushioning with good shock absorption.
Pros & Cons:
These materials are lightweight, cost-efficient, and easy to process, making them suitable for mass production. TPU’s durability surpasses EVA, but it is typically more expensive. EVA is softer and more comfortable but less durable over time, especially under heavy wear.
Impact on Application:
Ideal for sports and casual footwear, thermoplastics are favored for their performance in shock absorption and flexibility. They are particularly suitable for markets with active lifestyles, such as in Africa and South America.
International Buyer Considerations:
Regulatory compliance, especially regarding VOC emissions and recyclability, is vital. Buyers should consider regional standards like ASTM or DIN for testing durability and safety. The environmental impact of thermoplastics is increasingly scrutinized, prompting a shift toward recyclable options, especially in Europe.
Summary Table of Material Considerations
| Material | Typical Use Case for mens vs womens shoe size | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leather | Formal, casual, high-end shoes for both genders | Durable, breathable, premium appearance | High cost, sensitive to environmental conditions | High |
| Synthetic Polymers | Casual, fashion, athletic shoes for both genders | Cost-effective, versatile, wide color options | Less durable, environmental concerns, less breathable | Med |
| Thermoplastics (TPU, EVA) | Sports, casual, comfort-focused footwear | Lightweight, shock absorption, flexible | EVA less durable, TPU more expensive | Low to Med |
By understanding these materials’ properties and regional compliance considerations, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that optimize product performance, cost-efficiency, and market acceptance across diverse international markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for mens vs womens shoe size
Manufacturing Processes for Men’s vs Women’s Shoes: A B2B Perspective
Understanding the manufacturing workflows for men’s and women’s shoes is crucial for international buyers seeking consistent quality and reliable supply chains. While core processes are similar, subtle differences impact production, quality control, and supplier verification.
Main Manufacturing Stages
1. Material Preparation
– Men’s Shoes: Typically utilize sturdier leathers, heavier soles, and reinforced components to meet durability expectations. Upper materials often include full-grain or nubuck leathers, while insoles emphasize support.
– Women’s Shoes: Frequently incorporate lighter, more flexible materials such as softer leathers, textiles, or synthetics. Fashion-driven designs may demand innovative materials like mesh, embellishments, or delicate trims.
– B2B Insight: Suppliers catering to both markets often segment their material sourcing to optimize for specific product categories, affecting lead times and costs.
2. Forming and Cutting
– Men’s Shoes: Larger sizes necessitate precise cutting and shaping, often involving automated cutting machines that maximize material yield. Last shaping is critical, with molds designed for stability and longevity.
– Women’s Shoes: Smaller, more varied sizes and designs require adaptable cutting techniques, often with more intricate pattern pieces. The focus is on aesthetic detailing and comfort.
– B2B Implication: Confirm supplier capacity for handling diverse sizes, especially for bulk orders across different regions.
3. Assembly
– Men’s Shoes: Emphasize structural integrity, with reinforced stitching, stronger sole attachments, and often, additional support features like arch supports.
– Women’s Shoes: Focus on aesthetic details, comfort features, and decorative elements, requiring skilled craftsmanship and sometimes handwork.
– B2B Insight: Evaluate the supplier’s skill level and machinery capability, particularly for complex designs or specialty finishes.
4. Finishing and Quality Checks
– Men’s Shoes: Require rigorous finishing to ensure durability, including sole sealing, edge finishing, and surface polishing.
– Women’s Shoes: Prioritize aesthetic perfection, including embellishments, color matching, and detailed surface treatments.
– B2B Tip: Suppliers with integrated finishing lines typically demonstrate higher consistency; request detailed process documentation.
Quality Assurance Protocols: Industry Standards and Best Practices
Quality assurance (QA) in footwear manufacturing is essential for compliance, customer satisfaction, and minimizing returns. International standards like ISO 9001 serve as foundational benchmarks, complemented by industry-specific certifications.
International and Industry-Specific Standards
- ISO 9001: Focuses on quality management systems, ensuring consistent processes and continuous improvement.
- CE Certification (Europe): Confirms product safety and compliance with European Union directives, critical for markets like France and other EU countries.
- API (American Petroleum Institute): Less relevant for footwear but applicable if suppliers use certain synthetic materials requiring API standards.
- Other Certifications: Oeko-Tex, REACH, and BSCI may also be relevant, especially for eco-friendly or ethically produced footwear.
Key Quality Control (QC) Checkpoints
1. Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
– Ensures raw materials meet specifications before production.
– Critical for controlling leather quality, synthetic materials, and components like soles and laces.
– B2B buyers should request supplier IQC reports, certificates of conformity, and raw material test reports.
2. In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
– Conducted during manufacturing to identify defects early.
– Includes dimensional checks, stitching quality, sole attachment, and surface inspections.
– Use of statistical process control (SPC) tools helps monitor process stability.
3. Final Quality Control (FQC)
– Performed on finished products before packaging.
– Focuses on overall appearance, fit, comfort, and durability.
– Common testing methods include visual inspection, dimensional measurement, and functional testing (e.g., bend tests, sole adhesion).
Testing Methods and Validation
- Durability Testing: Simulates wear conditions, such as flexing, abrasion, and sole adhesion.
- Comfort Testing: Ensures proper fit and support, especially critical for women’s footwear designed for extended wear.
- Environmental Testing: Checks resistance to humidity, temperature variations, and UV exposure, particularly important for exports to diverse climates.
Verifying Supplier Quality for International B2B Buyers
To mitigate risks and ensure product quality, B2B buyers should adopt comprehensive verification strategies:
1. Factory Audits
– Conduct or commission third-party audits aligned with standards like SA8000, BSCI, or Sedex.
– Focus on production capabilities, QC processes, and compliance with labor and environmental standards.
– For regions like Egypt, France, or South America, tailor audits to local regulations and industry norms.
2. Quality Documentation and Certification Verification
– Request detailed quality manuals, test reports, and certification copies.
– Cross-verify certificates with issuing bodies to prevent counterfeit documentation.
3. Sample Inspection and Testing
– Prior to bulk orders, insist on pre-production samples for testing against agreed specifications.
– Use third-party labs for independent testing, especially for compliance with regional standards like CE or REACH.
4. Ongoing Monitoring
– Implement regular site visits and random inspections.
– Utilize digital platforms for real-time QC reporting and communication.
Special Considerations for Regional Buyers
Africa and South America:
Suppliers may face challenges related to infrastructure and resource availability. Prioritize suppliers with ISO 9001 certification and proven track records. Conduct thorough audits and request detailed QC reports to verify their quality systems.
Middle East (e.g., Egypt):
Regional exporters often need to meet specific import standards, such as CE or local safety regulations. Establish clear documentation requirements and consider partnering with suppliers experienced in export compliance.
Europe (e.g., France):
European buyers demand high compliance with environmental and safety standards. Verify supplier certifications such as REACH, Oeko-Tex, and CE. Engage in supplier audits focusing on adherence to these standards and their QC processes.
Final Recommendations for B2B Buyers
- Establish clear quality specifications aligned with regional standards.
- Vet suppliers through a combination of audits, certification checks, and sample testing.
- Build long-term relationships with suppliers committed to continuous improvement and transparency.
- Leverage third-party inspection agencies, especially when sourcing from regions with variable quality controls.
- Incorporate regional compliance requirements into supplier contracts to mitigate legal and market access risks.
By understanding the nuanced manufacturing processes and rigorous quality assurance practices tailored for men’s and women’s footwear, international buyers can better manage supplier relationships, ensure product consistency, and confidently meet market demands across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for mens vs womens shoe size Sourcing
Cost Structure Analysis for Men’s vs Women’s Shoe Sourcing
Understanding the cost components involved in sourcing men’s and women’s shoes is crucial for international B2B buyers. Although both categories share many similarities, subtle differences influence overall pricing and profitability.
Materials: Women’s shoes often incorporate more delicate or varied materials such as fine leather, textiles, or decorative elements, which can increase material costs by approximately 10-20% compared to men’s shoes. Men’s shoes typically use sturdier, often less costly materials, although premium options like exotic leathers significantly impact costs.
Labor: Production complexity influences labor costs. Women’s shoes with intricate designs, embellishments, or additional components (e.g., heels, decorative straps) require more skilled labor, potentially increasing labor costs by 15-25%. Men’s shoes generally have more straightforward construction, leading to shorter assembly times and lower labor expenses.
Manufacturing Overheads: Overhead costs—machine setup, tooling, and factory operations—are relatively consistent across both segments but can vary depending on design complexity. Customization or higher-end finishes in women’s shoes tend to elevate overhead costs proportionally.
Tooling & Equipment: Producing women’s footwear with unique shapes or decorative elements may necessitate specialized tooling, increasing initial investment. Conversely, men’s shoe molds are often more standardized, reducing tooling costs.
Quality Control & Certification: Higher quality standards, especially for premium brands, influence inspection costs. Certifications such as ISO or sustainability standards add to expenses, with premium segments demanding stricter QC protocols, impacting both men’s and women’s footwear differently depending on the target market.
Logistics & Shipping: Shoe weight, packaging, and order volume impact logistics. Women’s shoes, especially those with delicate materials, may require specialized packaging, increasing shipping costs marginally. Larger volume orders typically benefit from reduced per-unit logistics costs.
Price Influencers and Variability
Several factors impact the final FOB (Free on Board) and landed prices:
-
Volume & MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Higher volumes reduce unit costs significantly, often by 10-25%. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should negotiate for favorable MOQ terms to optimize cost-efficiency.
-
Customization & Specifications: Custom designs, branding, or specific material requests increase costs by 15-30%. Standard models are more cost-effective but may limit differentiation in competitive markets.
-
Material Choices: Premium or sustainable materials add 20-40% to base costs. Buyers targeting eco-conscious or luxury segments should factor in these premiums.
-
Quality & Certifications: Meeting international standards (e.g., OEKO-TEX, ISO) can add 5-15% to manufacturing costs but enhance marketability, especially in Europe and the Middle East.
-
Supplier & Country Factors: Suppliers in China, Vietnam, or India typically offer competitive pricing, but costs vary based on local labor rates, infrastructure, and trade policies. European suppliers may charge a premium but offer shorter lead times and higher certifications.
-
Incoterms & Logistics: Choosing FOB or CIF terms influences total landed costs. Buyers should consider Incoterms that optimize control over shipping and customs clearance, especially in regions with complex import regulations.
Buyer Tips for Cost Optimization
-
Negotiate Volume Discounts & MOQs: Establish long-term relationships and negotiate for better terms as order volumes grow, particularly important for emerging markets in Africa and South America.
-
Prioritize Standard Models for Cost Savings: Customization adds costs; balancing design needs with cost-efficiency can improve margins.
-
Leverage Multiple Suppliers & Countries: Diversify sourcing to mitigate risks and leverage regional price differences, especially between high-cost European suppliers and more competitive Asian manufacturers.
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just unit price but also shipping, customs duties, inspection costs, and lead times, which vary significantly across regions.
-
Stay Informed on Trade Policies & Incoterms: Be aware of tariffs, trade agreements, and import restrictions that could influence landed costs, particularly in markets like Egypt or France.
Indicative Price Ranges (for reference only)
- Men’s shoes: $20–$50 FOB for standard models from Asian manufacturers; premium or customized shoes can range from $50–$120.
- Women’s shoes: $25–$60 FOB for standard designs; high-end or bespoke options may exceed $120.
Disclaimer: Prices fluctuate based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific product requirements. Buyers should conduct due diligence and request detailed quotations.
By thoroughly analyzing these components and factors, B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can strategically optimize sourcing costs, negotiate effectively, and improve overall profitability in the competitive footwear market.
Spotlight on Potential mens vs womens shoe size Manufacturers and Suppliers
- (No specific manufacturer data was available or requested for detailed profiling in this section for mens vs womens shoe size.)*
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for mens vs womens shoe size
Key Technical Properties for Shoe Size Specifications
1. Size Standardization and Measurement Systems
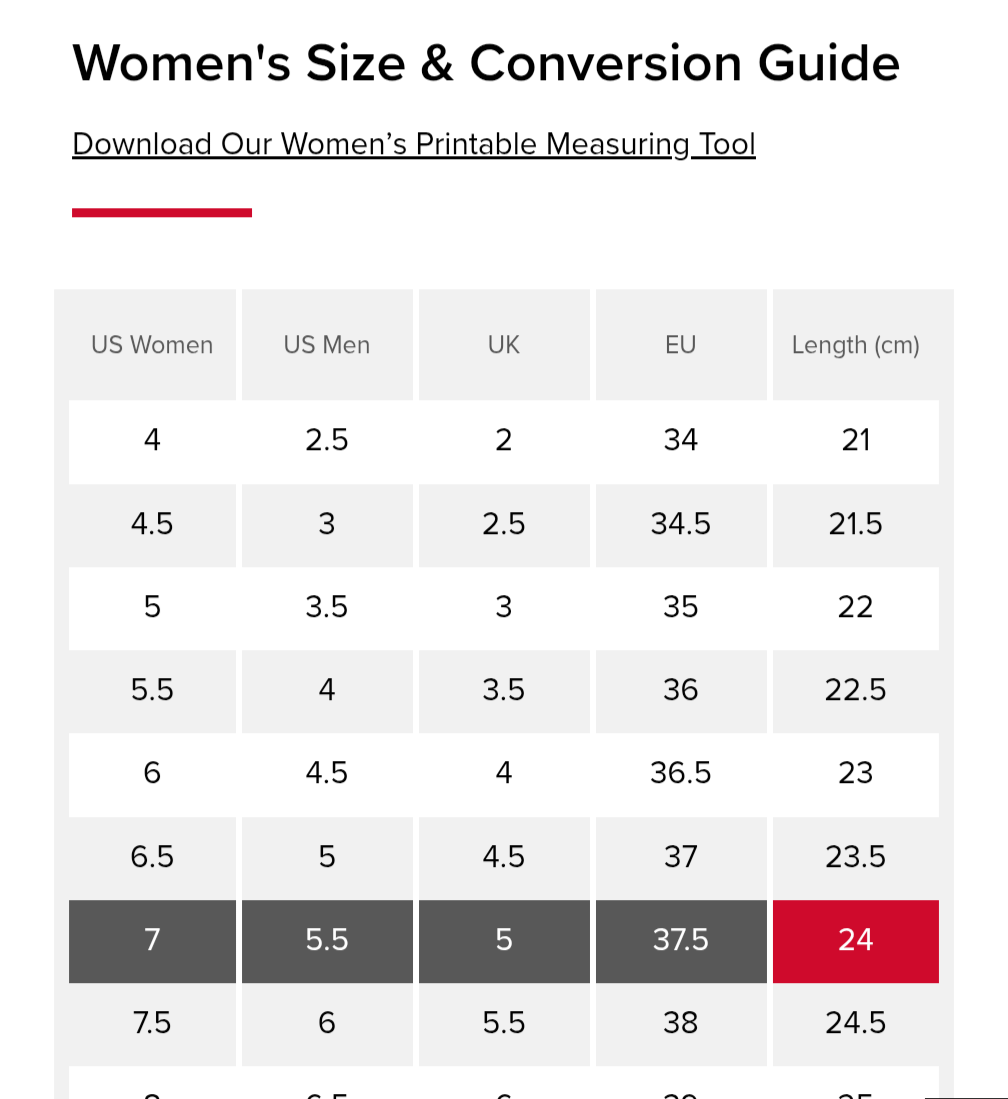
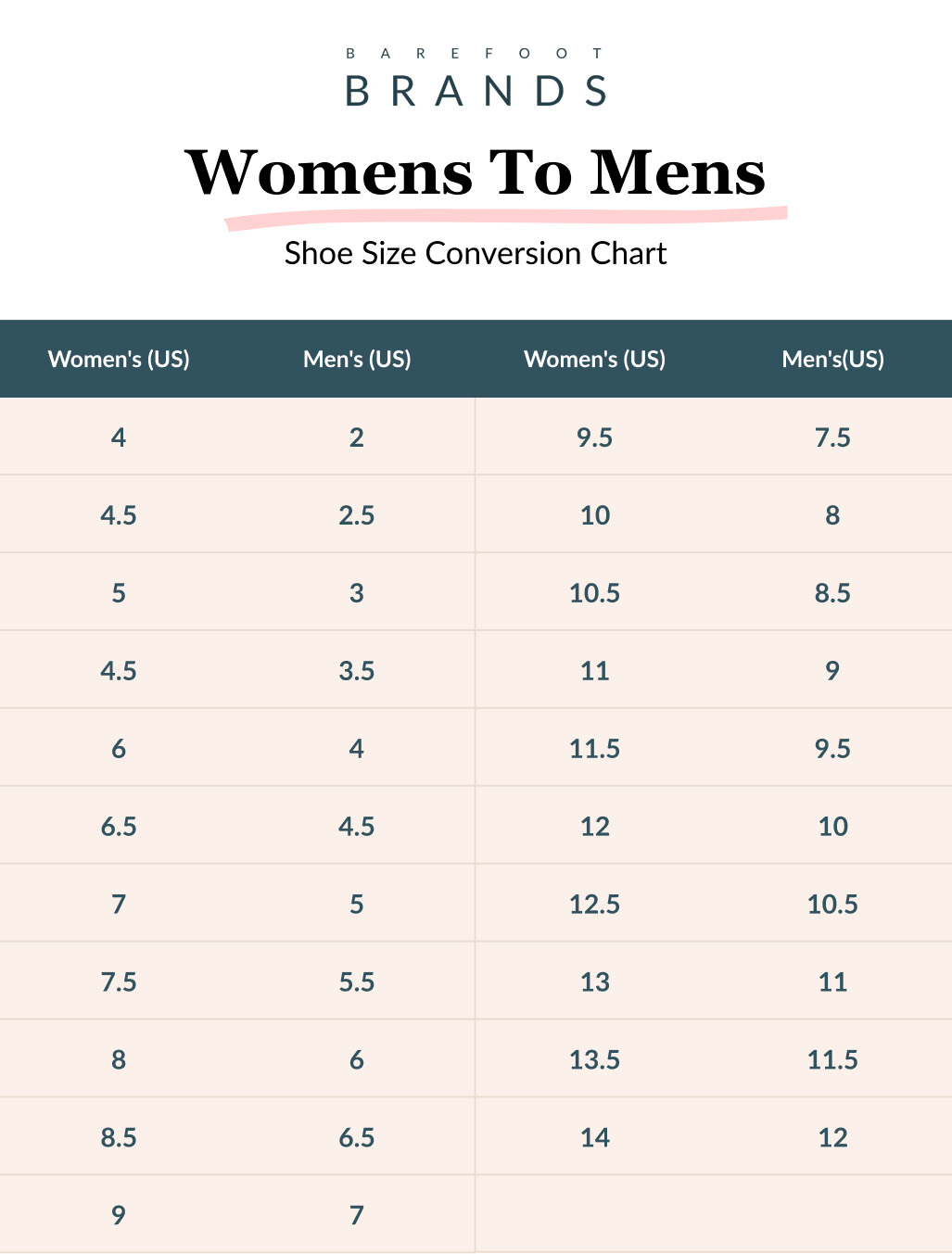
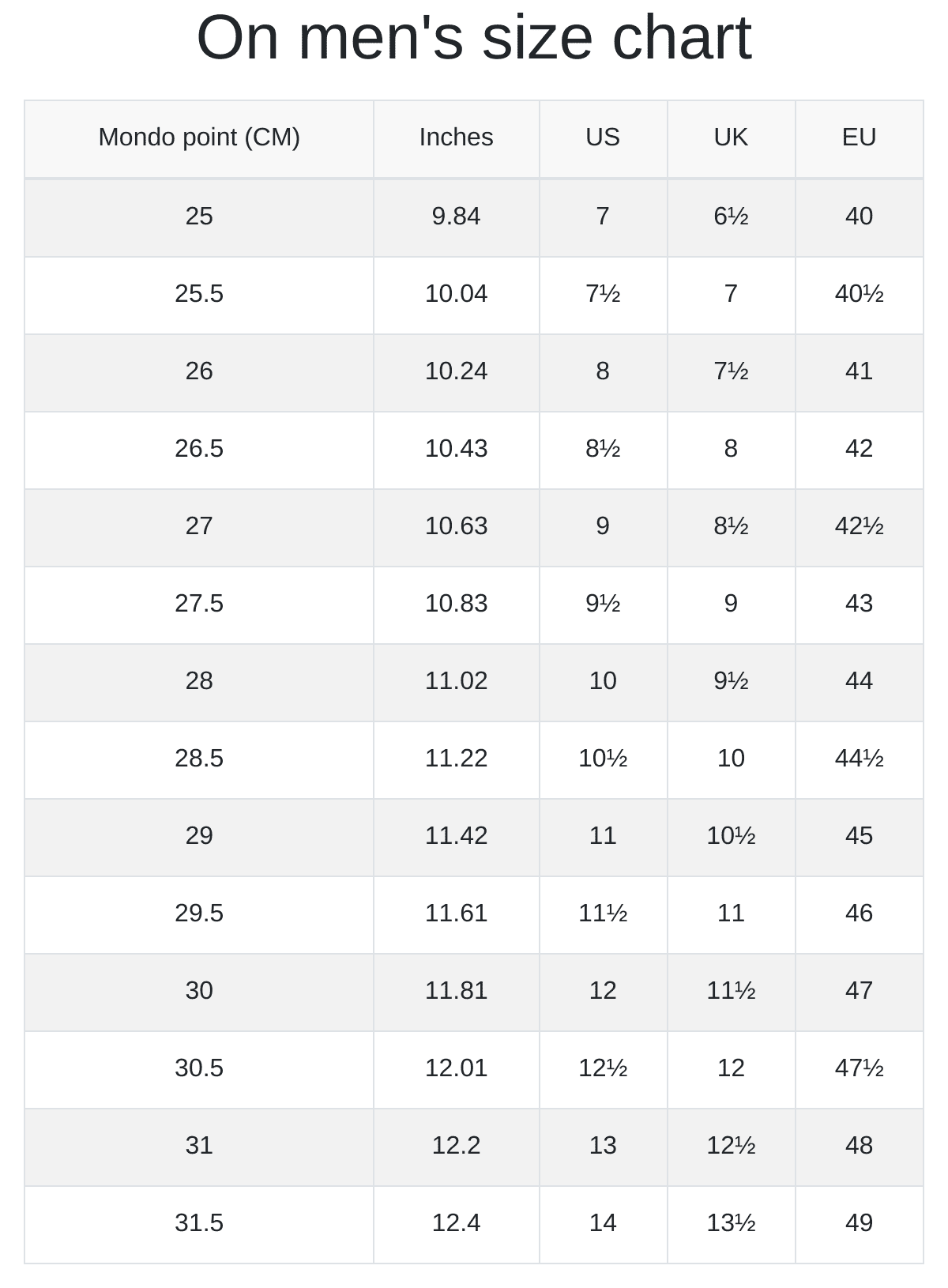
Different regions employ distinct sizing systems—e.g., US, EU, UK, and CM. For international B2B transactions, understanding these standards is crucial, as they influence product compatibility and customer satisfaction. Accurate conversion charts and clear labeling help prevent mismatches, especially when sourcing from or exporting to diverse markets.
2. Material Grade and Quality
The raw materials used in manufacturing, such as leather, synthetic fabrics, or rubber, are classified by quality grades. Higher-grade materials typically ensure better durability, comfort, and aesthetic appeal, which can justify premium pricing. B2B buyers should specify material grades in purchase agreements to maintain consistent product quality.
3. Tolerance and Dimensional Accuracy
Tolerance refers to the permissible deviation in shoe dimensions (length, width, and volume). Tight tolerances ensure consistent sizing, reducing returns and exchanges. For international trade, specifying acceptable tolerance levels aligns manufacturing outputs with market expectations, especially when dealing with sizing differences across regions.
4. Weight and Structural Integrity
Weight influences shipping costs and consumer perception. Structural integrity relates to the shoe’s ability to withstand wear without deforming. Both properties are vital for logistics planning and product durability assurance in B2B supply chains.
5. Finish and Surface Treatments
Surface properties, including coating, polishing, or waterproofing, impact the shoe’s appearance and functionality. Clear specifications on surface treatments help maintain brand standards and meet regional preferences, especially for premium or specialized footwear.
Essential Industry and Trade Terms
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to manufacturers producing shoes under another company’s brand name. Understanding OEM relationships allows buyers to source products tailored to their specifications, often at lower costs and with flexible customization options.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
The smallest quantity a supplier is willing to produce per order. Knowledge of MOQ helps buyers plan inventory levels, negotiate pricing, and assess production feasibility, especially for new or niche markets.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
A formal process where buyers solicit price and delivery terms from multiple suppliers. Effectively managing RFQs ensures competitive pricing and clear communication of technical specifications, reducing procurement risks.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Standardized trade terms defining responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and customs clearance. Familiarity with Incoterms like FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, Freight) allows buyers to optimize logistics costs and clarify risk transfer points.
5. Lead Time
The duration from order placement to product delivery. Accurate knowledge of lead times enables better planning and inventory management, especially important for seasonal or trend-driven footwear markets.
6. Certification and Compliance Terms
Includes standards such as ISO, CE, or regional safety certifications. Ensuring compliance with relevant certifications mitigates legal risks and enhances market acceptance, particularly when exporting to regions with strict safety standards.
Conclusion:
For international B2B buyers, a thorough understanding of these technical properties and trade terms enhances negotiation leverage, ensures product consistency, and streamlines supply chain operations. Clear communication of specifications and terminologies mitigates risks associated with sizing mismatches, quality discrepancies, and logistical uncertainties, fostering stronger global trade relationships.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the mens vs womens shoe size Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global footwear industry is experiencing rapid transformation driven by technological advancements, shifting consumer preferences, and evolving sourcing strategies. For B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial to maintaining competitive advantage.
Emerging trends include the integration of digital tools like 3D sizing and virtual fitting technologies, which enhance accuracy in matching shoe sizes across diverse markets. These innovations reduce returns and improve customer satisfaction, making them attractive for bulk sourcing. Additionally, the rise of direct-to-consumer (DTC) models has prompted brands to prioritize agility in supply chains, often leading to shorter lead times and more flexible order quantities—beneficial for B2B buyers seeking responsiveness to local demand fluctuations.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Market dynamics reveal a notable divergence in sourcing patterns for men’s versus women’s footwear. Men’s shoe sizes tend to be more standardized, simplifying inventory management for bulk orders. Conversely, women’s shoes exhibit a broader size spectrum and style diversity, requiring more nuanced sourcing strategies. Regions like Egypt and France are increasingly adopting advanced inventory management software to navigate these complexities, enabling better stock allocation aligned with regional preferences.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Furthermore, sustainability considerations are becoming a decisive factor in sourcing decisions. Many brands are prioritizing eco-friendly materials and transparent supply chains, driven by consumer demand and regulatory pressures. B2B buyers can leverage these trends by partnering with suppliers who employ innovative manufacturing processes, such as 3D printing and recycled materials, to reduce environmental impact while meeting market expectations.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability has transitioned from a peripheral concern to a core requirement in the footwear supply chain, especially in the context of men’s and women’s shoe sizes. For B2B buyers, sourcing from suppliers committed to ethical practices offers multiple benefits, including brand reputation enhancement, compliance with international standards, and long-term cost savings.
Environmental impacts of shoe manufacturing—such as water consumption, chemical use, and waste generation—are especially pertinent given the volume and diversity of sizes involved. For women’s footwear, with its wider array of styles and materials, sustainable sourcing often involves selecting suppliers who utilize organic, recycled, or biodegradable materials. Men’s shoes, typically more utilitarian, benefit from innovations in eco-friendly leather alternatives and low-impact manufacturing processes.
Certifications like Fair Trade, Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS), and Leather Working Group (LWG) are valuable indicators of ethical compliance. B2B buyers should prioritize partnerships with suppliers demonstrating transparency and accountability across their supply chains. This includes ensuring fair labor practices, reducing carbon footprints, and implementing waste reduction initiatives.
Additionally, embracing ‘green’ materials—such as plant-based dyes or recycled rubber—can significantly lower the environmental footprint of shoe production. For regions like Africa and South America, where natural resources are abundant, sourcing sustainable materials locally can also foster regional economic development and reduce logistics-related emissions.
Brief Evolution/History (Optional)
The footwear sector has historically relied on traditional manufacturing techniques, often involving extensive manual labor and resource-intensive processes. Over recent decades, technological innovations—such as automated cutting, 3D printing, and sustainable material development—have reshaped sourcing and production paradigms.
This evolution is especially relevant for B2B buyers seeking to align with global sustainability standards. The shift towards eco-conscious manufacturing not only addresses regulatory and consumer expectations but also drives cost efficiencies through waste reduction and energy savings. As the industry continues to evolve, regional markets like Egypt and France are becoming hubs for sustainable footwear innovation, influencing global sourcing strategies and market offerings.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of mens vs womens shoe size
1. How can I ensure that the shoe sizes provided by suppliers match international standards, especially when dealing with different regional sizing systems?
To verify size accuracy, request detailed size charts that include both regional and international standards (e.g., US, EU, UK). Ask suppliers for calibration certificates or third-party lab testing reports confirming sizing accuracy. It’s also advisable to conduct sample orders before bulk purchases, especially from new suppliers, to physically verify fit. For consistency, specify exact measurements (e.g., foot length in centimeters or inches) in your purchase agreements. Establish clear communication channels with suppliers to clarify sizing queries early, reducing returns and mismatched inventory.
2. What are key factors to consider when vetting international suppliers for men’s and women’s shoes regarding size consistency and quality?
Prioritize suppliers with proven experience exporting to your target markets and those who provide detailed size charts and quality certifications (ISO, CE, etc.). Review their quality control processes, including sample testing and third-party audits. Ask for references from other B2B buyers in your region. Confirm their ability to accommodate customization, such as sizing adjustments for regional preferences. Additionally, check their capacity for consistent production to ensure supply chain reliability, which is critical when managing inventory across diverse markets like Africa, Europe, or South America.
3. How flexible are suppliers in customizing shoe sizes for different regional markets, and what should I negotiate upfront?
Many suppliers can customize sizing within certain ranges, but it’s essential to specify target markets’ sizing standards (e.g., French, UK, US sizes). Negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) for customized sizes and clarify lead times for such adjustments. Ensure your contract details the scope of customization, including branding, sizing, and packaging. Discuss sample development costs and approval processes early to avoid delays. Establish clear communication channels with the supplier’s technical team to address regional sizing nuances, reducing the risk of mismatched inventory and customer dissatisfaction.
4. What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs), lead times, and payment terms for sourcing men’s and women’s shoes internationally?
MOQs vary depending on supplier capacity, often ranging from 300-1,000 pairs per style. Lead times generally span 45-90 days from order confirmation to delivery, but can be shorter with established suppliers. Payment terms commonly include 30% upfront and 70% prior to shipment, or letters of credit for larger orders. Negotiate flexible payment options, especially if your purchase volume is lower or if you’re testing new suppliers. Building strong relationships can help secure better terms, faster lead times, and priority production slots.
5. What quality assurance procedures and certifications should I request from international shoe suppliers?
Request suppliers to provide quality certificates such as ISO 9001, CE, or other relevant safety and compliance standards based on your target market. Insist on pre-shipment inspections or third-party audits to verify sizing accuracy, material quality, and workmanship. Ask for detailed product testing reports, including durability, colorfastness, and chemical safety. Establish a quality control process, including sample approval before mass production. Regular audits and quality checks during production help maintain standards, reducing the risk of costly returns and reputational damage in diverse markets.
6. How can I effectively manage logistics and shipping to ensure timely delivery of men’s and women’s shoes across different regions?
Partner with experienced freight forwarders familiar with your target markets, such as Egypt, France, or South America. Use Incoterms like FOB or CIF to clarify responsibilities and costs. Consolidate shipments when possible to reduce costs and lead times. Track shipments actively and establish clear communication with logistics providers for updates. Consider regional warehousing or distribution centers to streamline last-mile delivery. Planning ahead for customs clearance, tariffs, and import duties is critical, especially when dealing with different regional regulations, to prevent delays and additional costs.
7. How should I handle disputes related to sizing discrepancies or quality issues with international suppliers?
Establish clear contractual clauses outlining quality standards, inspection procedures, and dispute resolution processes, such as arbitration or local courts. Maintain detailed documentation of all communications, sample approvals, and inspection reports. If issues arise, communicate promptly with the supplier, providing evidence to support your claims. Consider engaging third-party inspection agencies for unbiased assessments. Building strong, transparent relationships with suppliers helps resolve disputes amicably, but always have fallback options, including legal counsel familiar with international trade laws, to protect your interests.
8. What strategies can I implement to build long-term relationships with reliable suppliers for men’s and women’s shoes?
Focus on consistent communication, prompt payments, and constructive feedback to foster trust. Place smaller, regular orders initially to test reliability before scaling up. Offer constructive feedback on sizing and quality to help suppliers improve their offerings. Develop mutual understanding of market needs, including regional sizing preferences, to align product development. Consider supplier certification programs or partnership agreements that incentivize quality and timely delivery. Investing in supplier relationships enhances supply chain stability, reduces lead times, and ensures better pricing, crucial for maintaining competitiveness across African, European, South American, and Middle Eastern markets.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for mens vs womens shoe size
Conclusion and Future Outlook
Effective strategic sourcing in the mens versus womens shoe market requires a nuanced understanding of regional sizing standards, consumer preferences, and supply chain dynamics. By establishing strong partnerships with reliable manufacturers and leveraging data-driven insights, B2B buyers can optimize inventory management, reduce sizing discrepancies, and enhance customer satisfaction across diverse markets.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
As international markets continue to evolve, staying adaptable and informed will be vital. Emphasizing local sourcing where feasible, diversifying supplier bases, and investing in quality assurance can mitigate risks associated with size standardization and logistical complexities. Additionally, embracing innovative technologies such as digital sizing tools and 3D foot scanning can further streamline operations and improve fit accuracy.
Looking ahead, proactive engagement with emerging markets—particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—will be crucial. By aligning sourcing strategies with regional consumer behaviors and regulatory frameworks, buyers can unlock new growth opportunities. Ultimately, a strategic, flexible approach will be the key to sustaining competitive advantage in the dynamic mens and womens shoe industry.