Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Shoe Soles
Guide to Shoe Soles
- Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for shoe soles
- Understanding shoe soles Types and Variations
- Key Industrial Applications of shoe soles
- Strategic Material Selection Guide for shoe soles
- In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for shoe soles
- Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for shoe soles Sourcing
- Spotlight on Potential shoe soles Manufacturers and Suppliers
- Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for shoe soles
- Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the shoe soles Sector
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of shoe soles
- Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for shoe soles
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for shoe soles
In the highly competitive footwear industry, the quality and durability of shoe soles are critical determinants of product success. For B2B buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—such as those sourcing from Kenya or Spain—understanding the nuances of the global shoe sole market is essential to making strategic procurement decisions. Shoe soles not only influence comfort and style but also impact overall product lifespan, brand reputation, and consumer satisfaction.
This comprehensive guide is designed to empower you with actionable insights into every facet of the shoe sole supply chain. It covers the different types of soles—ranging from rubber and polyurethane to eco-friendly options—along with the most common materials, manufacturing processes, and quality control standards. You’ll find detailed guidance on sourcing reliable suppliers, evaluating costs, and navigating market trends that influence pricing and availability.
By equipping you with knowledge about key industry players, sourcing strategies, and frequently asked questions, this guide aims to streamline your procurement process and mitigate risks. Whether you are expanding your product line or seeking to optimize existing supply chains, understanding the intricacies of the global shoe sole market will enable you to negotiate better deals, ensure product quality, and maintain a competitive edge in your target markets.
Understanding shoe soles Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rubber Soles | Flexible, durable, slip-resistant, often molded or cut | Casual footwear, work boots, sports shoes | Pros: Cost-effective, high durability, excellent grip. Cons: Less formal appearance, may wear faster in certain environments. |
| Leather Soles | Classic, smooth surface, breathable, often stitched or glued | Formal shoes, dress footwear | Pros: Premium look, easy to repair, comfortable. Cons: Less water-resistant, can be slippery when wet. |
| Polyurethane (PU) Soles | Lightweight, shock-absorbing, versatile, moldable | Fashion shoes, casual and work shoes | Pros: Comfortable, lightweight, good shock absorption. Cons: Less eco-friendly, can degrade faster under UV exposure. |
| EVA (Ethylene Vinyl Acetate) | Soft, lightweight, highly cushioning, flexible | Athletic shoes, casual sneakers | Pros: Superior cushioning, lightweight, affordable. Cons: Less durable, prone to compression over time. |
| Vibram or Rubber Outsoles | Heavy-duty, slip-resistant, often lugged for traction | Work boots, hiking shoes, industrial safety footwear | Pros: Excellent traction, durability, suitable for tough environments. Cons: Heavier, higher cost, less flexible. |
Rubber Soles
Rubber soles are among the most versatile and widely used in B2B footwear manufacturing. Known for their durability and slip resistance, they are ideal for casual, work, and sports shoes. Rubber can be molded into various patterns to enhance grip and can be produced at scale, making them cost-effective for bulk purchasing. Buyers should consider the specific rubber compound, as some may wear faster under heavy use or in extreme conditions. For markets demanding rugged footwear, rubber soles offer a reliable, economical choice, but may lack the formal aesthetic preferred in luxury markets.
Leather Soles
Leather soles are synonymous with high-end, formal footwear. They offer a premium appearance, breathability, and comfort, making them a favorite in luxury shoe production. Leather soles are often stitched or glued, allowing for repairs and sole replacement, extending the product lifecycle. However, they are less water-resistant and can become slippery when wet, requiring additional treatment or anti-slip pads for certain applications. B2B buyers should evaluate the type of leather (full-grain, corrected grain) and sourcing quality, especially when catering to markets with high demand for elegant, durable dress shoes.
Polyurethane (PU) Soles
Polyurethane soles are valued for their flexibility, lightweight nature, and shock absorption capabilities. They are commonly used in fashion and casual shoes, where comfort and cost are priorities. PU soles can be easily molded into various shapes and textures, offering versatility for manufacturers. Buyers should consider the environmental impact, as PU is not biodegradable, and assess the sole’s density to balance comfort with longevity. For markets emphasizing comfort and affordability, PU soles are a strategic choice, but they may require more frequent replacement in demanding environments.
EVA (Ethylene Vinyl Acetate) Soles
EVA is renowned for its cushioning properties and lightweight profile, making it a top choice for athletic and casual footwear. Its soft, flexible nature enhances comfort, especially in sports shoes. EVA soles are generally inexpensive and easy to produce at scale, appealing to budget-conscious buyers. However, they tend to compress and lose their shape over time, reducing durability. B2B buyers should weigh the need for comfort against expected product lifespan, especially in high-usage scenarios. For premium or long-lasting footwear, combining EVA with other sole materials can optimize performance.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Vibram or Heavy-Duty Rubber Outsoles
Vibram and similar heavy-duty rubber outsoles are designed for extreme conditions, such as hiking, industrial work, or safety footwear. They feature deep lug patterns for traction and high abrasion resistance, making them suitable for rugged environments. These soles are heavier and more expensive but offer unmatched durability and grip. B2B buyers targeting markets like outdoor gear, industrial safety, or heavy-duty workwear should prioritize these soles for their robustness. However, they may be less suitable for fashion or casual footwear due to weight and appearance considerations. Proper sourcing and quality control are crucial to ensure the soles meet safety and durability standards.
This overview provides B2B buyers with critical insights into the most common shoe sole types, enabling informed sourcing decisions tailored to specific market needs and product specifications.
Key Industrial Applications of shoe soles
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of shoe soles | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction & Heavy Industry | Anti-fatigue insoles and protective soles for safety footwear | Enhances worker safety, reduces fatigue, and improves productivity | Durability under heavy wear, slip resistance, compliance with safety standards |
| Sports & Athletic Equipment | Specialized soles for sports footwear (e.g., running, hiking, court sports) | Improves performance, provides shock absorption, and reduces injury risk | High-performance materials, consistent quality, customization options |
| Medical & Healthcare | Orthopedic and therapeutic shoe soles | Offers pain relief, supports mobility, and meets health regulations | Biocompatibility, compliance with medical standards, customization flexibility |
| Fashion & Footwear Manufacturing | Trend-driven, stylish soles for casual and luxury shoes | Adds aesthetic appeal, supports branding, and meets consumer demand | Design versatility, material quality, compatibility with various uppers |
| Industrial & Military | Heavy-duty, reinforced soles for tactical and work boots | Ensures durability, slip resistance, and protection in harsh environments | Rugged materials, high abrasion resistance, compliance with military standards |
Construction & Heavy Industry
Shoe soles used in construction and heavy industry primarily serve as safety footwear components. These soles are designed to withstand harsh environments, provide slip resistance, and reduce fatigue for workers on-site. International B2B buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East prioritize soles made from durable, high-performance materials such as rubber composites or reinforced polyurethanes. Suppliers should focus on sourcing soles that meet safety standards like ASTM or EN ISO, ensuring compliance with local regulations and durability under heavy wear. These soles contribute to worker safety and operational efficiency, making them a critical procurement item for industrial safety gear providers.
Sports & Athletic Equipment
In the sports sector, shoe soles are engineered for performance enhancement. They incorporate shock absorption, energy return, and specialized grip features tailored to specific activities such as running, hiking, or court sports. For B2B buyers, especially from Europe and South America, sourcing high-quality, innovative soles can differentiate their product lines. Materials like EVA, rubber compounds, and advanced polymers are essential for durability and performance. Customization options, including branding and design, are also valued. Reliable supply chains and adherence to international sports standards ensure these soles meet the rigorous demands of athletes and sports brands globally.
Medical & Healthcare
Orthopedic and therapeutic soles are critical in medical footwear, providing support and pain relief for patients with mobility issues. B2B buyers from regions like Kenya or Spain seek soles made from biocompatible, hypoallergenic materials that can be customized to individual needs. Suppliers should prioritize sourcing soles that comply with medical device regulations, such as ISO 13485, and offer consistent quality control. These soles often require features like arch support, cushioning, and flexibility. Their application enhances patient comfort and mobility, making them essential for healthcare providers and orthotic manufacturers.
Fashion & Footwear Manufacturing
Fashion-focused shoe soles play a vital role in the aesthetic and branding aspects of footwear. They are used in casual, luxury, and designer shoes to add style, color, and texture. B2B buyers from Europe and South America look for soles that are versatile in design, made from high-quality materials like rubber, leather, or innovative composites. Customization options—such as embossed patterns, color matching, and branding—are highly sought after. Suppliers must ensure reliable delivery, design flexibility, and adherence to environmental standards, especially as sustainability becomes a key purchasing criterion in fashion industries globally.
Industrial & Military
Heavy-duty, reinforced soles are essential for tactical, military, and rugged work boots. These soles are engineered for durability, slip resistance, and protection against extreme conditions. International buyers, particularly from Africa and the Middle East, require soles that withstand high abrasion, chemical exposure, and heavy loads. Sourcing considerations include high-quality rubber compounds, reinforced layers, and compliance with military or industrial safety standards like MIL-STD or EN ISO 20345. These soles are vital for ensuring safety, operational efficiency, and longevity in demanding environments.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for shoe soles
Analysis of Common Shoe Sole Materials from a B2B Perspective
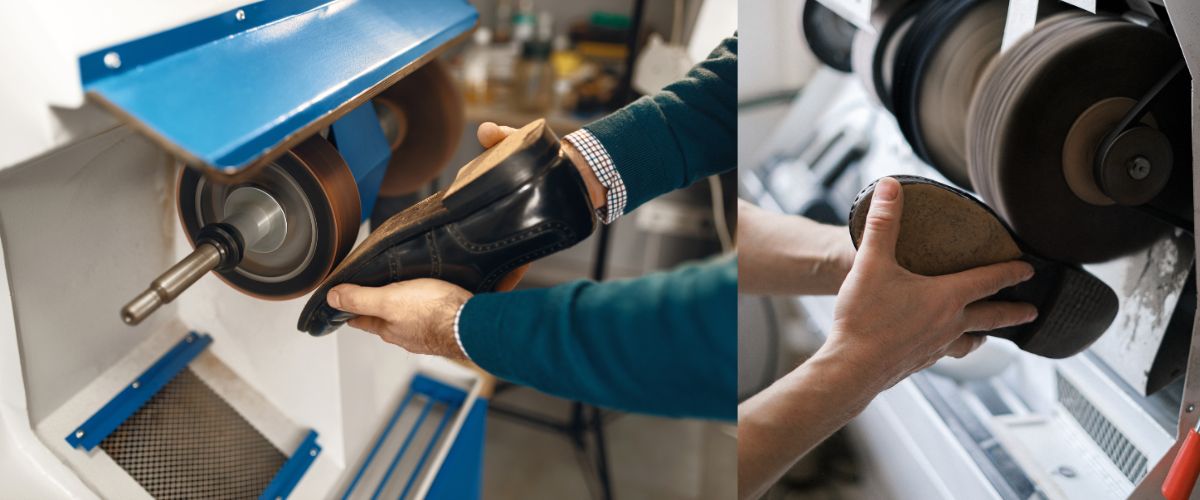
Rubber (Natural and Synthetic)
Rubber remains the most prevalent material for shoe soles due to its excellent flexibility, shock absorption, and slip resistance. Natural rubber offers superior elasticity and resilience, while synthetic variants like EVA (ethylene-vinyl acetate) and SBR (styrene-butadiene rubber) provide cost-effective alternatives with consistent quality. Rubber soles perform well across a wide temperature range, typically from -20°C to 60°C, making them suitable for diverse climates. They also exhibit good chemical and water resistance, which is vital for outdoor and industrial footwear.
From a manufacturing standpoint, rubber soles require molds and vulcanization, which can increase initial setup costs but benefit from economies of scale. Durability is high, especially for outdoor and work shoes, but softer rubber compounds may wear faster under abrasive conditions. For international buyers, rubber soles meet many global standards, including ASTM and ISO, and are widely accepted across markets like Kenya, Spain, and South America. However, sourcing natural rubber may involve supply chain considerations, especially in regions with limited rubber plantations.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Polyurethane (PU)
Polyurethane is prized for its lightweight nature and excellent cushioning properties, making it popular in athletic and casual footwear. It exhibits good abrasion resistance and maintains flexibility over a broad temperature spectrum, generally from -10°C to 50°C. PU soles are resistant to oils, greases, and many chemicals, which enhances their longevity in industrial environments.
Manufacturing polyurethane soles involves pouring or molding processes, often requiring specialized equipment. While the initial costs can be higher than rubber, the lightweight characteristic reduces transportation costs, an important factor for international logistics. PU soles tend to be more rigid than rubber but can be formulated for softer, more flexible finishes. They are compliant with major standards such as ASTM and DIN, facilitating acceptance in European and Middle Eastern markets. Buyers should consider the environmental impact, as some PU formulations may involve volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and seek suppliers adhering to eco-friendly practices.
Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE)
TPE materials are increasingly favored for their versatility and eco-friendliness. They combine the elastic properties of rubber with the processing advantages of plastics, allowing for easy manufacturing via injection molding. TPE soles offer good flexibility, slip resistance, and moderate durability, suitable for casual, fashion, and light-duty footwear.
Their resistance to water, chemicals, and temperature extremes (around -30°C to 50°C) makes them adaptable for various environments. TPEs are generally more cost-effective than high-grade PU or rubber, with the added benefit of recyclability, aligning with sustainability trends in Europe and environmentally conscious markets in South America and Africa. International buyers should verify supplier compliance with environmental standards such as REACH and RoHS, especially when sourcing from regions with strict regulations. TPE soles are suitable for markets demanding lightweight, eco-friendly solutions, but may not yet match the wear resistance of rubber or PU in heavy-duty applications.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for shoe soles | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rubber (Natural & Synthetic) | Outdoor, work, casual shoes | Excellent durability, slip resistance, shock absorption | Higher manufacturing complexity, environmental concerns with natural rubber sourcing | Med |
| Polyurethane (PU) | Athletic, casual, comfort shoes | Lightweight, good cushioning, chemical resistance | Higher initial tooling costs, less flexible than rubber | Med |
| Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE) | Fashion, casual, eco-friendly footwear | Recyclable, easy processing, eco-friendly | Moderate wear resistance, less suitable for heavy-duty use | Low |
This detailed analysis provides international B2B buyers with a clear understanding of the strengths and limitations of each material, enabling informed decisions aligned with market demands, compliance standards, and logistical considerations across regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for shoe soles
Manufacturing Processes of Shoe Soles
The production of shoe soles involves a series of meticulously controlled stages, each critical to ensuring durability, comfort, and compliance with international standards. Understanding these processes enables B2B buyers to evaluate supplier capabilities and quality consistency.
Material Preparation
The journey begins with selecting and preparing raw materials such as rubber (natural or synthetic), polyurethane (PU), thermoplastic elastomers (TPE), EVA (ethylene-vinyl acetate), and thermoplastics. Suppliers often source these materials from reputable providers adhering to ISO standards, ensuring consistency in quality. Material preparation involves mixing, compounding, and sometimes pre-molding, which are crucial for achieving the desired physical properties.
Key considerations for buyers:
– Verify supplier sourcing certifications (ISO 9001, ISO 14001).
– Request detailed material specifications and test reports.
– Ensure materials meet regional safety standards, e.g., REACH compliance for Europe.
Forming and Molding
The core shaping of soles occurs through processes such as injection molding, compression molding, or rotational molding. Injection molding is prevalent for precision and complex designs, employing high-pressure injection of molten material into molds. Compression molding involves placing pre-heated material into a mold and applying pressure, suitable for large-volume production.
Techniques to assess:
– Consistency in mold temperature and cycle times.
– Use of CAD/CAM technology for precise mold design.
– Implementation of automation to reduce variability.
Assembly and Integration
In many cases, the sole is assembled with other components such as mid-soles or insoles, often via adhesive bonding, heat welding, or mechanical fastening. The bonding process should adhere to industry standards to prevent delamination or premature failure.
Critical points for buyers:
– Confirm the adhesive types used (e.g., polyurethane-based adhesives).
– Check for proper bonding strength through sample testing.
– Ensure assembly processes are compatible with environmental regulations.
Finishing and Surface Treatment
Finishing involves trimming excess material, embossing logos, adding tread patterns, and applying surface treatments like coatings or anti-slip layers. These steps influence the aesthetic appeal and functional performance of the sole.
Quality insights:
– Evaluate the precision of surface details.
– Verify the durability of surface coatings via standardized abrasion tests.
– Assess anti-slip properties through slip resistance testing.
Quality Control in Shoe Sole Manufacturing
Robust quality assurance (QA) is essential for international B2B transactions, especially when dealing with diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Adherence to global standards and rigorous internal checks ensure product reliability and compliance.
International Standards and Certifications
- ISO 9001: The backbone of quality management systems; ensures consistent process control.
- ISO 14001: Environmental management, increasingly important for eco-conscious markets.
- CE Marking (European Conformity): Mandated for footwear sold within the EU, indicating compliance with safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For suppliers targeting the oil and gas industry, especially relevant if soles are used in specialized applications.
Actionable tip: Confirm that suppliers possess current certifications and are willing to provide audit reports and certification documents for verification.
Quality Control Checkpoints
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon receipt for compliance with specifications, including physical properties, chemical composition, and safety standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during manufacturing—checking mold temperatures, cycle times, adhesion quality, and dimensional accuracy.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Post-production inspection of finished soles, including visual examination, dimensional checks, and functional testing such as slip resistance and abrasion.
Common testing methods include:
– Hardness testing: Using durometers to ensure material resilience.
– Tensile strength and elongation tests: Assess bonding and material performance.
– Abrasion resistance: Via Taber abraser or similar equipment.
– Slip resistance: Using standardized slip testers (e.g., DIN 51130 or ASTM D2047).
Third-Party Inspections and Audits
For B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa or South America, engaging third-party inspection agencies (e.g., SGS, Bureau Veritas) is crucial for verifying supplier claims. These inspections can include factory audits, sample testing, and process reviews.
Best practices:
– Conduct pre-shipment inspections to verify batch quality.
– Review detailed inspection reports and test data.
– Establish clear quality criteria and communicate these expectations upfront.
Navigating Quality Assurance for International Markets
Different markets impose unique compliance and testing requirements. European buyers must prioritize CE certification and adherence to REACH regulations, while Middle Eastern markets might emphasize flame retardant properties or specific durability standards.
Buyers from Africa or South America should consider logistical factors such as local testing facilities and the availability of third-party inspectors. Establishing strong communication channels with suppliers and insisting on transparent documentation can mitigate risks.
Practical Tips for B2B Buyers
- Supplier Evaluation: Conduct comprehensive audits focusing on manufacturing capabilities, quality control infrastructure, and certification validity.
- Sample Testing: Request samples for independent testing aligned with target market standards before large orders.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Implement periodic audits and require detailed production reports to ensure sustained quality.
- Documentation: Maintain detailed records of certifications, inspection reports, and test results to facilitate customs clearance and market compliance.
By understanding the intricacies of manufacturing processes and embedding rigorous quality assurance practices, international B2B buyers can significantly reduce risks, ensure compliance, and foster long-term supplier relationships. This proactive approach is especially vital when sourcing from diverse regions, where standards and infrastructure may vary, but the need for reliable, high-quality shoe soles remains universal.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for shoe soles Sourcing
Cost Structure Breakdown for Shoe Sole Sourcing
Understanding the comprehensive cost structure of shoe soles is essential for effective negotiation and strategic sourcing. The primary components include raw materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control, logistics, and profit margins.
Materials: The choice of materials—such as rubber, EVA, TPU, or leather—significantly influences cost. Premium materials with higher durability or eco-friendly properties tend to command higher prices. Material costs can range from $1 to $5 per pair, depending on quality and specifications.
Labor: Manufacturing labor costs vary widely based on the geographic location of the supplier. For instance, Asian factories might charge between $0.50 to $2 per pair, while Eastern European or Latin American suppliers might range from $1 to $3. Countries like Kenya or Brazil may offer competitive labor costs, but quality standards must be carefully evaluated.
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes factory expenses such as machinery depreciation, utilities, and administrative costs. Overhead can add approximately 10-20% to the direct manufacturing costs.
Tooling and Setup: Initial tooling costs are typically a one-time expense, ranging from $500 to $5,000 depending on complexity. For ongoing production, these costs are amortized over volume, impacting unit costs especially at lower MOQs.
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure product consistency and compliance with certifications. QC costs may add 5-10% to the unit price, particularly when third-party testing or certifications (ISO, REACH, etc.) are required.
Logistics and Incoterms: Shipping costs depend on volume, destination, and chosen Incoterms. FOB (Free On Board) is common, allowing buyers to manage freight, while CIF (Cost, Insurance, Freight) includes shipping costs in the price. Freight for a 40-foot container from Asia to Europe or Africa can range from $2,000 to $5,000. Additional costs include customs duties, taxes, and inland transportation.
Profit Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin of 10-30%, influenced by order volume, relationship strength, and market competition.
Price Influencers Impacting Shoe Sole Costs
Several factors directly affect the final pricing structure for international buyers:
-
Order Volume & MOQ: Higher volumes usually lead to lower unit costs due to economies of scale. Suppliers often offer discounts for large orders, with MOQs ranging from 500 to 5,000 pairs.
-
Specifications & Customization: Custom molds, specific designs, or specialized materials increase costs. Complex geometries or unique features can add 10-30% to the base price.
-
Material Choices: Eco-friendly or high-performance materials tend to be more expensive, affecting the overall cost. Suppliers with access to sustainable materials may charge a premium.
-
Certification & Quality Standards: Certifications like ISO, REACH, or specific regional standards (e.g., EU safety regulations) can elevate costs due to testing and compliance efforts.
-
Supplier Location & Capabilities: Suppliers in China, Vietnam, or India often offer competitive prices, but European or Middle Eastern suppliers may charge more due to higher wages and stricter standards. However, proximity can reduce logistics costs and lead times.
-
Incoterms & Shipping: FOB terms favor buyers who can manage freight, potentially reducing overall costs. DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) simplifies logistics but increases the price, as it includes all customs and inland transport.
Actionable Tips for International B2B Buyers
- Negotiate Based on Volume & Long-term Partnership: Larger orders or committed future business can unlock better pricing and flexible MOQs.
- Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond unit price, consider logistics, customs, lead times, and quality assurance costs to evaluate the true cost.
- Leverage Local Advantages: For buyers in Africa, South America, or Europe, sourcing from nearby suppliers can reduce shipping costs and lead times, but may come with higher unit prices. Conversely, Asian suppliers often offer lower prices but require careful quality management.
- Request Detailed Cost Breakdowns: Insist on transparent quotations that specify material costs, tooling, QC, and logistics to identify potential savings.
- Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: Prices can fluctuate based on raw material markets, currency exchange rates, and geopolitical factors, especially impacting suppliers in regions like the Middle East or South America.
Disclaimer
Indicative prices for shoe soles can vary significantly based on the above factors, with typical ranges from $2 to $8 per pair for standard designs in bulk. Premium, customized, or eco-friendly soles may cost upwards of $10. Always conduct due diligence and request multiple quotes to benchmark fair market prices for your specific requirements.
By comprehensively understanding these cost components and influencers, international B2B buyers can make informed sourcing decisions, optimize their supply chain, and negotiate effectively to achieve competitive pricing without compromising quality.
Spotlight on Potential shoe soles Manufacturers and Suppliers
- (No specific manufacturer data was available or requested for detailed profiling in this section for shoe soles.)*
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for shoe soles
Critical Technical Properties for Shoe Soles
1. Material Composition and Grade
The primary material used in sole manufacturing—such as rubber, EVA (ethylene vinyl acetate), polyurethane, or thermoplastic rubber—directly influences durability, flexibility, and comfort. Material grade refers to the quality level, which affects performance and lifespan. For B2B buyers, specifying the required grade ensures that the soles meet the expected standards for wear resistance and environmental conditions. High-grade materials typically command higher prices but offer superior longevity, crucial for premium or safety footwear.
2. Tolerance and Dimensional Accuracy
Tolerance defines the permissible variation in the sole’s dimensions (length, width, thickness). Precise tolerances are vital for consistent fit, especially when soles are integrated into mass-produced shoes. Suppliers should provide detailed tolerance ranges to avoid issues with assembly or fit, which could lead to increased returns or dissatisfaction. For international buyers, understanding and negotiating tolerances ensures product uniformity across large orders.
3. Slip Resistance and Traction
This property measures the sole’s grip on various surfaces, often quantified through slip resistance ratings. For footwear intended for industrial, outdoor, or safety use, high slip resistance is non-negotiable. Buyers should verify that soles meet relevant safety standards (e.g., ASTM, DIN) to prevent liability and ensure wearer safety. Testing reports or certifications from suppliers are critical documentation.
4. Flexibility and Comfort
Flexibility affects how the sole adapts to foot movement, impacting comfort and foot health. It’s especially important for casual, athletic, or work shoes. Manufacturers often specify flexibility through bend tests or hardness ratings. For international buyers, understanding these properties helps select soles suitable for specific markets or user needs, avoiding costly product mismatches.
5. Environmental Resistance
Soles should withstand environmental factors such as moisture, UV exposure, and temperature fluctuations. Resistance properties include waterproofing, UV stability, and abrasion resistance. Buyers operating in diverse climates—from humid Africa to snowy Europe—must ensure the soles’ durability aligns with local conditions, reducing warranty claims and enhancing customer satisfaction.
6. Weight and Density
The weight of the sole impacts overall shoe weight, influencing comfort and market perception. Density affects cushioning and shock absorption. Lighter soles are preferred for athletic or casual shoes, while denser soles may offer better durability for work footwear. Accurate specifications help buyers balance performance with cost and comfort.
Essential Industry and Trade Terms
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Refers to companies that produce soles based on the buyer’s specifications and branding. Understanding OEM relationships helps buyers communicate their design requirements clearly and negotiate customization options. OEM agreements often include confidentiality clauses to protect proprietary designs.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
The smallest number of units a supplier is willing to produce or sell in a single order. Knowledge of MOQ helps buyers plan procurement budgets and production schedules. Lower MOQs are advantageous for testing new designs or entering new markets, while higher MOQs often reduce unit costs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
A formal request sent to suppliers asking for price, lead time, and terms for specific soles. RFQs are essential for comparing suppliers and ensuring competitive pricing. Clear, detailed RFQs expedite the procurement process and improve accuracy in quotations.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Standardized trade terms published by the ICC that define responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and customs clearance. For example, FOB (Free on Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) specify who bears costs and risks at each stage of transit. Understanding Incoterms helps international buyers manage logistics and avoid unexpected costs.
5. Lead Time
The period from order placement to delivery. Knowing lead times allows buyers to synchronize production schedules and inventory management, especially when planning for seasonal demand or urgent projects. Reliable suppliers provide transparent lead time estimates to facilitate planning.
6. Certification and Compliance
Refers to official documentation verifying that soles meet safety, environmental, and quality standards (e.g., REACH, ISO). Ensuring compliance avoids legal issues and market entry barriers, particularly in Europe and the Middle East where regulatory standards are strict.
By mastering these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, negotiate effectively, and establish reliable supply chains for shoe soles across diverse markets.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the shoe soles Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global shoe soles market is influenced by a combination of technological advancements, evolving consumer preferences, and supply chain innovations. Key drivers include the rising demand for durable, lightweight, and comfortable soles, especially as footwear trends shift toward athleisure and sustainable products. For international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these drivers is crucial to sourcing effectively.
Emerging trends include the adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies like 3D printing and automation, which enhance customization and reduce lead times. Additionally, the integration of smart features—such as embedded sensors for fitness tracking—though still nascent, signals future opportunities for innovative sole designs.
Sourcing trends are increasingly favoring localized production to mitigate risks associated with global disruptions, such as COVID-19 impacts or geopolitical tensions. For example, African manufacturers are expanding their technical capabilities, while European suppliers are investing in sustainable materials and eco-friendly processes. Middle Eastern companies often serve as intermediaries, offering flexible sourcing options across continents.
Market dynamics are shaped by fluctuating raw material prices—particularly rubber, EVA foam, and thermoplastics—and by evolving trade policies. Buyers from Kenya, Spain, and other regions should closely monitor tariff changes, import-export regulations, and regional trade agreements to optimize sourcing strategies. Leveraging digital platforms and industry networks can also facilitate access to reliable suppliers and real-time market intelligence.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in the B2B Sector
Sustainability has become a critical factor in B2B sourcing for shoe soles. Environmental concerns center around the carbon footprint of manufacturing processes, the use of non-renewable resources, and waste management. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate transparent, eco-conscious practices, aligning with global standards such as ISO 14001 or B Corp certifications.
Eco-friendly materials like bio-based rubbers, recycled thermoplastics, and natural latex are gaining traction. These materials not only reduce environmental impact but also appeal to consumers demanding ethically produced footwear. For instance, soles made from recycled ocean plastics or plant-based compounds can serve as a unique selling point for brands seeking differentiation.
Ethical sourcing involves ensuring fair labor practices, safe working conditions, and adherence to human rights standards across the supply chain. Many European and Middle Eastern companies are now requiring suppliers to provide traceability reports and third-party audits. Certification schemes such as Fair Trade or Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) are increasingly used as prerequisites for B2B transactions.
For African and South American buyers, establishing partnerships with certified suppliers can enhance credibility and market access. Investing in sustainable practices not only aligns with global environmental goals but also mitigates long-term risks related to regulatory changes and reputational damage. Collaborating with suppliers committed to continuous improvement in sustainability can provide a competitive edge in the evolving footwear market.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Brief Evolution/History (Optional)
The shoe soles sector has evolved from simple, functional designs to highly engineered components integrating advanced materials and manufacturing techniques. Historically, natural rubber and leather dominated the market, especially in regions like South America and Southeast Asia. The advent of synthetic polymers in the 20th century introduced greater flexibility and durability, transforming the industry.
In recent decades, sustainability has driven innovation, with a shift toward recycled and bio-based materials. Digital manufacturing methods, such as 3D printing, are now enabling rapid prototyping and customization—beneficial for B2B buyers seeking bespoke solutions. For regions like Kenya and Spain, understanding this evolution provides context for assessing supplier capabilities and technological readiness, ensuring alignment with future market trends and sustainability commitments.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of shoe soles
1. How can I effectively vet and select reliable shoe sole suppliers internationally?
Vetting international suppliers requires a multi-step approach. Start by requesting verified business licenses, certifications (such as ISO, REACH, or SGS), and references from previous clients. Conduct virtual audits or site visits when possible, especially for larger orders. Evaluate their production capacity, lead times, and quality control processes. Use trade platforms like Alibaba, Global Sources, or industry-specific directories to gather reviews and ratings. Establish clear communication channels and request samples to assess quality firsthand before committing. Building relationships with trusted agents or sourcing partners in key regions can also mitigate risks and ensure consistent supply.
2. How customizable are shoe soles for different markets, and what should I communicate to suppliers?
Most suppliers offer customization options, including variations in material, tread design, thickness, color, and branding. Clearly define your target market’s needs—e.g., durability for industrial use or comfort for fashion shoes—and communicate these specifications upfront. Share detailed technical drawings, sample references, or prototypes if available. Confirm with suppliers about their ability to customize within your required MOQ and lead times. Also, inquire about their flexibility in modifying designs over time to adapt to market trends or specific customer demands, ensuring your product stays competitive.
3. What are typical MOQs, lead times, and payment terms I should expect from international shoe sole suppliers?
MOQ requirements vary widely depending on supplier size and product complexity, ranging from 500 to 10,000 pairs. Lead times generally span 4 to 12 weeks, influenced by customization, material availability, and manufacturing capacity. Payment terms often include a 30% deposit upfront with the balance paid before shipment, or letters of credit for larger orders. Always negotiate terms that balance risk and cash flow, and consider establishing escrow accounts or using trade finance options. Building a strong relationship can sometimes lead to more flexible terms, especially for repeat orders or bulk purchasing.
4. What quality assurance measures and certifications should I verify before purchasing shoe soles?
Ensure your supplier complies with relevant safety and environmental standards pertinent to your target markets. Certifications such as ISO 9001 (quality management), REACH (chemical safety), and SGS testing reports are essential indicators of quality control. Request detailed QA procedures, including raw material testing, in-process inspections, and final product audits. For markets with strict regulations (e.g., Europe or the Middle East), verify compliance with specific standards like CE marking or local import requirements. Performing independent lab testing or third-party audits can further mitigate risks associated with quality issues or non-compliance.
5. How should I manage logistics and shipping when sourcing shoe soles internationally?
Coordinate closely with your supplier to understand their preferred shipping methods—air freight for urgent orders or sea freight for cost efficiency. Consider port proximity, customs procedures, and transit times in your planning. Engage experienced freight forwarders familiar with your destination country’s import regulations to streamline customs clearance. Always clarify who bears the shipping costs (FOB, CIF, DDP), and ensure proper documentation (commercial invoice, packing list, certificates). Establish clear lead times and contingency plans for delays, especially during peak seasons or global disruptions, to maintain supply chain resilience.
6. How do I handle disputes or quality issues with international shoe sole suppliers?
Start with detailed quality agreements and clear specifications to prevent misunderstandings. If issues arise, document defects thoroughly with photos and reports, and communicate promptly with your supplier. Many international contracts include arbitration clauses; consider using international arbitration bodies like ICC or LCIA for dispute resolution. Negotiate amicably, aiming for corrective actions such as replacement, rework, or refunds. Building strong, transparent communication channels and maintaining good relationships can often resolve disputes faster. Implement quality control inspections at different production stages to catch issues early and minimize costly returns or delays.
7. What are the key factors to consider when sourcing shoe soles for different climatic conditions?
Different climates demand specific sole features. For hot regions, prioritize soles with heat-resistant and UV-stable materials, while for wet or humid areas, opt for water-resistant and non-slip designs. For cold environments, consider soles with insulation or enhanced grip for icy surfaces. Evaluate the durability of materials under local conditions, such as exposure to salt, sand, or chemicals. Communicate these needs clearly to suppliers and request samples tested under simulated conditions. Local market preferences and safety standards should also influence material choice to ensure product acceptance and compliance.
8. How can I ensure sustainability and eco-friendliness in my shoe sole sourcing process?
Prioritize suppliers that provide eco-friendly materials like recycled rubber, bio-based polymers, or natural latex. Request documentation on their environmental management systems and sustainability certifications. Consider suppliers with transparent supply chains, responsible sourcing practices, and adherence to environmental standards like REACH or GreenScreen. Incorporate sustainability criteria into your supplier evaluation process and communicate your commitment to eco-friendly products to encourage suppliers to innovate accordingly. Additionally, explore options for biodegradable soles or those with lower carbon footprints, aligning your brand with global sustainability trends and appealing to environmentally conscious consumers.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for shoe soles
Final Insights and Future Directions for Shoe Sole Sourcing
Effective strategic sourcing is vital for B2B buyers seeking to optimize costs, ensure quality, and foster sustainable supply chains in the shoe sole industry. By diversifying sourcing regions—such as leveraging suppliers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—buyers can mitigate risks, access innovative materials, and capitalize on regional strengths. Emphasizing supplier transparency, quality assurance, and compliance standards further enhances value and resilience.
Looking ahead, technological advancements like digital procurement platforms, blockchain for traceability, and sustainable manufacturing practices will increasingly shape sourcing strategies. Buyers from regions like Kenya, Spain, and beyond should prioritize building strong supplier relationships, conducting rigorous due diligence, and embracing innovation to stay competitive.
Actionable takeaway: Develop a comprehensive sourcing plan that balances cost, quality, and sustainability while exploring emerging markets and technological tools. By doing so, international B2B buyers can secure a competitive edge and foster long-term success in the evolving shoe sole industry. The future belongs to those who proactively adapt and build resilient supply chains aligned with global trends.