Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Shoe Parts
Guide to Shoe Parts
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for shoe parts
- Understanding shoe parts Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of shoe parts
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for shoe parts
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for shoe parts
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for shoe parts Sourcing
- Spotlight on Potential shoe parts Manufacturers and Suppliers
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for shoe parts
- Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the shoe parts Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of shoe parts
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for shoe parts
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for shoe parts
In the highly competitive footwear industry, the quality, availability, and cost of shoe parts can make or break a manufacturer’s ability to meet market demands and maintain profitability. For international B2B buyers—from burgeoning markets in Africa and South America to established hubs in Europe and the Middle East—understanding the complexities of sourcing shoe components is essential for strategic growth. Whether sourcing outsole rubbers, insoles, laces, or specialized hardware, the global supply chain offers vast opportunities but also presents challenges such as fluctuating costs, varying quality standards, and geopolitical considerations.
This comprehensive guide aims to equip you with the critical insights needed to navigate the global market effectively. It covers a broad spectrum of topics, including the different types of shoe parts, materials used, manufacturing and quality assurance processes, reliable supplier networks, and cost optimization strategies. Additionally, we will address market trends and frequently asked questions to clarify common concerns faced by international buyers.
For B2B buyers from diverse regions, this guide provides actionable intelligence to make informed sourcing decisions that align with your quality standards, budget constraints, and delivery timelines. By understanding the intricacies of global supply chains and regional sourcing nuances, you can better capitalize on emerging opportunities, mitigate risks, and build resilient partnerships that support your long-term growth in the competitive footwear sector.
Understanding shoe parts Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Upper Components | Encompasses vamp, quarter, and tongue; crafted from leather, synthetic, or fabric | Footwear manufacturing, customization, repairs | Pros: Wide material options, customizable; Cons: Quality varies, sourcing complexity |
| Sole Units | Includes outsole, midsole, and insole; made from rubber, EVA, leather | Sole replacement, OEM production, bespoke shoes | Pros: Durable, wide variety of materials; Cons: May require precise fitting processes |
| Fasteners & Closures | Zippers, laces, buckles, hook-and-loop straps | Fastening systems, fashion footwear, orthopedics | Pros: Functional and aesthetic options; Cons: Compatibility issues, durability concerns |
| Decorative & Functional Elements | Stitching, overlays, embellishments, logos | Branding, design differentiation, customization | Pros: Enhances appeal and brand identity; Cons: Increased manufacturing complexity |
| Reinforcements & Supports | Toe caps, heel counters, shanks, arch supports | Safety footwear, orthopedics, heavy-duty work shoes | Pros: Added durability and support; Cons: Higher production costs, weight considerations |
Upper Components
The upper is the visible part of the shoe that covers the foot, comprising elements like the vamp, quarter, and tongue. Made from materials such as leather, synthetic fabrics, or textiles, the upper plays a crucial role in comfort, aesthetics, and durability. For B2B buyers, sourcing high-quality uppers involves evaluating material consistency, supplier reliability, and customization options. Manufacturers often seek suppliers who can provide different finishes, patterns, and eco-friendly options, especially for markets demanding sustainable footwear. Cost, lead times, and material certifications are key considerations when establishing supply agreements.
Sole Units
Sole units include the outsole, midsole, and insole, forming the foundation of the shoe. They are crafted from various materials like rubber, EVA foam, or leather, each offering different levels of flexibility, cushioning, and durability. For international buyers, especially in regions with diverse climate conditions, selecting soles that balance durability and comfort is essential. OEM and large-scale manufacturers prioritize sourcing from suppliers with consistent quality control, as sole failure impacts product reputation. Customizable sole designs also support branding and differentiation, but require precise specifications to avoid mismatches during assembly.
Fasteners & Closures
Fastening mechanisms such as laces, zippers, buckles, and hook-and-loop straps provide security and adjustability. These components are crucial in both functional and fashion-oriented footwear. B2B buyers should evaluate material durability, ease of assembly, and compatibility with shoe designs. For markets like Europe and South America, where fashion trends evolve rapidly, flexible and innovative closure systems can offer competitive advantages. Suppliers offering a broad range of closure options with reliable quality and consistent supply chains enable buyers to meet diverse consumer preferences efficiently.
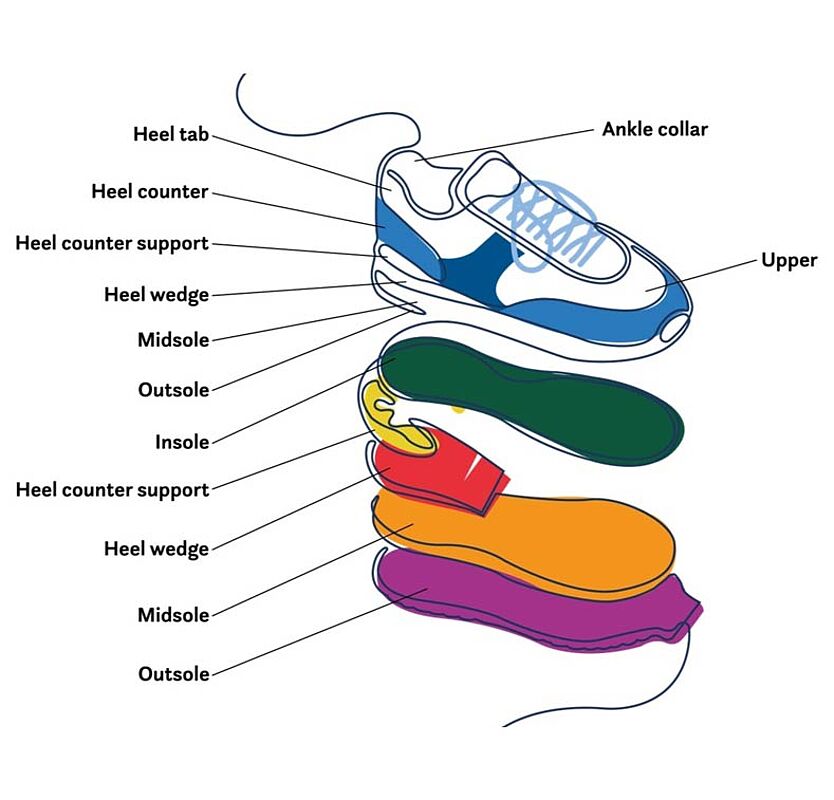
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Decorative & Functional Elements
Stitching, overlays, logos, embellishments, and other decorative features contribute significantly to a shoe’s aesthetic appeal and brand identity. These elements often require specialized manufacturing processes, making supplier expertise critical. For international buyers, sourcing decorative components involves assessing quality control, lead times, and ability to customize designs for different markets. Functional elements such as branding overlays or reflective accents also enhance safety and visibility, especially for outdoor or work footwear. Balancing design flexibility with cost-effectiveness is vital for successful procurement.
Reinforcements & Supports
Components like toe caps, heel counters, shanks, and arch supports are essential for durability, safety, and comfort, particularly in work or orthopedic shoes. These parts are typically made from reinforced plastics, metals, or composite materials. B2B buyers in sectors such as safety footwear or orthopedics focus on sourcing reliable, high-strength reinforcements that meet safety standards and ergonomic requirements. Cost considerations include material durability and manufacturing complexity, as these parts often involve additional processing steps. Ensuring consistent quality and compliance with regional safety regulations is vital for long-term supplier relationships.
Key Industrial Applications of shoe parts
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of shoe parts | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Footwear Manufacturing | Shoe soles, insoles, uppers, and heel components | Ensures product durability, comfort, and aesthetic appeal | Material quality, compliance with safety standards, customization options |
| Sports & Performance Gear | Specialized cleats, spikes, and orthotic inserts | Enhances athlete performance, provides specialized support | Material flexibility, lightweight design, high wear resistance |
| Medical & Orthopedic Devices | Orthopedic shoe parts, custom insoles | Offers tailored support, reduces patient discomfort, improves mobility | Precision manufacturing, biocompatible materials, customization capabilities |
| Industrial & Safety Equipment | Protective footwear components (steel toes, puncture plates) | Increases safety, reduces workplace injuries | Impact resistance, compliance with safety standards, sourcing reliable suppliers |
| Luxury & Fashion Accessories | Decorative shoe parts, embellishments, luxury heels | Adds aesthetic value, supports branding, differentiates products | High-quality materials, design flexibility, brand authenticity assurance |
Footwear Manufacturing
Shoe parts such as soles, insoles, uppers, and heels are fundamental to the production of consumer and industrial footwear. These components determine the durability, comfort, and visual appeal of finished shoes. For international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, Europe, and the Middle East, sourcing high-quality, compliant shoe parts ensures their products meet global standards and consumer expectations. Customization options allow for branding and design differentiation, which is crucial in competitive markets. Reliable supply chains and adherence to safety and environmental standards are vital considerations to avoid disruptions and ensure product integrity.
Sports & Performance Gear
In the sports sector, shoe parts such as specialized cleats, spikes, and orthotic inserts are tailored for high performance and athlete safety. These components need to be lightweight, durable, and capable of withstanding intense wear and tear. For buyers in regions with a strong sports culture, sourcing innovative, high-performance shoe parts can provide a competitive edge. Materials should offer flexibility, shock absorption, and high grip. Ensuring suppliers meet international standards for impact resistance and material safety is essential to maintain product quality and athlete trust.
Medical & Orthopedic Devices
Orthopedic shoe parts and custom insoles are critical for medical applications, aiding mobility and reducing discomfort for patients with specific needs. These shoe parts require precision manufacturing, often involving biocompatible and hypoallergenic materials. B2B buyers, especially from regions with growing healthcare sectors like South America and the Middle East, should prioritize suppliers capable of producing customized solutions with consistent quality. Ensuring compliance with medical standards and certifications enhances credibility and patient safety, making sourcing from reputable manufacturers a strategic imperative.
Industrial & Safety Equipment
Protective footwear components such as steel toes, puncture-resistant plates, and slip-proof soles are essential in industrial environments. These shoe parts enhance worker safety, prevent injuries, and help companies comply with occupational safety regulations. For international buyers, especially those in manufacturing hubs like France or Brazil, sourcing impact-resistant, durable, and certified safety components is crucial. Reliable suppliers with proven safety certifications and consistent quality control processes mitigate risks and ensure workforce safety.
Luxury & Fashion Accessories
Decorative shoe parts, embellishments, and luxury heels contribute significantly to brand identity and product differentiation in high-end markets. These components often involve intricate designs, high-quality materials, and craftsmanship that appeal to luxury consumers. For B2B buyers from fashion-forward regions such as Europe and the Middle East, sourcing premium, authentic, and customizable shoe parts supports brand positioning and innovation. Attention to material authenticity, finish quality, and flexibility in design are key sourcing considerations to meet the expectations of discerning customers.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for shoe parts
Analysis of Common Materials for Shoe Parts
Leather
Leather remains one of the most traditional and widely used materials in shoe manufacturing, especially for uppers and linings. Its key properties include excellent breathability, flexibility, and aesthetic appeal. High-quality leather can offer durability and a premium feel, making it suitable for luxury and everyday footwear. However, leather’s susceptibility to water damage and environmental degradation can limit its use in wet or humid conditions unless treated appropriately.
From a manufacturing perspective, leather requires specialized processing, which can increase costs and complexity. For international buyers, compliance with environmental standards such as REACH (Europe) or other regional regulations is crucial, especially regarding tanning agents and chemical treatments. Leather sourcing from regions like South America (e.g., Brazil) offers cost advantages but demands strict quality control to meet international standards.
Thermoplastics (e.g., TPU, PVC)
Thermoplastics like Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) and Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) are increasingly popular for shoe soles, midsoles, and decorative parts. These materials are valued for their excellent impact resistance, flexibility, and ease of molding. TPU, in particular, provides superior abrasion resistance and elasticity, making it ideal for high-performance sports shoes.
The advantages of thermoplastics include relatively low manufacturing costs and the ability to produce complex shapes efficiently. However, some thermoplastics, especially PVC, can emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during processing, raising environmental and health concerns. Buyers from regions with strict environmental regulations (e.g., Europe) should verify compliance with standards like REACH or RoHS. Additionally, thermoplastics are generally resistant to moisture and chemicals, suitable for various media exposure.
Rubber (Natural and Synthetic)
Rubber is a core material for outsoles and heel components due to its resilience, slip resistance, and shock absorption qualities. Natural rubber offers excellent elasticity and durability but can be more expensive and sensitive to environmental conditions like ozone and UV exposure. Synthetic rubbers (e.g., SBR, EPDM) provide better weather resistance and can be tailored for specific performance needs.
From a manufacturing standpoint, rubber’s vulcanization process adds complexity but ensures long-lasting performance. International buyers should consider sourcing from regions with established rubber industries, such as South America or Southeast Asia, to ensure quality and cost efficiency. Compliance with standards like ASTM D2000 (for rubber properties) or regional environmental regulations is vital, especially for exports to Europe and the Middle East.
Synthetic Fabrics (e.g., Nylon, Polyester)
Synthetic fabrics are commonly used for shoe linings, uppers, and reinforcement layers. Nylon and polyester are favored for their strength, lightweight nature, and resistance to environmental factors such as moisture and abrasion. These materials are often used in combination with other materials to enhance performance.
Their advantages include lower costs, ease of processing, and the ability to meet various international standards for safety and environmental impact. Buyers should consider the fabric’s flame retardancy, dye fastness, and compliance with regional standards like JIS (Japan), DIN (Germany), or ASTM (USA). Sourcing from regions with well-developed textile industries, such as Europe or South America, can provide high-quality options at competitive prices.
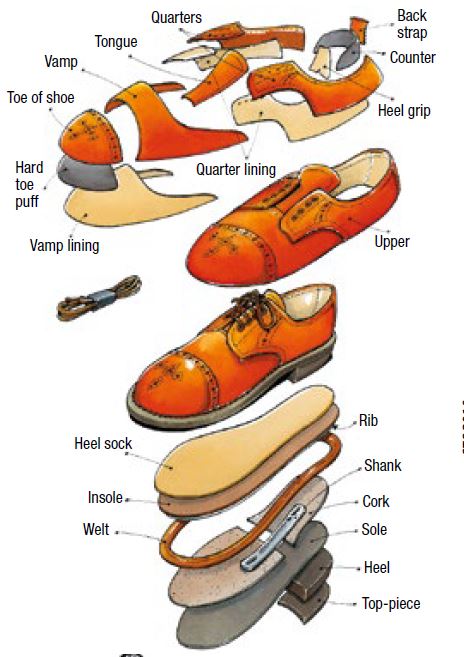
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for shoe parts | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leather | Uppers, linings, decorative elements | Breathability, aesthetic appeal, flexibility | Water susceptibility, environmental impact, cost | High |
| Thermoplastics (TPU, PVC) | Soles, midsoles, decorative overlays | Impact resistance, moldability, cost efficiency | Environmental concerns (VOCs), recyclability | Med |
| Rubber (Natural & Synthetic) | Outsoles, heel components | Durability, slip resistance, shock absorption | Cost (natural rubber), environmental sensitivity | Med |
| Synthetic Fabrics (Nylon, Polyester) | Linings, upper reinforcement, straps | Strength, lightweight, moisture resistance | Flammability, dye fastness, environmental standards | Low |
This comprehensive analysis aims to guide international B2B buyers in selecting optimal materials based on performance, cost, and regional considerations. Understanding these factors ensures better supply chain decisions, compliance adherence, and product quality across diverse markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for shoe parts
Manufacturing Processes for Shoe Parts
The production of shoe parts involves several meticulously coordinated stages, each critical to ensuring high quality and consistency. Understanding these processes enables B2B buyers to better evaluate supplier capabilities and ensure product compliance with international standards.
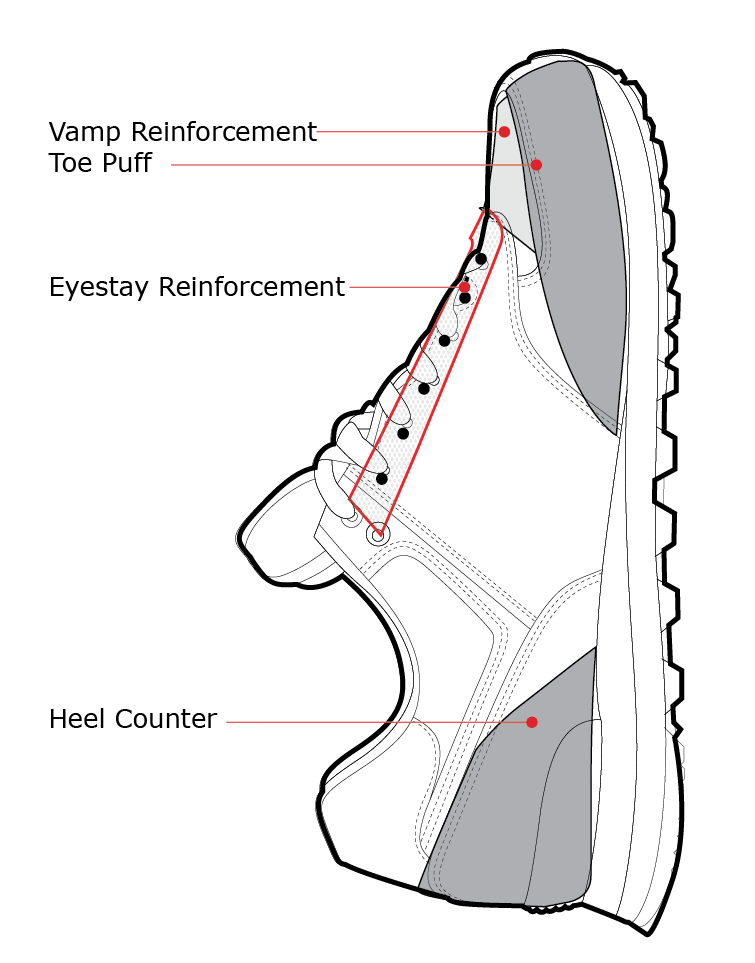
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
1. Material Preparation and Procurement
The process begins with sourcing raw materials such as leather, synthetic fabrics, rubber, EVA foam, and plastics. Suppliers often have specialized procurement channels to guarantee material authenticity and compliance with safety standards. For buyers, verifying certificates of origin and material test reports is essential to confirm quality and sustainability claims.
2. Material Processing and Forming
Once materials are procured, they undergo processing tailored to the specific shoe part. For example, leather might be cut, embossed, or treated to achieve desired textures, while synthetic components are molded or extruded. Techniques such as laser cutting, die-cutting, and thermoforming are common. Precision in this stage impacts fit, durability, and aesthetic appeal.
3. Assembly and Bonding
Assembly involves joining various components—such as soles, uppers, and linings—using adhesives, stitching, or mechanical fasteners. Advanced techniques like ultrasonic welding and heat sealing are increasingly adopted for seamless bonds, especially in waterproof or lightweight footwear. Proper assembly ensures structural integrity and longevity.
4. Finishing and Quality Control
The final stages include trimming, surface finishing, painting, and quality checks. Surface treatments like polishing or embossing enhance visual appeal, while coating processes improve water resistance or UV stability. Finishing also involves inspecting for defects, ensuring uniformity, and preparing the parts for shipment.
Quality Assurance (QA) and Control (QC) in Shoe Part Manufacturing
Robust QA/QC protocols are vital for international B2B transactions, especially given the diverse regulatory landscapes of Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. They help mitigate risks, ensure compliance, and uphold brand reputation.
1. International Standards and Certifications
– ISO 9001: The cornerstone of quality management, ISO 9001 certification indicates a manufacturer’s commitment to continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. It covers process control, documentation, and corrective actions.
– Industry-Specific Certifications: Depending on the target market, additional certifications may be required. For instance, CE marking for footwear sold within the European Economic Area (EEA), ensuring compliance with safety and environmental standards. In some cases, certifications like REACH (chemical safety) or ASTM standards are relevant.
2. Key QC Checkpoints
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspection of raw materials before they enter production. Tests include material composition verification, physical properties, and batch traceability.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during manufacturing. This involves dimensional checks, adhesion tests, seam strength tests, and visual inspections to detect defects early.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive assessment of finished parts. Includes dimensional accuracy, surface finish, color consistency, and functional testing (e.g., flexing, adhesion durability).
3. Common Testing Methods
– Mechanical Testing: Tensile strength, tear resistance, and flexibility tests ensure parts withstand real-world stresses.
– Chemical Testing: Verifies absence of harmful substances, such as heavy metals or phthalates, aligning with regulations like REACH and CPSIA.
– Environmental Testing: Accelerated aging, UV exposure, and water resistance tests simulate long-term wear and environmental effects.
4. Verification and Supplier Audits
B2B buyers should conduct supplier audits, either in-house or via third-party inspection agencies, to verify QC processes and facilities. Audits include reviewing quality documentation, observing manufacturing practices, and sampling products for independent testing. Requesting detailed QC reports and certificates is standard practice to ensure transparency.
Considerations for International B2B Buyers
1. Navigating Regional Standards and Expectations
Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must be aware of specific standards and consumer expectations. For instance, European markets demand high compliance with chemical safety and environmental directives, while Middle Eastern markets may prioritize durability and thermal comfort. Understanding these nuances helps tailor supplier assessments.
2. Quality Documentation and Traceability
Reliable suppliers provide detailed documentation, including test reports, certificates of compliance, and batch traceability records. B2B buyers should verify these documents through direct communication or third-party verification to prevent counterfeit or substandard parts entering their supply chain.
3. Engaging Third-Party Inspection and Certification
Employing reputable inspection agencies (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas, Intertek) for pre-shipment inspections adds an extra layer of assurance. These agencies can conduct physical audits, product sampling, and laboratory testing aligned with buyer-specific standards, which is especially critical for buyers unfamiliar with supplier manufacturing practices.
4. Building Long-Term Quality Partnerships
Establishing ongoing relationships with trusted manufacturers who consistently meet quality benchmarks fosters stability and reduces supply chain risks. Regular audits, performance reviews, and feedback loops are essential for maintaining high standards over time.
Final Recommendations for B2B Buyers
- Due Diligence: Prioritize suppliers with ISO 9001 certification and relevant industry-specific standards.
- Quality Testing: Request comprehensive test reports and conduct independent testing when possible.
- Inspection Protocols: Implement rigorous pre-shipment inspections via third-party agencies to verify compliance.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Demand detailed documentation on materials, production processes, and QC results to ensure traceability and accountability.
- Market Adaptation: Tailor QC expectations based on regional market requirements, consumer preferences, and regulatory frameworks.
By understanding and rigorously applying these manufacturing and quality assurance principles, international B2B buyers can significantly reduce risks, ensure product quality, and foster long-term, mutually beneficial partnerships in the global shoe parts industry.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for shoe parts Sourcing
Cost Structure Breakdown for Shoe Parts Sourcing
Understanding the detailed cost components involved in shoe parts manufacturing is essential for effective sourcing. The primary cost drivers include:
- Materials: The choice of raw materials—such as rubber, leather, textiles, or synthetics—significantly impacts unit costs. Premium materials with certifications (e.g., eco-labels, quality standards) tend to be more expensive but may add value for brand positioning.
- Labor: Labor costs vary widely depending on the country of manufacture. For instance, Asian suppliers typically offer lower wages, while European or Middle Eastern factories may have higher labor costs but often adhere to stricter labor standards.
- Manufacturing Overheads: These encompass factory utilities, machinery depreciation, and administrative expenses. Overheads are often embedded in the unit price but can fluctuate based on factory efficiency and scale.
- Tooling & Setup: Initial tooling costs are usually one-time expenses associated with molds or specialized equipment. These are amortized over large production runs, making them less significant for small or custom orders.
- Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes, including certifications (ISO, BSCI), add to costs but are crucial for ensuring product consistency and compliance with international standards.
- Logistics & Shipping: International shipping costs depend on shipment volume, weight, and destination. Incoterms (FOB, CIF, DDP) significantly influence who bears these costs and at what stage.
- Profit Margin: Supplier margins vary based on market competitiveness, order volume, and negotiation. Typically, margins range from 10% to 30%, but strategic negotiations can influence this.
Factors Influencing Pricing
Several variables shape the final pricing landscape:
- Order Volume & MOQ: Larger orders generally attract discounts due to economies of scale. Many suppliers offer tiered pricing, rewarding buyers who can commit to higher volumes or lower MOQs.
- Specifications & Customization: Customized shoe parts—such as specific colors, finishes, or technical features—tend to increase costs due to additional tooling or processing.
- Material Selection: Opting for standard, readily available materials reduces costs, whereas premium or specialized materials increase the price.
- Quality Certifications & Standards: Products meeting international standards (e.g., REACH, OEKO-TEX) often command higher prices but can provide a competitive advantage.
- Supplier Location & Capabilities: Suppliers in regions with lower operational costs (e.g., parts of Asia or Africa) can offer more competitive prices, but buyers must consider lead times and communication barriers.
- Incoterms & Delivery Terms: FOB terms shift responsibility to the buyer for shipping, whereas CIF or DDP includes logistics costs, impacting the total landed cost.
Strategic Tips for International B2B Buyers
- Negotiate Effectively: Leverage order volume commitments, long-term partnerships, or payment terms to negotiate better prices and conditions.
- Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond unit price, consider shipping, customs duties, compliance costs, and potential delays. A cheaper unit price might be offset by higher logistics or compliance expenses.
- Understand Pricing Nuances: Prices can vary based on currency fluctuations, geopolitical factors, or regional supply chain disruptions. Stay informed about market trends in your sourcing regions.
- Sample & Quality Assurance: Always request samples before large orders, especially when sourcing from new suppliers. This minimizes risk and clarifies expectations.
Price Ranges & Indicative Costs (Disclaimers Apply)
While actual costs fluctuate based on specifications and sourcing regions, approximate price ranges for common shoe parts are:
- Rubber Outsoles: $1.50 – $4.00 per pair
- Leather Upper Components: $2.00 – $6.00 per piece
- Textile Linings: $0.50 – $2.00 per piece
- Shoe Insole Components: $0.50 – $1.50 per pair
- Metal or Plastic Hardware (e.g., eyelets, buckles): $0.10 – $0.50 each
These prices are indicative and should be used as a starting point for negotiations and cost planning.
By thoroughly analyzing each component and understanding the influencing factors, international B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can make informed decisions, optimize costs, and build resilient supply chains for shoe parts sourcing.
Spotlight on Potential shoe parts Manufacturers and Suppliers
- (No specific manufacturer data was available or requested for detailed profiling in this section for shoe parts.)*
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for shoe parts
Critical Technical Properties for Shoe Parts
1. Material Grade and Composition
The quality and durability of shoe parts largely depend on the material grade used. For example, leather, synthetic fabrics, and rubber each have standardized grades indicating strength, flexibility, and wear resistance. High-grade materials ensure longevity and customer satisfaction, which are vital for brand reputation. B2B buyers should specify the required material grade to ensure suppliers meet performance standards and comply with regional safety or quality certifications.
2. Tolerance and Dimensional Accuracy
Tolerance refers to the permissible deviation in the size and shape of shoe components, such as soles, heels, or uppers. Precise tolerances are crucial for proper assembly and comfort, reducing issues like misalignment or gaps. Suppliers providing tight tolerances demonstrate better quality control, which minimizes rework and delays in production. Clearly defining acceptable tolerance levels in purchase agreements helps avoid misunderstandings and ensures consistent product quality.
3. Flexibility and Hardness
Properties like flexibility (for materials such as soles or uppers) and hardness (for heel counters or reinforcements) directly impact shoe performance. For instance, a sole that’s too stiff may reduce comfort, while insufficient hardness could compromise support. B2B buyers should specify required flexibility and hardness ratings aligned with the shoe’s intended use, ensuring the supplier provides suitable materials for the target market.
4. Resistance Properties
Key resistance properties include water resistance, abrasion resistance, and UV stability. These determine how well the shoe parts withstand environmental conditions and daily wear. For regions with high humidity or frequent exposure to harsh elements, selecting parts with appropriate resistance properties is essential. Suppliers should provide certification or test reports confirming these characteristics.
5. Weight and Thickness
Weight impacts comfort, especially for sports or casual footwear, while thickness influences durability and aesthetic appeal. Lightweight materials reduce fatigue, whereas thicker components may enhance longevity. B2B buyers must balance these properties according to end-user needs and specify minimum or maximum weight and thickness parameters.
Common Industry and Trade Terms
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to companies that produce shoe parts based on designs provided by the brand or retailer. OEM agreements are common when buyers want to maintain control over product specifications and branding. Understanding OEM arrangements helps buyers evaluate supplier capabilities and intellectual property considerations.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
The smallest quantity of shoe parts a supplier is willing to produce or sell in a single order. MOQs are critical for planning procurement budgets and production schedules. Buyers from regions with smaller markets should negotiate MOQs to avoid excessive inventory or costs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
A formal process where buyers request pricing, lead times, and technical details from suppliers. An RFQ ensures transparency and competitive pricing. Providing clear specifications in RFQs helps suppliers deliver accurate quotes, expediting the procurement process.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Standardized trade terms defined by the International Chamber of Commerce, specifying responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and customs clearance. Common Incoterms like FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) clarify who bears costs at each shipping stage. Understanding Incoterms reduces misunderstandings and legal risks in international transactions.
5. Lead Time
The period from order placement to delivery. Accurate knowledge of lead times helps manage production schedules and inventory levels, especially in regions with variable logistics infrastructure. Communicating and negotiating realistic lead times is essential for smooth supply chain management.
6. Certification and Compliance Terms
Terms like ISO, REACH, or CE indicate adherence to safety, environmental, and quality standards. Confirming supplier certifications ensures products meet regional regulations, reducing risks of customs delays or product recalls. For international buyers, verifying compliance is a critical step before large-scale procurement.
This structured understanding of technical properties and trade terminology empowers international B2B buyers to make informed decisions, negotiate effectively, and establish reliable supply chains for high-quality shoe parts across diverse markets.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the shoe parts Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global shoe parts sector is experiencing dynamic shifts driven by technological innovation, evolving consumer preferences, and geopolitical factors. For international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these drivers is crucial to optimize sourcing strategies and stay competitive.
Emerging trends include the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies—such as automation, IoT, and data analytics—which enhance manufacturing efficiency and quality control. Digital platforms now facilitate real-time sourcing and supply chain transparency, enabling buyers to evaluate suppliers on parameters like lead times, capacity, and compliance more effectively.
Market dynamics are influenced by fluctuating raw material prices, especially for leather, rubber, and synthetic components. Countries like Brazil and France are significant players, offering both traditional and innovative materials, while regions like the Middle East are increasingly investing in synthetic and alternative materials to meet sustainability goals.
For African and South American buyers, sourcing from regions with developing manufacturing hubs can provide cost advantages but requires careful vetting for quality and consistency. European buyers often focus on premium, technologically advanced, and sustainable shoe parts, emphasizing compliance with strict regulations. Navigating these diverse market conditions demands a nuanced understanding of regional supply chain capabilities, trade policies, and emerging sourcing channels such as e-marketplaces and direct manufacturer partnerships.
Overall, the sector is characterized by a shift toward shorter supply chains and diversified sourcing bases, driven by geopolitical uncertainties and the need for resilience. Buyers should leverage data-driven insights, foster strong supplier relationships, and stay attuned to regional innovations to capitalize on market opportunities.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of strategic sourcing in the shoe parts industry. Manufacturers and buyers are increasingly prioritizing environmentally friendly materials, ethical labor practices, and transparent supply chains to meet consumer demand and regulatory standards.
Eco-conscious sourcing involves selecting materials with low environmental impact, such as recycled plastics, organic textiles, and sustainably harvested leather. Certifications like FSC (Forest Stewardship Council), GRS (Global Recycled Standard), and OEKO-TEX are vital indicators of commitment to sustainability and can serve as key criteria during supplier evaluation.
Ethical sourcing extends beyond materials to encompass fair labor practices, safe working conditions, and fair wages. Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East are particularly attentive to these aspects, driven by consumer activism and stricter regulations. Engaging with suppliers who hold credible social responsibility certifications helps mitigate risks related to reputational damage and supply chain disruptions.
Incorporating sustainability into sourcing strategies can also yield operational benefits, such as reduced waste, lower energy consumption, and enhanced brand value. Many suppliers are now investing in greener manufacturing processes, such as waterless dyeing or renewable energy use, responding to the rising demand for sustainable shoe parts.
For B2B buyers, establishing long-term partnerships with certified, environmentally responsible suppliers is essential. Regular audits, transparent reporting, and collaborative improvement initiatives can reinforce ethical standards and foster innovation aligned with sustainability goals.
Brief Evolution/History
The shoe parts industry has evolved significantly over the past century, transitioning from primarily handcrafted, locally sourced components to highly automated, globally integrated supply chains. Initially dominated by regional manufacturers in Europe and North America, the sector expanded rapidly with the rise of mass production in Asia during the late 20th century.
In recent decades, technological advancements and increased emphasis on sustainability have reshaped the landscape. The adoption of digital sourcing platforms, advanced materials, and eco-friendly manufacturing processes reflects a broader industry shift toward efficiency, innovation, and responsibility. For international B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is vital to navigating current complexities and capitalizing on emerging opportunities in diverse regional markets.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of shoe parts
1. How can I effectively vet international suppliers of shoe parts to ensure quality and reliability?
Effective vetting begins with comprehensive research. Start by requesting verified business licenses, certifications (ISO, CE, etc.), and third-party audit reports. Review their production facilities through virtual tours or on-site visits if feasible. Check references from other clients, especially those in your region or industry, to gauge their reputation. Consider ordering sample products to assess quality firsthand. Additionally, evaluate their communication responsiveness and transparency. Partnering with suppliers who have a proven track record in compliance, quality, and timely delivery minimizes risks and builds a trustworthy supply chain.
2. What are the key considerations when requesting customization of shoe parts from international suppliers?
When seeking customization, clearly define your specifications, including materials, dimensions, colors, and finishes. Communicate your requirements in detail and request detailed prototypes or samples before bulk production. Confirm whether the supplier has experience with your specific customization needs and inquire about their capabilities for small or large batch modifications. Clarify lead times for customization, as these can vary significantly. Establish quality standards and inspection processes upfront. Also, discuss potential additional costs and minimum order quantities (MOQs) related to customization to avoid surprises later.
3. How do I determine appropriate MOQs, lead times, and payment terms with international shoe parts suppliers?
Start by understanding the supplier’s production capacity and typical MOQs, which often depend on the complexity of the parts. Negotiating flexible MOQs can be advantageous, especially for testing new suppliers or prototypes. Lead times generally range from 4 to 12 weeks, depending on complexity and location; always request detailed schedules. Payment terms vary but commonly include 30% upfront and 70% upon shipment or delivery. Consider using trade finance options like letters of credit to mitigate risks. Establish clear, written agreements on these terms to ensure transparency and smooth transactions.
4. What certifications and quality assurance measures should I look for in international shoe parts suppliers?
Ensure the supplier holds relevant industry certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management, ISO 14001 for environmental standards, or specific certifications for hazardous materials if applicable. Request detailed quality assurance protocols, including incoming raw material inspections, in-process checks, and final quality testing reports. Suppliers with modern testing facilities or partnerships with third-party labs demonstrate commitment to quality. Regular audits and compliance with international standards reduce defect rates, ensuring your product meets safety and durability requirements, especially critical when supplying to regulated markets like Europe or the Middle East.
5. How can I manage international logistics effectively to ensure timely delivery of shoe parts?
Establish a clear logistics plan considering shipping modes (air, sea, land) based on cost, volume, and urgency. Work with freight forwarders experienced in your target markets, who can handle customs clearance and documentation efficiently. Use Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) to define responsibility and cost-sharing clearly. Track shipments in real-time via digital platforms to anticipate delays. Build buffer times into your schedule for customs inspections or unforeseen disruptions. Maintaining strong communication with your supplier and logistics partners minimizes delays and ensures you meet your production schedules.
6. How should I handle disputes or quality issues with international shoe parts suppliers?
First, have a detailed contract specifying quality standards, inspection procedures, and dispute resolution processes. Conduct joint inspections upon receipt of goods and document any discrepancies with photos and detailed reports. Engage in open, constructive communication with the supplier to resolve issues amicably. If disagreements persist, consider mediation or arbitration under internationally recognized frameworks like ICC or UNCITRAL. Maintain a record of all correspondence and agreements. Building long-term relationships based on transparency and trust often results in quicker resolutions and better future cooperation.
7. What are best practices for ensuring compliance with import regulations and standards in different regions?
Research and stay updated on import regulations, tariffs, and safety standards in your target markets—whether it’s Europe’s CE marking, Brazil’s INMETRO certification, or Middle Eastern standards. Work with local customs brokers or consultants to navigate complex documentation and compliance requirements. Ensure your supplier provides all necessary certificates, test reports, and declarations. Implement a robust internal compliance checklist and conduct periodic audits of your supply chain. Proper documentation and adherence to regional standards prevent customs delays, fines, or product recalls, safeguarding your market reputation.
8. How can I build long-term, sustainable relationships with international shoe parts suppliers?
Focus on transparent communication, timely payments, and mutual respect. Regularly visit suppliers or host virtual meetings to foster trust and understand their capabilities and challenges. Share forecasts and collaborate on product development to align your supply chain with your business growth. Establish clear performance metrics and conduct periodic reviews. Offering consistent orders and constructive feedback encourages supplier loyalty. Consider joint quality improvement programs or sustainability initiatives. Building a partnership mindset, rather than transactional relationships, results in reliable supply, better terms, and mutual growth over time.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for shoe parts
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for shoe parts
Effective strategic sourcing is critical for international B2B buyers aiming to optimize quality, reduce costs, and ensure supply chain resilience in the competitive footwear industry. By diversifying supplier bases, leveraging global manufacturing hubs, and embracing innovative procurement strategies, buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can secure reliable access to high-quality shoe parts while mitigating risks associated with geopolitical or logistical disruptions.
Key takeaways include the importance of building strong supplier relationships, utilizing data-driven sourcing decisions, and exploring emerging markets for cost efficiencies and technological advancements. Emphasizing sustainability and compliance also enhances brand reputation and aligns with global market expectations.
Looking ahead, continuous market analysis and proactive engagement with suppliers will be vital for staying ahead in this dynamic sector. International buyers should prioritize strategic partnerships, invest in supply chain transparency, and adopt digital tools to streamline procurement processes.
As the footwear industry evolves, those who adopt a forward-thinking sourcing approach will be better positioned to capitalize on new opportunities and navigate uncertainties. Now is the time for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to refine their sourcing strategies and build resilient, sustainable supply chains for long-term success.